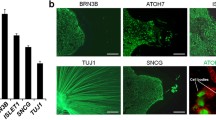
Abstract
PNU-282987, a selective alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, has previously been shown to have both neurogenic and broad regenerative effects in the adult murine retina. The objective of this study was to assay the molecular mechanism by which PNU-282987 promotes the production of Muller-derived progenitor cells through signaling via the resident retinal pigment epithelium. These Muller-derived progenitor cells generate a myriad of differentiated neurons throughout the retina that have previously been characterized by morphology. Herein, we demonstrate that topical application of PNU-282987 stimulates production of functional neurons as measured by electroretinograms. Further, we examine the mechanism of how this phenomenon occurs through activation of this atypical receptor using a transcriptomic approach isolated retinal pigment epithelium activated by PNU-282987 and in whole retina. We provide evidence that PNU-282987 causes a bi-modal signaling event in which early activation primes the retina with an inflammatory response and developmental signaling cues, followed by an inhibition of gliotic mechanisms and a decrease in the immune response, ending with upregulation of genes associated with specific retinal neuron generation. Taken together, these data provide evidence that PNU-282987 activates the retinal pigment epithelium to signal to Muller glia to produce Muller-derived progenitor cells, which can differentiate into new, functional neurons in adult mice. These data not only increase our understanding of how adult mammalian retinal regeneration can occur, but also provide therapeutic promise for treating functional vision loss.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
RNAseq dataset generated has been deposited to NCBI GEO GSE156758.
References
Ail D, Perron M (2017) Retinal degeneration and regeneration-lessons from fishes and amphibians. Curr Pathobiol Rep 5:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40139-017-0127-9
Araki M (2014) A novel mode of retinal regeneration: the merit of a new Xenopus model. Neural Regen Res 9:2125–2127. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.147942
Blackshaw S, Harpavat S, Trimarchi J et al (2004) Genomic analysis of mouse retinal development. PLoS Biol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020247
Blackshaw S, Sanes JR (2021) Turning lead into gold: reprogramming retinal cells to cure blindness. J Clin Invest 131:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI146134
Boulton M, Dayhaw-Barker P (2001) The role of the retinal pigment epithelium: topographical variation and ageing changes. Eye 15:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2001.141
Bringmann A, Iandiev I, Pannicke T et al (2009) Cellular signaling and factors involved in Müller cell gliosis: neuroprotective and detrimental effects. Prog Retin Eye Res 28:423–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2009.07.001
Buffo A, Rite I, Tripathi P et al (2008) Origin and progeny of reactive gliosis: a source of multipotent cells in the injured brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:3581–3586. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709002105
Burda JE, Sofroniew MV (2014) Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron 81:229–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.034
Chiba C (2014) The retinal pigment epithelium: an important player of retinal disorders and regeneration. Exp Eye Res 123:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2013.07.009
Diacou R, Zhao Y, Zheng D et al (2018) Six3 and Six6 are jointly required for the maintenance of multipotent retinal progenitors through both positive and negative regulation. Cell Rep 25:2510-2523.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.106
Dmitrieva NA, Strang CE, Keyser KT (2007) Expression of alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells of the rabbit retina. J Histochem Cytochem 55:461–476. https://doi.org/10.1369/jhc.6A7116.2006
Dutt K, Douglas P, Cao Y (2010) RPE-secreted factors: influence differentiation in human retinal cell line in dose- and density-dependent manner. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor 3:144–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12177-011-9076-4
Dyer MA, Cepko CL (2000) Control of Müller glial cell proliferation and activation following retinal injury. Nat Neurosci 3:873–880. https://doi.org/10.1038/78774
Elsaeidi XF, Macpherson XP, Mills EA et al (2018) Notch suppression collaborates with Ascl1 and Lin28 to unleash a regenerative response in fish retina, but not in mice. J Neurosci 38:2246–2261. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2126-17.2018
Epstein DJ, Martinu L, Michaud JL et al (2000) Members of the bHLH-PAS family regulate Shh transcription in forebrain regions of the mouse CNS. Development 127:4701–4709
Fabregat A, Korninger F, Viteri G, Sidiropoulos K, Marin-Garcia P, Ping P, Wu G, Stein L, D'Eustachio P, Hermjakob H (2018) Reactome graph database: Efficient access to complex pathway data. PLoS Comput Biol 14(1):e1005968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005968
Gallina D, Todd L, Fischer AJ (2014) A comparative analysis of Müller glia-mediated regeneration in the vertebrate retina. Exp Eye Res 123:121–130
Garcia AL, Udeh A, Kalahasty K, Hackam AS (2018) A growing field: the regulation of axonal regeneration by Wnt signaling. Neural Regen Res 13:43–52. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.224359
Goldman D (2014) retina regeneration. 15. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3723
Hamon A, García-García D, Ail D et al (2019) Linking YAP to Müller glia quiescence exit in the degenerative retina. Cell Rep 27:1712-1725.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.045
Haynes T, Luz-Madrigal A, Reis ES et al (2013) Complement anaphylatoxin C3a is a potent inducer of embryonic chick retina regeneration. Nat Commun 4:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3312
Hitchcock P, Raymond P (1992) Retinal regeneration. Trends Neurosci 15:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-2236(92)90020-9
Hoang T, Wang J, Boyd P et al (2020) Gene regulatory networks controlling vertebrate retinal regeneration. Science (80- )370. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb8598
Inana G, Murat C, An W et al (2018) RPE phagocytic function declines in age-related macular degeneration and is rescued by human umbilical tissue derived cells. J Transl Med 16:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1434-6
Joly S, Pernet V, Samardzija M, Grimm C (2011) PAX6-positive müller glia cells express cell cycle markers but do not proliferate after photoreceptor injury in the mouse retina. Glia 59:1033–1046. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.21174
Jorstad NL, Wilken MS, Grimes WN et al (2017) Stimulation of functional neuronal regeneration from Müller glia in adult mice. Nature 548:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23283
Jorstad NL, Wilken MS, Todd L et al (2020) STAT signaling modifies Ascl1 chromatin binding and limits neural regeneration from Müller Glia in adult mouse retina. Cell Rep 30:2195-2208.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.075
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acid Res 28(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kawakami K, Ohto H, Takizawa T, Saito T (1996) Identification and expression of six family genes in mouse retina. FEBS Lett 393:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(96)00899-X
Kim TW, Piao J, Koo SY et al (2021) Biphasic activation of WNT signaling facilitates the derivation of midbrain dopamine neurons from hESCs for translational use. Cell Stem Cell 28:343–355.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2021.01.005
Knight JK, Raymond PA (1995) Retinal pigmented epithelium does not transdifferentiate in adult goldfish. J Neurobiol 27:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.480270402
Kubo F, Takeichi M, Nakagawa S (2003) Wnt2b controls retinal cell differentiation at the ciliary marginal zone. Development 130:587–598
Lahne M, Nagashima M, Hyde DR, Hitchcock PF (2020) Reprogramming Müller glia to regenerate retinal neurons. Annu Rev vis Sci 6:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-vision-121219-081808
Lenkowski JR, Raymond PA (2014) Müller glia: stem cells for generation and regeneration of retinal neurons in teleost fish. Prog Retin Eye Res 40:94–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.12.007
Letourneau A, Cobellis G, Fort A et al (2015) HSA21 Single-minded 2 (SIM2) binding sites co-localize with super-enhancers and pioneer transcription factors in pluripotent mouse ES cells. PLoS ONE 10:e0126475. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126475
Linn CL, Webster SE, Webster MK (2018) Eye drops for delivery of bioactive compounds and BrdU to stimulate proliferation and label mitotically active cells in the adult rodent retina. Bio-Protoc 8:e3076
Liu W, Cvekl A (2017) Six3 in a small population of progenitors at E8.5 is required for neuroretinal specification via regulating cell signaling and survival in mice | Elsevier Enhanced Reader. Dev Biol 428:164–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.05.026
Lupo G, Novorol C, Smith JR et al (2013) Multiple roles of Activin/Nodal, bone morphogenetic protein, fibroblast growth factor and Wnt/ b-catenin signalling in the anterior neural patterning of adherent human embryonic stem cell cultures. Open Biol. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.120167
Martins T, Meghini F, Florio F, Kimata Y (2017) The APC/C coordinates retinal differentiation with G1 arrest through the Nek2-dependent modulation of wingless signaling. Dev Cell 40:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2016.12.005
Mcmahon JA, Takada S, Zimmerman LB et al (1998) Noggin-mediated antagonism of BMP signaling is required for growth and patterning of the neural tube and somite. Genes Dev 12:1438–1452
Mi H, Thomas P (2009) PANTHER pathway: an ontology-based pathway database coupled with data analysis tools. Methods Mol Biol 563:123–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-175-2_7
Miesfeld JB, Glaser T, Brown NL (2018) The dynamics of native Atoh7 protein expression during mouse retinal histogenesis, revealed with a new antibody. Gene Expr Patterns 27:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gep.2017.11.006
Nelson BR, Ueki Y, Reardon S et al (2011) Genome-wide analysis of Müller glial differentiation reveals a requirement for notch signaling in postmitotic cells to maintain the glial fate. PLoS ONE 6:22817. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022817
Osakada F, Ooto S, Akagi T et al (2007) Wnt signaling promotes regeneration in the retina of adult mammals. J Neurosci 27:4210–4219. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4193-06.2007
Paris JR, Sklar NC, Linn CL (2021) BrdU positive cells induced in a genetic mouse model of glaucoma. J Opthalmaology vis Sci 6:1–8
Park SW, Ahn JK, Heo H (2012) Spontaneous malignant glaucoma in a longstanding hypotonous eye. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 43:2110–1. https://doi.org/10.3928/15428877-20121025-01
Patel AK, Park KK, Hackam AS (2017) Wnt signaling promotes axonal regeneration following optic nerve injury in the mouse. Neuroscience 343:372–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.12.020
Paulo JA, Brucker WJ, Hawrot E (2009) Proteomic analysis of an a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor interactome. J Proteome Res 8:1849–1858. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr800731z.Proteomic
Pran S, Sardar B, Münch R et al (2017) Retinal cell death dependent reactive proliferative gliosis in the mouse retina. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09743-8
Ramachandran R, Zhao XF, Goldman D (2011) Ascl1a/Dkk/β-catenin signaling pathway is necessary and glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibition is sufficient for zebrafish retina regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:15858–15863. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1107220108
Raymond PA, Barthel LK, Bernardos RL, Perkowski JJ (2006) Molecular characterization of retinal stem cells and their niches in adult zebrafish. BMC Dev Biol 6:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-6-36
Reh TA, Levine EM (1998) Multipotential stem cells and progenitors in the vertebrate retina
Reichenbach A, Bringmann A (2013) New functions of müller cells. Glia 61:651–678
Robel S, Berninger B, Götz M (2011) The stem cell potential of glia: lessons from reactive gliosis. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:88–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2978
Sharma P, Gupta S, Chaudhary M et al (2020) Biphasic role of Tgf-β signaling during Müller glia reprogramming and retinal regeneration in zebrafish. iScience 23:100817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2019.100817
Sparrrow JR, Hicks D, Hamel CP (2010) The retinal pigment epithelium in health and disease. Curr Mol Med 10:802–823. https://doi.org/10.2174/156652410793937813
Singh A, Tsonis PA (2010) Focus on molecules: Six3 - master or apprentice? Exp Eye Res 90:535–536
Stanchfield ML, Webster SE, Webster MK, Linn CL (2020) Involvement of HB-EGF / Ascl1 / Lin28a genes in dedifferentiation of adult mammalian Müller glia. Front Mol Biosci 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00200
Strauss O (2005) The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev 85:845–881
Tétreault N, Champagne MP, Bernier G (2009) The LIM homeobox transcription factor Lhx2 is required to specify the retina field and synergistically cooperates with Pax6 for Six6 trans-activation. Dev Biol 327:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.12.022
Todd L, Finkbeiner C, Wong CK, Hooper MJ, Reh TA (2021) Efficient stimulation of retinal regeneration from Müller glia in adult mice using combinations of proneural bHLH transcription factors. Cell Rep 37:109857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109857
Udeh A, Dvoriantchikova G, Carmy T et al (2019) Wnt signaling induces neurite outgrowth in mouse retinal ganglion cells. Exp Eye Res 182:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2019.03.004
VandenBosch LS, Reh TA (2020) Epigenetics in neuronal regeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol 97:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.04.001
Vecino E, Rodriguez FD, Ruzafa N et al (2016) Glia-neuron interactions in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 51:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.06.003
Walker DP, Wishka DG, Piotrowski DW et al (2006) Design, synthesis, structure – activity relationship, and in vivo activity of azabicyclic aryl amides as a 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists. Bioorganic 14:8219–8248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2006.09.019
Wan J, Goldman D (2017) Opposing actions of Fgf8a on notch signaling distinguish two Müller glial cell populations that contribute to retina growth and regeneration. Cell Rep 19:849–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.009
Wan J, Ramachandran R, Goldman D (2012) HB-EGF is necessary and sufficient for Müller glia dedifferentiation and retina regeneration. Dev Cell 22:334–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2011.11.020
Wang X, Choi JH, Ding J et al (2013) HOXC9 directly regulates distinct sets of genes to coordinate diverse cellular processes during neuronal differentiation. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-830
Webster MK, Barnett BJ, Stanchfield ML et al (2019) Stimulation of retinal pigment epithelium with an a 7 nAChR agonist leads to Müller glia dependent neurogenesis in the adult mammalian retina. Investig Ophthalmol vis Sci 60:570–579
Webster SE, Sklar NC, Spitsbergen JB et al (2021) Stimulation of α7 nAChR leads to regeneration of damaged neurons in adult mammalian retinal disease models. Exp Eye Res 210:108717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2021.108717
Webster MK, Cooley-themm CA, Barnett JD et al (2017) Evidence of BrdU positive retinal neurons after application of an Alpha7 nicotinic acetylchoine receptor agonist. 437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.01.029.Evidence
Yao K, Qiu S, Tian L et al (2016) Wnt regulates proliferation and neurogenic potential of Müller glial cells via a Lin28/let-7 miRNA-dependent pathway in adult mammalian retinas. Cell Rep 17:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.078
Yasumuro H, Sakurai K, Toyama F et al (2017) Implications of a multi-step trigger of retinal regeneration in the adult newt. Biomedicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5020025
Zhang X, Bao L, Yang L et al (2012) Roles of intracellular fibroblast growth factors in neural development and functions. Sci China Life Sci 55:1038–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-012-4412-x
Acknowledgements
A special thanks to J. Duncan for his expert consultation and access to qRT-PCR equipment as well as to M. Stanchfield for assistance with cell culture maintenance and to E. Levine for use of the transgenic mice he developed.
Funding
This study was funded by NIH #EY027970 to C. Linn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SEW designed and performed all experiments, generated data and figures, and wrote the manuscript. JBS performed the ERG experiments. MKW assisted in the design of the genome editing scheme and with bioinformatics. DL performed the intravitreal injections and aided in the writing of the manuscript. DCO contributed to the study design and writing the manuscript. CTT generated whole retina RNAseq dataset. CL acted as project manager, edited the final manuscript and obtained the funding for this project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webster, S.E., Spitsbergen, J.B., Linn, D.M. et al. Transcriptome Changes in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Post-PNU-282987 Treatment Associated with Adult Retinal Neurogenesis in Mice. J Mol Neurosci 72, 1990–2010 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02049-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02049-z