Abstract
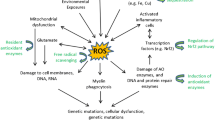
Oxidative stress has been reported in Wilson’s disease with neurological manifestation (WDNM), but there is a paucity of studies on the role of adjunctive antioxidant therapy. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of adjunctive vitamin C and E treatment in reducing oxidative stress and improving clinical outcomes. Forty-nine patients with WDNM were included and their clinical details were noted. Glutathione (GSH), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured using spectrophotometer at baseline and follow-up. All patients received zinc with or without chelating therapy, and 32 of them prescribed vitamin C (500 mg/day) and E (400 mg/day). Clinical outcomes at 6, 12, and 24 months were categorized as improved, static, or worsened based on improvement in Burke-Fahn-Marsden (BFM) score (>10%) and/or severity grade (> 1). Baseline parameters were similar between two groups; except BFM score was higher in the antioxidant group. At follow-up, the antioxidant group had higher GSH, TAC, and lower MDA levels compared with baseline. Patients on antioxidant treatment experienced improvement more frequently at 6 (53.1% vs. 29.4%), 12 (62.5% vs. 29.4%), and 24 months (68.8% vs. 35.3%) compared with those without antioxidant treatment. In WDNM, adjunctive vitamin C and E treatment reduce oxidative stress and improve clinical outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardo-Colon A, Vest V, Clark A, Cooper ML, Calkins DJ, Harrison FE, Rex TS (2018) Antioxidants prevent inflammation and preserve the optic projection and visual function in experimental neurotrauma. Cell Death Dis 9:1097. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1061-4
Betti M et al (2011) Dietary supplementation with alpha-tocopherol reduces neuroinflammation and neuronal degeneration in the rat brain after kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Free Radic Res 45:1136–1142. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2011.597750
Brewer GJ et al (2009) Treatment of Wilson's disease with tetrathiomolybdate: V. control of free copper by tetrathiomolybdate and a comparison with trientine translational research. J Lab Clin Med 154:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2009.05.002
Bruha R et al (2012) Decreased serum antioxidant capacity in patients with Wilson disease is associated with neurological symptoms. J Inherit Metab Dis 35:541–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-011-9422-5
Bull PC, Thomas GR, Rommens JM, Forbes JR, Cox DW (1993) The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet 5:327–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1293-327
Chen DB, Feng L, Lin XP, Zhang W, Li FR, Liang XL, Li XH (2012) Penicillamine increases free copper and enhances oxidative stress in the brain of toxic milk mice. 7:e37709–PloS one. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037709
Chen H, Pellett LJ, Andersen HJ, Tappel AL (1993) Protection by vitamin E, selenium, and beta-carotene against oxidative damage in rat liver slices and homogenate. Free Radic Biol Med 14:473–482
Choi BS, Zheng W (2009) Copper transport to the brain by the blood-brain barrier and blood-CSF barrier. Brain Res 1248:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.10.056
Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, Folstein MF (1993) Population-based norms for the mini-mental state examination by age and educational level. JAMA 269:2386–2391
Cummings JL (1997) The neuropsychiatric inventory: assessing psychopathology in dementia patients. Neurology 48:S10–S16
Czlonkowska A et al (2018) Wilson disease. Nature reviews Disease primers 4:21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0018-3
Dalgic B, Sonmez N, Biberoglu G, Hasanoglu A, Erbas D (2005) Evaluation of oxidant stress in Wsilson's disease and non-Wilsonian chronic liver disease in childhood. Turk J Gastroenterol 16:7–11
European Association for Study of Liver (2012) EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson's disease. J Hepatol 56:671–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.11.007
Ferenci P (2017) Diagnosis of Wilson disease. Handbook of clinical neurology 142:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63625-6.00014-8
Grimm G et al (1991) Comparison of functional and structural brain disturbances in Wilson's disease. Neurology 41:272–276
Gromadzka G et al (2014) Treatment with D-penicillamine or zinc sulphate affects copper metabolism and improves but not normalizes antioxidant capacity parameters in Wilson disease. Biometals 27:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9694-3
Guan JZ, Guan WP, Maeda T (2018) Vitamin E administration erases an enhanced oxidation in multiple sclerosis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 96:1181–1183. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2018-0246
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001
Kalita J, Kumar V, Chandra S, Kumar B, Misra UK (2014a) Worsening of Wilson disease following penicillamine therapy. Eur Neurol 71:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1159/000355276
Kalita J, Kumar V, Misra UK (2016) A study on apoptosis and anti-apoptotic status in Wilson disease. Mol Neurobiol 53:6659–6667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9570-y
Kalita J, Kumar V, Misra UK, Bora HK (2018) Memory and learning dysfunction following copper toxicity: biochemical and immunohistochemical basis. Mol Neurobiol 55:3800–3811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0619-y
Kalita J, Kumar V, Misra UK, Ranjan A, Khan H, Konwar R (2014b) A study of oxidative stress, cytokines and glutamate in Wilson disease and their asymptomatic siblings. J Neuroimmunol 274:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.06.013
Kalita J, Kumar V, Ranjan A, Misra UK (2015) Role of oxidative stress in the worsening of neurologic Wilson disease following chelating therapy. NeuroMolecular Med 17:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8364-8
Kalita J, Misra UK, Kumar V, Parashar V (2019) Predictors of seizure in Wilson disease: a clinico-radiological and biomarkers study. Neurotoxicology 71:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2018.12.005
Kalita J, Misra UK, Pradhan PK (2011) Oromandibular dystonia in encephalitis. J Neurol Sci 304:107–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2011.02.001
Kim JJ, Kim YS, Kumar V (2019) Heavy metal toxicity: An update of chelating therapeutic strategies. J Trace Elem Med Biol 54:226–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.05.003
Krystkowiak P et al (2007) Reliability of the Burke-Fahn-Marsden scale in a multicenter trial for dystonia. Mov Disord 22:685–689. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21392
Kumar V, Kalita J, Bora HK, Misra UK (2016) Relationship of antioxidant and oxidative stress markers in different organs following copper toxicity in a rat model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 293:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.01.007
Litwin T, Dziezyc K, Karlinski M, Chabik G, Czepiel W, Czlonkowska A (2015) Early neurological worsening in patients with Wilson's disease. J Neurol Sci 355:162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.06.010
Mehvari J, Motlagh FG, Najafi M, Ghazvini MR, Naeini AA, Zare M (2016) Effects of vitamin E on seizure frequency, electroencephalogram findings, and oxidative stress status of refractory epileptic patients. Adv Biomed Res 5:36. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.178780
Musacco-Sebio R et al (2014) Oxidative damage to rat brain in iron and copper overloads. Metallomics 6:1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3mt00378g
Nagamine T et al (1997) The possible role of zinc and metallothionein in the liver on the therapeutic effect of IFN-alpha to hepatitis C patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 58:65–76
Nagasaka H, Takayanagi M, Tsukahara H (2009) Children's toxicology from bench to bed--Liver Injury (3): oxidative stress and anti-oxidant systems in liver of patients with Wilson disease. J Toxicol Sci 34(Suppl 2):SP229–SP236
Ogihara H, Ogihara T, Miki M, Yasuda H, Mino M (1995) Plasma copper and antioxidant status in Wilson's disease. Pediatr Res 37:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199502000-00016
Pansani AP et al (2018) Long-term monotherapy treatment with vitamin E reduces oxidative stress, but not seizure frequency in rats submitted to the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 88:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.09.027
Rana SV, Verma S (1997) Protective effects of GSH, alpha-tocopherol, and selenium on lipid-peroxidation in liver and kidney of copper fed rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289900458
Rey AI, Lopez-Bote CJ (2001) Effect of dietary copper and vitamin E supplementation, and extensive feeding with acorn and grass on longissimus muscle composition and susceptibility to oxidation in Iberian pigs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 85:281–292
Roberts EA, Schilsky ML, American Association for Study of Liver D (2008) Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: an update. Hepatology 47:2089–2111. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22261
Schosinsky KH, Lehmann HP, Beeler MF (1974) Measurement of ceruloplasmin from its oxidase activity in serum by use of o-dianisidine dihydrochloride. Clin Chem 20:1556–1563
Shay KP, Moreau RF, Smith EJ, Smith AR, Hagen TM (2009) Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.026
Smirnova J, Kabin E, Järving I, Bragina O, Tõugu V, Plitz T, Palumaa P (2018) Copper(I)-binding properties of de-coppering drugs for the treatment of Wilson disease. α-Lipoic acid as a potential anti-copper agent. Sci Rep 8:1463–1463. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19873-2
Sokol RJ, McKim JM Jr, Devereaux MW (1996) alpha-tocopherol ameliorates oxidant injury in isolated copper-overloaded rat hepatocytes. Pediatr Res 39:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199604001-01565
Tanzi RE et al (1993) The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet 5:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1293-344
Thomas GR, Forbes JR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW (1995) The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet 9:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0295-210
Tsuchiya H, Bates CJ (1997) Vitamin C and copper interactions in guinea-pigs and a study of collagen cross-links. Br J Nutr 77:315–325
von Herbay A, de Groot H, Hegi U, Stremmel W, Strohmeyer G, Sies H (1994) Low vitamin E content in plasma of patients with alcoholic liver disease, hemochromatosis and Wilson's disease. J Hepatol 20:41–46
Wiles C (1990) Quantification of neurologic deficit. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 53:628
Wu P, Dong J, Cheng N, Yang R, Han Y, Han Y (2019) Inflammatory cytokines expression in Wilson's disease. Neurol Sci 40:1059-1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3680-z
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics Approval
The research has been approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee, SGPGIMS, Lucknow (Ethic No. A-03: PGI/IMP/IEC/56/19.08.2011).
Abbreviations
BFM Burke-Fahn-MarsdenCNS Central nervous systemCu CopperGSH GlutathioneLPO Lipid peroxidation MRI Magnetic resonance imagingMDA MalondialdehydeWD Wilson’s diseaseTAC Total antioxidant capacity
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
Free copper induces oxidative stress in Wilson’s disease.
Vitamin C and E treatment lower oxidative stress.
Adjunctive antioxidant therapy improves outcomes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, J., Kumar, V., Misra, U.K. et al. Adjunctive Antioxidant Therapy in Neurologic Wilson’s Disease Improves the Outcomes. J Mol Neurosci 70, 378–385 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01423-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01423-8