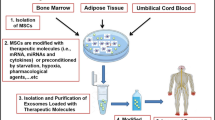
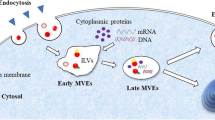
Abstract
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a highly prevalent diabetic complication characterized at the molecular level by mitochondrial dysfunction and deleterious oxidative damage. No effective treatments for DPN are currently available. The present study was developed to examine the impact of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (BMSCs) overexpressing sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) on DPN through antioxidant activity and the preservation of mitochondrial homeostasis. A DPN model was established using 20-week-old diabetic model mice (db/db). Exosomes were prepared from control BMSCs (exo-control) and BMSCs that had been transduced with a SIRT1 lentivirus (exo-SIRT1). Sensory and motor nerve conduction velocity values were measured to assess neurological function, and mechanical and thermal sensitivity were analyzed in these animals. Exo-SIRT1 preparations exhibited a high loading capacity and readily accumulated within peripheral nerves following intravenous administration, whereupon they were able to promote improved neurological recovery relative to exo-control treatment. DPN mice exhibited significantly improved nerve conduction velocity following exo-SIRT1 treatment. Relative to exo-control-treated mice, those that underwent exo-SIRT1 treatment exhibited significantly elevated TOMM20 and Nrf2/HO-1 expression, reduced MDA levels, increased GSH and SOD activity, and increased MMP. Together, these results revealed that both exo-control and exo-SIRT1 administration was sufficient to reduce the morphological and behavioral changes observed in DPN model mice, with exo-SIRT1 treatment exhibiting superior therapeutic efficacy. These data thus provide a foundation for future efforts to explore other combinations of gene therapy and exosome treatment in an effort to alleviate DPN.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An J, Zhang X, Jia K, Zhang C, Zhu L, Cheng M, Hao J (2021) Trichostatin A increases BDNF protein expression by improving XBP-1s/ATF6/GRP78 axis in Schwann cells of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Biomed Pharmacother 133:111062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111062
Ben Y, Hao J, Zhang Z, Xiong Y, Zhang C, Chang Y, Xu Q (2021) Astragaloside IV inhibits mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis of the dorsal root ganglion in diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats through modulation of the SIRT1/p53 signaling pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 14:1647–1661. https://doi.org/10.2147/dmso.S301068
Bheereddy P, Yerra VG, Kalvala AK, Sherkhane B, Kumar A (2021) SIRT1 activation by polydatin alleviates oxidative damage and elevates mitochondrial biogenesis in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41(7):1563–1577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00923-1
Carafa V, Nebbioso A, Altucci L (2012) Sirtuins and disease: the road ahead. Front Pharmacol 3:4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2012.00004
Chandrasekaran K, Salimian M, Konduru SR, Choi J, Kumar P, Long A, Russell JW (2019) Overexpression of Sirtuin 1 protein in neurons prevents and reverses experimental diabetic neuropathy. Brain 142(12):3737–3752. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz324
Deuis JR, Dvorakova LS, Vetter I (2017) Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front Mol Neurosci 10:284. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00284
Durán AM, Beeson WL, Firek A, Cordero-MacIntyre Z, De León M (2022) Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty-acid supplementation upregulates protective cellular pathways in patients with type 2 diabetes exhibiting improvement in painful diabetic neuropathy. Nutrients 14(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040761
Fan B, Chopp M, Zhang ZG, Liu XS (2021) Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with engineered mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes enriched with microRNA-146a provide amplified therapeutic efficacy. Exp Neurol 341:113694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113694
Fan B, Li C, Szalad A, Wang L, Pan W, Zhang R, Liu XS (2020) Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes ameliorate peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 63(2):431–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-05043-0
Gundu C, Arruri VK, Sherkhane B, Khatri DK, Singh SB (2022) Indole-3-propionic acid attenuates high glucose induced ER stress response and augments mitochondrial function by modulating PERK-IRE1-ATF4-CHOP signalling in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Arch Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2021.2024577
Ii M, Nishimura H, Kusano KF, Qin G, Yoon YS, Wecker A, Losordo DW (2005) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase mediates statin-induced restoration of vasa nervorum and reversal of diabetic neuropathy. Circulation 112(1):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.104.511964
Jia Y, Yang J, Lu T, Pu X, Chen Q, Ji L, Luo C (2021) Repair of spinal cord injury in rats via exosomes from bone mesenchymal stem cells requires sonic hedgehog. Regen Ther 18:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reth.2021.08.007
Li X, Xie X, Lian W, Shi R, Han S, Zhang H, Li M (2018) Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp Mol Med 50(4):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0058-5
Nakagawa T, Guarente L (2011) Sirtuins at a glance. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 6):833–838. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.081067
Schemies J, Uciechowska U, Sippl W, Jung M (2010) NAD(+) -dependent histone deacetylases (sirtuins) as novel therapeutic targets. Med Res Rev 30(6):861–889. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.20178
Singh A, Raghav A, Shiekh PA, Kumar A (2021) Transplantation of engineered exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate diabetic peripheral neuropathy under electrical stimulation. Bioact Mater 6(8):2231–2249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.01.008
Srivastava A, Rathore S, Munshi A, Ramesh R (2022) Organically derived exosomes as carriers of anticancer drugs and imaging agents for cancer treatment. Semin Cancer Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.02.020
Tesfaye S, Boulton AJ, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, Valensi P (2010) Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 33(10):2285–2293. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-1303
van Dam PS (2002) Oxidative stress and diabetic neuropathy: pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment perspectives. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18(3):176–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.287
Wang L, Chopp M, Szalad A, Lu X, Lu M, Zhang T, Zhang ZG (2019) Angiopoietin-1/Tie2 signaling pathway contributes to the therapeutic effect of thymosin β4 on diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci Res 147:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2018.10.005
Wang X, Huan Y, Li C, Cao H, Sun S, Lei L, Shen Z (2020) Diphenyl diselenide alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes by modulating oxidative stress. Biochem Pharmacol 182:114221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114221
Wang X, Zhou G, Zhou W, Wang X, Wang X, Miao C (2021) Exosomes as a new delivery vehicle in inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmaceutics 13(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101644
Wei W, Guo X, Gu L, Jia J, Yang M, Yuan W (2021) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes suppress phosphate-induced aortic calcification via SIRT6-HMGB1 deacetylation. Stem Cell Res Ther 12(1):235. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02307-8
Yang K, Wang Y, Li YW, Chen YG, Xing N, Lin HB, Yu XP (2022) Progress in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Biomed Pharmacother 148:112717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112717
Yang Y, Luo L, Cai X, Fang Y, Wang J, Chen G, Cao P (2018) Nrf2 inhibits oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via protection of mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol Med 120:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.007
Yerra VG, Kalvala AK, Kumar A (2017) Isoliquiritigenin reduces oxidative damage and alleviates mitochondrial impairment by SIRT1 activation in experimental diabetic neuropathy. J Nutr Biochem 47:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.05.001
Zhou G, Yan M, Guo G, Tong N (2019) Ameliorative effect of berberine on neonatally induced type 2 diabetic neuropathy via modulation of BDNF, IGF-1, PPAR-γ, and AMPK expressions. Dose Response 17(3):1559325819862449. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559325819862449
Funding
The work was supported by the Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission (grant number: 2022KY583) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (grant number: LQ19H160014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection and analysis were performed by Lizhen Shan, Fenfen Zhan, Detao Lin, Fabo Feng, Xinji Chen, and Xiaolin Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Lizhen Shan, Fenfen Zhan, and Di Yang, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital (Approval No. 20200033). and all experiments were conducted in strict accordance with NIH Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, L., Zhan, F., Lin, D. et al. SIRT1-Enriched Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Alleviate Peripheral Neuropathy via Conserving Mitochondrial Function. J Mol Neurosci 72, 2507–2516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02091-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02091-x