Abstract
Our study aimed to explore the molecular mechanisms and novel target genes of neuropathic pain via bioinformatics analysis. Gene expression profiling of GSE30691 which was consisted of sciatic nerve lesion and sham control samples at 3 days, 7 days, 21 days, and 40 days (D3, D7, D21, and D40) after injury were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified for all the four time points. Overlapped DEGs for all the four time points were used for functional and weighted co-expression modular analysis. Afterwards, protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was analyzed by MCODE (Molecular Complex Detection) and BiNGO. Pathway network was constructed according to the enriched pathways of PPI network and relevant pathways selected from the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database. There were 355 overlapped DEGs for all the four time points. Two co-expression modules had significant positive correlations with disease. The top ten hub DEGs in the PPI network were Fos, Tp53, Csk, Map2k2, Stat3, Ccl2, Pxn, Tgfb1, Notch1, and Prkacb. Fos, Dusp1, Tp53, Tgfb1, and Map2k2 participated in MAPK signaling pathway, while Csk participated in chemokine signaling pathway. The expressions of Fos, Tp53, Csk, and Map2k2 were significantly increased at D3. Tp53, Csk, and Map2k2 continued overexpressing until at D7, and an elevated tendency in Csk expression could be observed until at D21. The expression of Fos reached up to the highest at D40. Fos, Tp53, Csk, and Map2k2 might be the potential biomarkers related to neuropathic pain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aadithya KV, Ravindran B, Michalak TP, Jennings NR, Bachrach Y, Markakis E, Procaccia AD, Rosenschein JS, Saberi A, Resnick E (2010) Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc Networks 1:215–239
Ardakani MJE, Safaei A, Oskouie AA, Haghparast H, Haghazali M, Shalmani HM, Peyvandi H, Naderi N, Zali MR (2016) Evaluation of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma using Protein-Protein Interaction Networks. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 9(S14)
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B 57:289–300
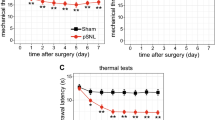
Bourquin AF, Süveges M, Pertin M, Gilliard N, Sardy S, Davison AC, Spahn DR, Decosterd I (2006) Assessment and analysis of mechanical allodynia-like behavior induced by spared nerve injury (SNI) in the mouse. Pain 122:14.e11–14.e14
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32
Costigan M, Belfer I, Griffin RS, Dai F, Barrett LB, Coppola G, Wu T, Kiselycznyk C, Poddar M, Lu Y, Diatchenko L, Smith S, Cobos EJ, Zaykin D, Allchorne A, Gershon E, Livneh J, Shen PH, Nikolajsen L, Karppinen J, Mannikko M, Kelempisioti A, Goldman D, Maixner W, Geschwind DH, Max MB, Seltzer Z, Woolf CJ (2010) Multiple chronic pain states are associated with a common amino acid-changing allele in KCNS1. Brain 133:2519–2527
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ, Sciaky D, King BL, McMorran R, Wiegers J, Wiegers TC, Mattingly CJ (2017) The comparative toxicogenomics database: update 2017. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D972–D978. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw838
De Vry J, Kuhl E, Franken-Kunkel P, Eckel G (2004) Pharmacological characterization of the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 491:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.03.051
Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Backonja M, Farrar JT, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS, Kalso EA, Loeser JD, Miaskowski C, Nurmikko TJ (2007) Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain 132:237–251
Fernándezmartos CM, Gonzálezfernández C, González P, Maqueda A, Arenas E, Rodríguez FJ (2011) Differential expression of Wnts after spinal cord contusion injury in adult rats. PLoS One 6:e27000
Géranton SM, Jiménezdíaz L, Torsney C, Tochiki KK, Stuart SA, Leith JL, Lumb BM, Hunt SP (2009) A rapamycin-sensitive signaling pathway is essential for the full expression of persistent pain states. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29:15017–15027
Gosling C (2009) Encyclopedia of distances. Ref Rev 24:1–583
Huang DWSB, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57
Jaggi AS, Singh N (2011) Role of different brain areas in peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Brain Res 1381:187–201
Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabási AL, Oltvai ZN (2001) Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 411:41–42
Ji RR, Th GR, Malcangio M, Strichartz GR (2009) MAP kinase and pain. Brain Res Rev 60:135–148
Jin HM, Chong MP, Dong EM, Kim SN, Chang WC, Kim KH (2001) Fos expression in the brain of neuropathic pain rats. Kor J Anesthesiol 41:229
Kehlet H, Jensen TS, Woolf CJ (2006) Persistent postsurgical pain: risk factors and prevention. Lancet 367:1618–1625
Kiguchi N, Kobayashi Y, Kishioka S (2012) Chemokines and cytokines in neuroinflammation leading to neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12:55–61
Kim SH, Chung JM (1992) An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 50:355–363
Kwon M, Han J, Kim UJ et al (2017) Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling in the insular cortex alleviates neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury[J]. Front Mol Neurosci 10:79
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9:559
Li G, Lu X, Zhang S, Zhou Q, Zhang L (2015) mTOR and Erk1/2 signaling in the cerebrospinal fluid-contacting nucleus is involved in neuropathic pain. Neurochem Res 40:1053–1062
Ma W, Quirion R (2005) The ERK/MAPK pathway, as a target for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9:699–713
Maere S, Heymans K, Kuiper M (2005) BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics 21:3448–3449
Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, Tillu DV, Sanoja R, Yan J, Lark A, Khoutorsky A, Johnson J, Peebles KA, Lepow T (2011) Targeting adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in preclinical models reveals a potential mechanism for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 7:70
Parrish RS, Rd SH (2004) Effect of normalization on significance testing for oligonucleotide microarrays. J Biopharm Stat 14:575–589
Rao Y, Lee Y, Jarjoura D, Ruppert AS, Liu CG, Hsu JC, Hagan JP (2008) A comparison of normalization techniques for microRNA microarray data Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 7:Article22 doi:https://doi.org/10.2202/1544-6115.1287
Reddi D, Curran N (2014) Chronic pain after surgery: pathophysiology, risk factors and prevention. Postgrad Med J 90:222–227
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK (2015) Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47
Sanna MD, Stark H, Lucarini L, Ghelardini C, Masini E, Galeotti N (2015) Histamine H4 receptor activation alleviates neuropathic pain through differential regulation of ERK, JNK, and P38 MAPK phosphorylation. Pain 156:2492–2504
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Shields SD, Basbaum AI (2003) Spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain in the mouse: a behavioral and anatomic analysis. J Pain 4:465–470
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M, Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P (2017) The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D362–D368
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H, Wang Y (2014) RNA-seq analyses of multiple meristems of soybean: novel and alternative transcripts, evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol 14:169. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-169
White FA, Jung H, Miller RJ (2007) Chemokines and the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:20151–20158
Xue-song S, Jun-li C, Yan-bing X, Jian-hua H, Li-cai Z, Yin-ming Z (2005) Activation of ERK/CREB pathway in spinal cord contributes to chronic constrictive injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats1. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:789–798. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00123.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Cg., Wan, Hq., Ma, Kn. et al. Identification of Biomarkers Related to Neuropathic Pain Induced by Peripheral Nerve Injury. J Mol Neurosci 69, 505–515 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01322-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01322-y