Abstract
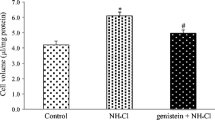
Previously, we showed that Src-mediated EGF receptor transactivation/ERK activation mediates ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling, which represents a major component of brain edema in hyperammonemic disorders. Here, we tested the role of PKC in the induction of this signaling pathway and its involvement in ammonia-mediated cell swelling. We found that incubating astrocytes with bisindolylmaleimide (BIM, an inhibitor of classical and novel PKC isoforms) or rottlerin, a PKCδ-specific inhibitor, attenuated the ammonia-induced phosphorylation of EGFR, while GF109203X had no effect on this pathway. We further found that BIM or rottlerin pretreatment inhibited the ammonia-induced phosphorylation of Src and that ammonia significantly increased the level of PKCδ pulled down by a Src antibody. AG1478, a specific EGFR kinase activity inhibitor, effectively inhibited phosphorylation at Tyr1068 but had no discernable effect on phosphorylation at Tyr845. Moreover, BIM or rottlerin abrogated ammonia-induced ERK phosphorylation. BIM-, rottlerin-, or GF109203X-treated astrocytes showed a significant reduction in cell swelling compared to that observed after treatment with ammonia alone. Finally, it was found that AG1478 attenuated ammonia-induced PKCα translocation to the particulate fraction. Taken together, our results indicate that PKCδ mediates ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling by activating Src and downstream EGF receptor/ERK signaling, which may contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric disorders associated with hyperammonemia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral LS, Martins Ferreira J, Predes D, Abreu JG, Noel F, Quintas LEM (2018) Telocinobufagin and marinobufagin produce different effects in LLC-PK1 cells: a case of functional selectivity of bufadienolides. Int J Mol Sci 19(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092769
Amos S, Martin PM, Polar GA, Parsons SJ, Hussaini IM (2005) Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate induces epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation via protein kinase Cdelta/c-Src pathways in glioblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 280(9):7729–7738. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409056200
Aschner M (2011) Volume measurements in cultured primary astrocytes. Methods Mol Biol 758:391–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-170-3_26
Atef ME, Anand-Srivastava MB (2016) Oxidative stress contributes to the enhanced expression of Gqalpha/PLCbeta1 proteins and hypertrophy of VSMC from SHR: role of growth factor receptor transactivation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 310(5):H608–H618. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00659.2015
Biscardi JS, Maa MC, Tice DA, Cox ME, Leu TH, Parsons SJ (1999) c-Src-mediated phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor on Tyr845 and Tyr1101 is associated with modulation of receptor function. J Biol Chem 274(12):8335–8343
Brown MT, Cooper JA (1996) Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim Biophys Acta 1287(2–3):121–149
Butterworth RF (2002) Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: a new look at ammonia. Metab Brain Dis 17(4):221–227. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1021989230535
Buzanska L, Zablocka B, Dybel A, Domanska-Janik K, Albrecht J (2000) Delayed induction of apoptosis by ammonia in C6 glioma cells. Neurochem Int 37(2–3):287–297
Cai L, Stevenson J, Geng X, Peng C, Ji X, Xin R, Rastogi R, Sy C, Rafols JA, Ding Y (2017) Combining normobaric oxygen with ethanol or hypothermia prevents brain damage from thromboembolic stroke via PKC-Akt-NOX modulation. Mol Neurobiol 54(2):1263–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9695-7
Cattaneo F, Iaccio A, Guerra G, Montagnani S, Ammendola R (2011) NADPH-oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species mediate EGFR transactivation by FPRL1 in WKYMVm-stimulated human lung cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med 51(6):1126–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.040
Chen Y, Peng FF, Jin J, Chen HM, Yu H, Zhang BF (2017) Src-mediated ligand release-independent EGFR transactivation involves TGF-beta-induced Smad3 activation in mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 493(2):914–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.121
Chen L, Jiang P, Li J, Xie Z, Xu Y, Qu W, Feng F, Liu W (2018) Periplocin promotes wound healing through the activation of Src/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways mediated by Na/K-ATPase. Phytomedicine 57:72–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.015
Dai H, Song D, Xu J, Li B, Hertz L, Peng L (2013) Ammonia-induced Na,K-ATPase/ouabain-mediated EGF receptor transactivation, MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling and ROS formation cause astrocyte swelling. Neurochem Int 63(6):610–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.09.005
Dai H, Jia G, Wang W, Liang C, Han S, Chu M, Mei X (2017a) Genistein inhibited ammonia induced astrocyte swelling by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation-mediated nitric oxide formation. Metab Brain Dis 32(3):841–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9975-6
Dai H, Jia G, Wang H, Yang J, Jiang H, Chu M (2017b) Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation is involved in the induction of human hepatoma SMMC7721 cell proliferation by insufficient radiofrequency ablation. Oncol Lett 14(2):2463–2467. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6463
Davis RJ, Czech MP (1985) Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82(7):1974–1978
Görg B, Karababa A, Schütz E, Paluschinski M, Schrimpf A, Shafigullina A, Castoldi M, Bidmon HJ, Häussinger D (2019) O-GlcNAcylation-dependent upregulation of HO1 triggers ammonia-induced oxidative stress and senescence in hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 71(5):930–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.020
Heidari R (2018) Brain mitochondria as potential therapeutic targets for managing hepatic encephalopathy. Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.12.030
Hsieh HL, Sun CC, Wang TS, Yang CM (2008) PKC-delta/c-Src-mediated EGF receptor transactivation regulates thrombin-induced COX-2 expression and PGE(2) production in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783(9):1563–1575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.03.016
Huang CY, Lin HJ, Chen HS, Cheng SY, Hsu HC, Tang CH (2013) Thrombin promotes matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression through the PKCdelta c-Src/EGFR/PI3K/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in human chondrocytes. Mediat Inflamm 2013:326041. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/326041
Jayakumar AR, Panickar KS, Murthy Ch R, Norenberg MD (2006) Oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation mediate ammonia-induced cell swelling and glutamate uptake inhibition in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci 26(18):4774–4784. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0120-06.2006
Jayakumar AR, Valdes V, Norenberg MD (2011) The Na-K-cl cotransporter in the brain edema of acute liver failure. J Hepatol 54(2):272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.06.041
Jayakumar AR, Tong XY, Curtis KM, Ruiz-Cordero R, Abreu MT, Norenberg MD (2014) Increased toll-like receptor 4 in cerebral endothelial cells contributes to the astrocyte swelling and brain edema in acute hepatic encephalopathy. J Neurochem 128(6):890–903. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12516
Jayakumar AR, Curtis KM, Panickar KS, Shamaladevi N, Norenberg MD (2016) Decreased STAT3 phosphorylation mediates cell swelling in ammonia-treated astrocyte cultures. Biology 5(4):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040048
Jung O, Choi YJ, Kwak TK, Kang M, Lee MS, Ryu J, Kim HJ, Lee JW (2013) The COOH-terminus of TM4SF5 in hepatoma cell lines regulates c-Src to form invasive protrusions via EGFR Tyr845 phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833(3):629–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.11.026
Kala G, Kumarathasan R, Peng L, Leenen FH, Hertz L (2000) Stimulation of Na+,K+-ATPase activity, increase in potassium uptake, and enhanced production of ouabain-like compounds in ammonia-treated mouse astrocytes. Neurochem Int 36(3):203–211
Kletzien RF, Pariza MW, Becker JE, Potter VR (1975) A method using 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture. Anal Biochem 68(2):537–544
Liang C, Du T, Zhou J, Verkhratsky A, Peng L (2014) Ammonium increases Ca(2+) signalling and up-regulates expression of TRPC1 gene in astrocytes in primary cultures and in the in vivo brain. Neurochem Res 39(11):2127–2135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1406-z
Marti-Carvajal AJ, Gluud C, Arevalo-Rodriguez I, Marti-Amarista CE (2019) Acetyl-L-carnitine for patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD011451. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011451.pub2
Saxena A, Scaini G, Bavaresco DV, Leite C, Valvassoria SS, Carvalho AF, Quevedo J (2017) Role of protein kinase C in bipolar disorder: a review of the current literature. Mol Neuropsychiatry 3(2):108–124. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480349
Song D, Du T (2014) Ammonium activates ouabain-activated signalling pathway in astrocytes: therapeutic potential of ouabain antagonist. Curr Neuropharmacol 12(4):334–341. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x12666140828222115
Sturgeon JP, Shawcross DL (2014) Recent insights into the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and treatments. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8(1):83–100. https://doi.org/10.1586/17474124.2014.858598
Wang T, Wang Y, Yamashita H (2009) Evodiamine inhibits adipogenesis via the EGFR-PKCalpha-ERK signaling pathway. FEBS Lett 583(22):3655–3659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.046
Wang F, Du T, Liang C, Verkhratsky A, Peng L (2015) Ammonium increases Ca(2+) signalling and upregulates expression of Cav1.2 gene in astrocytes in primary cultures and in the in vivo brain. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 214(2):261–274. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12500
Wang X, Tan C, Wang G, Cai JJ, Wang LP, Imperato-McGinley J, Zhu YS (2017) Dual action of NSC606985 on cell growth and apoptosis mediated through PKCdelta in prostatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol 51(5):1601–1610. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4138
Wang T, Liu C, Jia L (2018) The roles of PKCs in regulating autophagy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144(12):2303–2311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2731-4
Wang R, Zheng C, Jiang W, Xie X, Liao R, Zhou G (2019) Neuropeptide W regulates proliferation and differentiation of ATDC5: possible involvement of GPR7 activation, PKA and PKC-dependent signalling cascades. J Cell Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14118
Yang CM, Lee IT, Lin CC, Yang YL, Luo SF, Kou YR, Hsiao LD (2009) Cigarette smoke extract induces COX-2 expression via a PKCalpha/c-Src/EGFR, PDGFR/PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway and p300 in tracheal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 297(5):L892–L902. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00151.2009
Yi ZY, Liang QX, Meng TG, Li J, Dong MZ, Hou Y et al (2019) PKCbeta1 regulates meiotic cell cycle in mouse oocyte. Cell Cycle:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1564492
Funding
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81700519).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Hongliang Dai; data curation, Guizhi Jia; formal analysis, Guizhi Jia, Rui Wang and Yi Yue; funding acquisition, Hongliang Dai; investigation, Guizhi Jia; methodology, Guizhi Jia; project administration, Hongliang Dai; resources, Hongliang Dai; supervision, Hongliang Dai; validation, Guizhi Jia; writing–original draft, Guizhi Jia; writing–review & editing, Hongliang Dai.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, G., Wang, R., Yue, Y. et al. Activation of Protein Kinase Cδ Contributes to the Induction of Src/EGF Receptor/ERK Signaling in Ammonia-treated Astrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 70, 1110–1119 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01517-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01517-8