Abstract
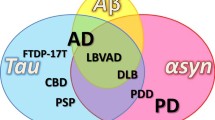
Tau and α-Synuclein (α-Syn) are abundant brain proteins with distinct biological functions. Findings suggest that interactions between α-Syn and tau at the cellular level cause disruption of cytoskeletal organization, axonal transport defects, and aberrant synaptic organization. The ability of tau and α-Syn to affect each other directly or indirectly might contribute to the overlap in the clinical and pathological features of tauopathies and synucleinopathies. The interactions between α-Syn and tau, and the underlying molecular pathogenic mechanisms, including induction and spread of protein aggregates, still deserve further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai Y, Yamazaki M, Mori O, Muramatsu H, Asano G, Katayama Y (2001) Alpha-synuclein-positive structures in cases with sporadic Alzheimer's disease: morphology and its relationship to tau aggregation. Brain Res 888:287–296
Arima K et al. (1999) Cellular co-localization of phosphorylated tau- and NACP/alpha-synuclein-epitopes in lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson's disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res 843:53–61
Badiola N et al. (2011) Tau enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in cellular models of synucleinopathy. PLoS One 6:e26609. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026609
Baksi S, Tripathi AK, Singh N (2016) Alpha-synuclein modulates retinal iron homeostasis by facilitating the uptake of transferrin-bound iron: implications for visual manifestations of Parkinson's disease. Free Radic Biol Med 97:292–306. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.06.025
Bancher C, Braak H, Fischer P, Jellinger KA (1993) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer lesions and intellectual status in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease patients. Neurosci Lett 162:179–182
Barbour R et al. (2008) Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener Dis 5:55–59. doi:10.1159/000112832
Bartels T, Choi JG, Selkoe DJ (2011) Alpha-synuclein occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer that resists aggregation. Nature 477:107–110. doi:10.1038/nature10324
Bendor JT, Logan TP, Edwards RH (2013) The function of alpha-synuclein. Neuron 79:1044–1066. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.09.004
Blum D et al. (2015) Mutant huntingtin alters tau phosphorylation and subcellular distribution. Hum Mol Genet 24:76–85. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu421
Botta-Orfila T et al. (2011) Lack of interaction of SNCA and MAPT genotypes in Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurol 18:e32. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03245.x
Chartier-Harlin MC et al. (2004) Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet 364:1167–1169. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17103-1
Clarimon J et al. (2009) Early-onset familial lewy body dementia with extensive tauopathy: a clinical, genetic, and neuropathological study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:73–82. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181927577
Cleveland DW, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW (1977a) Physical and chemical properties of purified tau factor and the role of tau in microtubule assembly. J Mol Biol 116:227–247
Cleveland DW, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW (1977b) Purification of tau, a microtubule-associated protein that induces assembly of microtubules from purified tubulin. J Mol Biol 116:207–225
Clinton LK, Blurton-Jones M, Myczek K, Trojanowski JQ, LaFerla FM (2010) Synergistic interactions between Abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein: acceleration of neuropathology and cognitive decline. J Neurosci 30:7281–7289. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0490-10.2010
Colom-Cadena M et al. (2013) MAPT H1 haplotype is associated with enhanced alpha-synuclein deposition in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol Aging 34:936–942. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.06.015
Davies P, Moualla D, Brown DR (2011) Alpha-synuclein is a cellular ferrireductase. PLoS One 6:e15814. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015814
Dixit R, Ross JL, Goldman YE, Holzbaur ELF (2008) Differential regulation of dynein and kinesin motor proteins by tau. Science 319:1086–1089. doi:10.1126/science.1152993
Do CB et al. (2011) Web-based genome-wide association study identifies two novel loci and a substantial genetic component for Parkinson's disease. PLoS Genet 7:e1002141. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002141
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Mabon ME, Miller DC, Golbe LI, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Concurrence of alpha-synuclein and tau brain pathology in the Contursi kindred. Acta Neuropathol 104:7–11. doi:10.1007/s00401-002-0563-3
Duka T, Duka V, Joyce JN, Sidhu A (2009) Alpha-synuclein contributes to GSK-3beta-catalyzed tau phosphorylation in Parkinson's disease models. FASEB J 23:2820–2830. doi:10.1096/fj.08-120410
Duka T, Rusnak M, Drolet RE, Duka V, Wersinger C, Goudreau JL, Sidhu A (2006) Alpha-synuclein induces hyperphosphorylation of tau in the MPTP model of parkinsonism. FASEB J 20:2302–2312
Elbaz A et al. (2011) Independent and joint effects of the MAPT and SNCA genes in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 69:778–792. doi:10.1002/ana.22321
Emmer KL, Waxman EA, Covy JP, Giasson BI (2011) E46K human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop Lewy-like and tau pathology associated with age-dependent, detrimental motor impairment. J Biol Chem 286:35104–35118. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.247965
Esposito A, Dohm CP, Kermer P, Bahr M, Wouters FS (2007) Alpha-synuclein and its disease-related mutants interact differentially with the microtubule protein tau and associate with the actin cytoskeleton. Neurobiol Dis 26:521–531
Febbraro F, Giorgi M, Caldarola S, Loreni F, Romero-Ramos M (2012) α-synuclein expression is modulated at the translational level by iron. Neuroreport 23:576–580. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e328354a1f0
Ferese R et al. (2015) Four copies of SNCA responsible for autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease in two Italian siblings. Parkinsons Dis 2015:546462. doi:10.1155/2015/546462
Fernandez-Nogales M et al. (2014) Huntington's disease is a four-repeat tauopathy with tau nuclear rods. Nat Med 20:881–885. doi:10.1038/nm.3617
Frasier M et al. (2005) Tau phosphorylation increases in symptomatic mice overexpressing A30P alpha-synuclein. Exp Neurol 192:274–287
Friedhoff P, von Bergen M, Mandelkow EM, Davies P, Mandelkow E (1998) A nucleated assembly mechanism of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15712–15717
Friedlich AL, Tanzi RE, Rogers JT (2007) The 5'-untranslated region of Parkinson's disease alpha-synuclein messengerRNA contains a predicted iron responsive element. Mol Psychiatry 12:222–223. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001937
Galpern WR, Lang AE (2006) Interface between tauopathies and synucleinopathies: a tale of two proteins. Ann Neurol 59:449–458. doi:10.1002/ana.20819
Garcia-Gorostiaga I et al. (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and tau genes interact in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. Ann Neurol 65:759–761 author reply 761-752
Giacobini E, Gold G (2013) Alzheimer disease therapy—moving from amyloid-beta to tau. Nat Rev Neurol 9:677–686. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2013.223
Giasson BI et al. (2003) Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 300:636–640. doi:10.1126/science.1082324
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease and Down’s syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:1131–1135
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Del Tredici K, Braak H (2013) 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat Rev Neurol 9:13–24. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2012.242
Goris A et al. (2007) Tau and alpha-synuclein in susceptibility to, and dementia in, Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 62:145–153
Gu Y, Oyama F, Ihara Y (1996) Tau is widely expressed in rat tissues. J Neurochem 67:1235–1244
Guo JL, Lee VM-Y (2011) Seeding of normal tau by pathological tau conformers drives pathogenesis of Alzheimer-like tangles. J Biol Chem 286:15317–15331. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.209296
Haggerty T, Credle J, Rodriguez O, Wills J, Oaks AW, Masliah E, Sidhu A (2011) Hyperphosphorylated tau in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing transgenic model of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurosci 33:1598–1610. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07660.x
Hamilton RL (2000) Lewy bodies in Alzheimer's disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain pathology (Zurich, Switzerland) 10:378–384
Himmler A, Drechsel D, Kirschner MW, Martin DW Jr (1989) Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol 9:1381–1388
Ibanez P et al. (2004) Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet 364:1169–1171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17104-3
Iseki E et al. (2003) Dementia with Lewy bodies from the perspective of tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol 105:265–270. doi:10.1007/s00401-002-0644-3
Ishizawa T, Mattila P, Davies PL, Wang D, Dickson DW (2003) Colocalization of tau and alpha-synuclein epitopes in Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:389–397
Ittner LM, Gotz J (2011) Amyloid-beta and tau—a toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:65–72. doi:10.1038/nrn2967
Ittner LM et al. (2010) Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-beta toxicity in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Cell 142:387–397
Joachim CL, Morris JH, Kosik KS, Selkoe DJ (1987) Tau antisera recognize neurofibrillary tangles in a range of neurodegenerative disorders. Ann Neurol 22:514–520. doi:10.1002/ana.410220411
Jun G et al. (2016) A novel Alzheimer disease locus located near the gene encoding tau protein. Mol Psychiatry 21:108–117. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.23
Kenner L et al. (1994) Expression of three- and four-repeat tau isoforms in mouse liver. Hepatology 20:1086–1089
Khandelwal PJ, Dumanis SB, Feng LR, Maguire-Zeiss K, Rebeck G, Lashuel HA, Moussa CE (2010) Parkinson-related parkin reduces alpha-synuclein phosphorylation in a gene transfer model. Mol Neurodegener 5:47. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-5-47
Khandelwal PJ, Dumanis SB, Herman AM, Rebeck GW, Moussa CE (2012) Wild type and P301L mutant tau promote neuro-inflammation and alpha-synuclein accumulation in lentiviral gene delivery models. Mol Cell Neurosci 49:44–53. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2011.09.002
Kotzbauer PT, Giasson BI, Kravitz AV, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2004) Fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau in familial Parkinson's disease caused by the A53T alpha-synuclein mutation. Exp Neurol 187:279–288. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.01.007
Kramer ML, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2007) Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurosci 27:1405–1410. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4564-06.2007
Kraybill ML et al. (2005) Cognitive differences in dementia patients with autopsy-verified AD, Lewy body pathology, or both. Neurology 64:2069–2073. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000165987.89198.65
Ksiezak-Reding H, Binder LI, Yen S-HC (1988) Immunochemical and biochemical characterization of tau proteins in normal and Alzheimer's disease brains with Alz 50 and tau-1. J Biol Chem 263:7948–7953
Kwok JBJ et al. (2005) GSK3B polymorphisms alter transcription and splicing in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 58:829–839. doi:10.1002/ana.20691
Labbe C et al. (2016) MAPT haplotype diversity in multiple system atrophy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.06.010
Laws SM et al. (2007) Fine mapping of the MAPT locus using quantitative trait analysis identifies possible causal variants in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Psychiatry 12:510–517. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001935
Lawson VA, Klemm HM, Welton JM, Masters CL, Crouch P, Cappai R, Ciccotosto GD (2011) Gene knockout of tau expression does not contribute to the pathogenesis of prion disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70:1036–1045. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e318235b471
Lee VM-Y, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1121
Lee VM, Giasson BI, Trojanowski JQ (2004) More than just two peas in a pod: common amyloidogenic properties of tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 27:129–134. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.01.007
Lei P et al. (2016) Lithium suppression of tau induces brain iron accumulation and neurodegeneration. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2016.96
Lei P, Ayton S, Appukuttan AT, Volitakis I, Adlard PA, Finkelstein DI, Bush AI (2015) Clioquinol rescues parkinsonism and dementia phenotypes of the tau knockout mouse. Neurobiol Dis 81:168–175. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.015
Lei P, Ayton S, Finkelstein DI, Adlard PA, Masters CL, Bush AI (2010) Tau protein: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:1775–1778
Lei P et al. (2012) Tau deficiency induces parkinsonism with dementia by impairing APP-mediated iron export. Nat Med 18:291–295. doi:10.1038/nm.2613
Lei P, Ayton S, Moon S, Zhang Q, Volitakis I, Finkelstein DI, Bush AI (2014) Motor and cognitive deficits in aged tau knockout mice in two background strains. Mol Neurodegener 9:29. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-9-29
Lewy FH (1913) Zur pathologischen Anatomie der Paralysis agitans. Dtsch Ztschr Nervenheilkunde 50:50–55
Li X et al. (2015) Enduring elevations of hippocampal amyloid precursor protein and iron are features of beta-amyloid toxicity and are mediated by tau. Neurotherapeutics 12:862–873. doi:10.1007/s13311-015-0378-2
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2012a) Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338:949–953. doi:10.1126/science.1227157
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2012b) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological α-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative α-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986. doi:10.1084/jem.20112457
Mamah CE et al. (2005) Interaction of alpha-synuclein and tau genotypes in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 57:439–443
Manivel P, Muthukumaran J, Kannan M, Krishna R (2011) Insight into residues involved in the structure and function of the breast cancer associated protein human gamma synuclein. J Mol Model 17:251–263. doi:10.1007/s00894-010-0718-4
Maroteaux L, Scheller RH (1991) The rat brain synucleins; family of proteins transiently associated with neuronal membrane. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 11:335–343
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82:4245–4249
Morris M, Koyama A, Masliah E, Mucke L (2011) Tau reduction does not prevent motor deficits in two mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 6:e29257. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029257
Muntané G, Dalfó E, MartInez A, Ferrer I (2008) Phosphorylation of tau and alpha-synuclein in synaptic-enriched fractions of the frontal cortex in Alzheimer's disease, and in Parkinson's disease and related alpha-synucleinopathies. Neuroscience 152:913–923. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.030
Mutez E et al. (2011) SNCA locus duplication carriers: from genetics to Parkinson disease phenotypes. Hum Mutat 32:E2079–E2090. doi:10.1002/humu.21459
Nalls MA et al. (2011) Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet 377:641–649. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62345-8
Oikawa T, Nonaka T, Terada M, Tamaoka A, Hisanaga S, Hasegawa M (2016) Alpha-synuclein fibrils exhibit gain of toxic function, promoting tau aggregation and inhibiting microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem 291:15046–15056. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.736355
Pachima YI, Zhou LY, Lei P, Gozes I (2016) Microtubule-tau interaction as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. J Mol Neurosci 58:145–152. doi:10.1007/s12031-016-0715-x
Papegaey A et al. (2016) Reduced tau protein expression is associated with frontotemporal degeneration with progranulin mutation. Acta neuropathologica communications 4:74. doi:10.1186/s40478-016-0345-0
Perez M et al. (2009) Tau—an inhibitor of deacetylase HDAC6 function. J Neurochem 109:1756–1766. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06102.x
Polymeropoulos MH et al. (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Qureshi HY, Paudel HK (2011) Parkinsonian neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and alpha-synuclein mutations promote tau protein phosphorylation at Ser262 and destabilize microtubule cytoskeleton in vitro. J Biol Chem 286:5055–5068. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.178905
Recasens A et al. (2014) Lewy body extracts from Parkinson disease brains trigger alpha-synuclein pathology and neurodegeneration in mice and monkeys. Ann Neurol 75:351–362. doi:10.1002/ana.24066
Regan P et al. (2015) Tau phosphorylation at serine 396 residue is required for hippocampal LTD. J Neurosci 35:4804–4812. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2842-14.2015
Renella R, Schlehe JS, Selkoe DJ, Williams DA, LaVoie MJ (2014) Genetic deletion of the GATA1-regulated protein alpha-synuclein reduces oxidative stress and nitric oxide synthase levels in mature erythrocytes. Am J Hematol 89:974–977. doi:10.1002/ajh.23796
Riedel M, Goldbaum O, Richter-Landsberg C (2009) Alpha-synuclein promotes the recruitment of tau to protein inclusions in oligodendroglial cells: effects of oxidative and proteolytic stress. J Mol Neurosci 39:226–234. doi:10.1007/s12031-009-9190-y
Roberson ED et al. (2007) Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Science 316:750–754. doi:10.1126/science.1141736
Roy B, Jackson GR (2014) Interactions between tau and alpha-synuclein augment neurotoxicity in a drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet 23:3008–3023. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu011
Sapir T, Frotscher M, Levy T, Mandelkow EM, Reiner O (2012) Tau's role in the developing brain: implications for intellectual disability. Hum Mol Genet 21:1681–1692. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr603
Satake W et al. (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet 41:1303–1307
Sekine T, Kagaya H, Funayama M, Li Y, Yoshino H, Tomiyama H, Hattori N (2010) Clinical course of the first Asian family with parkinsonism related to SNCA triplication. Mov Disord 25:2871–2875. doi:10.1002/mds.23313
Shipton OA et al. (2011) Tau protein is required for amyloid {beta}-induced impairment of hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 31:1688–1692. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2610-10.2011
Simón-Sánchez J et al. (2009) Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet 41:1308–1312. doi:10.1038/ng.487
Taes I et al. (2010) Tau levels do not influence human ALS or motor neuron degeneration in the SOD1G93A mouse. Neurology 74:1687–1693. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e042f7
Tong J et al. (2010) Brain alpha-synuclein accumulation in multiple system atrophy, Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: a comparative investigation. Brain 133:172–188. doi:10.1093/brain/awp282
Trotta L et al. (2012) SNCA and MAPT genes: independent and joint effects in Parkinson disease in the Italian population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:257–262. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.10.014
Voelzmann A, Okenve-Ramos P, Qu Y, Chojnowska-Monga M, Del Cano-Espinel M, Prokop A, Sanchez-Soriano N (2016) Tau and spectraplakins promote synapse formation and maintenance through Jun kinase and neuronal trafficking. Elife 5 doi:10.7554/eLife.14694
Wang W et al. (2011) A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17797–17802. doi:10.1073/pnas.1113260108
Wang Y, Mandelkow E (2016) Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:22–35. doi:10.1038/nrn.2015.1
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2011) Induction of intracellular tau aggregation is promoted by {alpha}-synuclein seeds and provides novel insights into the hyperphosphorylation of tau. J Neurosci 31:7604–7618. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0297-11.2011
Weingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW (1975) A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72:1858–1862
Wider C et al. (2012) An evaluation of the impact of MAPT, SNCA and APOE on the burden of Alzheimer's and Lewy body pathology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:424–429. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2011-301413
Wills J, Jones J, Haggerty T, Duka V, Joyce JN, Sidhu A (2010) Elevated tauopathy and alpha-synuclein pathology in postmortem Parkinson's disease brains with and without dementia. Exp Neurol 225:210–218. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.06.017
Xiao W, Shameli A, Harding CV, Meyerson HJ, Maitta RW (2014) Late stages of hematopoiesis and B cell lymphopoiesis are regulated by alpha-synuclein, a key player in Parkinson's disease. Immunobiology 219:836–844. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2014.07.014
Zhukareva V et al. (2001) Loss of brain tau defines novel sporadic and familial tauopathies with frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 49:165–175
Acknowledgments
The authors declare no conflict of interests. Supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571236), and SJ is the recipient of an Australian NHMRC Dementia Research Fellowship. Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health acknowledges the strong support from the Victorian Government and in particular, the funding from the Operational Infrastructure Support Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., James, S. & Lei, P. Interactions Between α-Synuclein and Tau Protein: Implications to Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Mol Neurosci 60, 298–304 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0829-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0829-1