Abstract
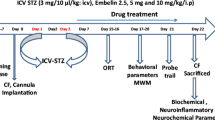
The present study was designed to investigate the effect of licofelone—a dual cyclooxygenase/5-lipoxygenase (COX/5-LOX) inhibitor in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin (ICV-STZ)-induced cognitive deficit and biochemical abnormalities in rats. ICV-STZ is a widely used model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. In this study, STZ was administered intracerebroventricular (ICV)-bilaterally 3 mg/kg in rats. The STZ-injected rats were treated with different doses of licofelone (2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) for 21 days. Cognitive functions were assessed by using Morris water maze and passive avoidance task. Levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), nitrite, reduced glutathione (GSH), and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity were determined to check oxidative stress and cholinergic function. Cytokine levels (IL-1β and TNF-α) were also determined as markers of neuroinflammation. Administration of STZ caused a significant increase in AChE activity and cognitive dysfunction. Increased oxidative stress and the proinflammatory cytokine levels were also observed following STZ administration in rats. Licofelone treatment attenuated STZ-induced cholinergic hypofunction and cognitive deficit in rats. In addition, licofelone attenuated STZ-induced oxidative stress and elevated cytokine levels. The cognitive enhancement following licofelone administration in STZ rats may be due to its ability to restore cholinergic functions or its antioxidant activity. These observed results suggest the therapeutic potential of dual COX/5-LOX inhibitors in neurodegenerative disorders associated with oxidative stress and cognitive impairment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasson KI, Savonenko A, Vidensky S, Goellner JJ, Zhang Y, Shaffer A et al (2001) Age-dependent cognitive deficits and neuronal apoptosis in cyclooxygenase-2 transgenic mice. J Neurosci 21:8198–8209
Baran H, Vass K, Lassmann H, Hornykiewicz O (1994) The cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase inhibitor BW755C protects rats against kainic acid-induced seizures and neurotoxicity. Brain Res 646:201–206
Barker GRI, Warburton CE (2009) Critical role of the cholinergic system for object-in-place associative recognition memory. Learn Mem 16:8–11
Bishnoi M, Bosgraaf CA, Abooj M, Zhong L, Premkumar LS (2011) Streptozotocin-induced early thermal hyperalgesia is independent of glycemic state of rats: role of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and inflammatory mediators. Mol Pain 7:1–11
Bruce-Keller AJ, Li YJ, Lovell MA, Kraemer PJ, Gary DS, Brown RR et al (1998) 4-Hydroxynonenal, a product of lipid peroxidation, damages cholinergic neurons and impairs visuospatial memory in rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:257–267
Butcher LL, Woolf NJ, Scheibel AB, Weschsler AF (1986) Central cholinergic systems: synopsis of anatomy and overview of physiology and pathology. The biological substrate of Alzheimer’s diseases. Academic, New York, pp 73–86
Calanni F, Laufer S (2003) Biochemistry and mediators of inflammation. In: Laufer S, Gay S, Brune K (eds) Inflammation and rheumatic diseases. The molecular basis of novel therapies. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 15–57
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N, Leon OS (2003) Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils. Neurosci Res 47:245–253
Consilvio C, Vincent AM, Feldman EL (2004) Neuroinflammation, COX-2, and ALS—a dual role? Exp Neurol 187:1–10
Deshmukh R, Sharma V, Mehan S, Sharma N, Bedi KL (2009) Amelioration of intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced cognitive dysfunction and oxidative stress by vinpocetine—a PDE1 inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 620:49–56
Dhull DK, Jindal A, Dhull RK, Aggarwal S, Bhateja D, Padi SSV (2011) Neuroprotective effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors in ICV-STZ induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in rats. J Mol Neurosci 46(1):223–235
Di Bona D, Plaia A, Vasto S, Cavallone L, Lescai F, Franceschi C et al (2008) Association between the interleukin-1β polymorphisms and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Res Rev 59:155–163
Di Bona D, Vasto S, Capurso C, Christiansen L, Deiana L, Franceschi C et al (2009) Effect of interleukin-6 polymorphisms on human longevity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev 8:36–42
Dulin JN, Karoly ED, Wang Y, Strobel HW, Grill RJ (2013) Licofelone modulates neuroinflammation and attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity in the chronic phase of spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 33:652–664
Edison P, Archer HA, Gerhard A, Hinz R, Pavese N, Turkheimer FE et al (2008) Microglia, amyloid, and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease: an [11C](R)PK11195-PET and [11C]PIB-PET study. Neurobiol Dis 32:412–419
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Central cholinergic systems and cognition. Annu Rev Psychol 48:649–684
Fillit H, Ding WH, Buee L, Kalman J, Altstiel L, Lawlor B et al (1991) Elevated circulating tumor necrosis factor levels in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 129:318–320
Firuzi O, Zhuo J, Chinnici CM, Wisniewski T, Pratico D (2008) 5-Lipoxygenase gene disruption reduces amyloid-beta pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 22:1169–1178
Gotz J, Gotz NN (2009) Animal models for Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia: a perspective. ASN Neuro 1:251–264
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glgowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannebaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15 N] nitrate in biological fluids. Ann Biochem Exp Med 126:131–135
Griffin WST, Stanley LC, Ling C, White L, Macleod V, Perrot LJ (1989) Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:7611–7615
Haense C, Kalbe E, Herholz K, Hohmann C, Neumaier B, Krais R, Heiss WD (2012) Cholinergic system function and cognition in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 33:867–877
Hein AM, O’Banion MK (2009) Neuroinflammation and memory: the role of prostaglandins. Mol Neurobiol 40:15–32
Hein AM, Stutzman DL, Bland ST, Barrientos RM, Watkins LR, Rudy JW et al (2007) Prostaglandins are necessary and sufficient to induce contextual fear learning impairments after interleukin-1 beta injections into the dorsal hippocampus. Neuroscience 150:754–763
Ishrat T, Hoda MN, Khan MB, Yousuf S, Ahmad M, Khan MM et al (2009) Amelioration of cognitive deficits and neurodegeneration by curcumin in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type (SDAT). Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:1–12
Kalonia H, Kumar P, Kumar A (2011) Licofelone attenuates quinolinic acid induced Huntington like symptoms: possible behavioral, biochemical and cellular alterations. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:607–615
Klegeris A, McGeer PL (2002) Cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors protect against mononuclear phagocyte neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging 23:787–794
Kumar A, Seghal N, Padi SSV, Naidu PS (2006a) Differential effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on intracerebroventricular colchicines induced dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 551:58–66
Kumar P, Padi SSV, Naidu PS, Kumar A (2006b) Effect of resveratrol on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced biochemical and behavioural changes: possible neuroprotective mechanisms. Behav Pharmacol 17:485–492
Kumar A, Vashist A, Kumar P, Kalonia H, Mishra J (2012) Potential role of licofelone, minocycline and their combination against chronic fatigue stress induced behavioral, biochemical and mitochondrial alterations in mice. Pharmacol Rep 64:1105–1115
Lammers CH, Schweitzer P, Facchinetti P, Arrang JM, Madamba SG, Siggins GR et al (1996) Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase and its activating protein: prominent hippocampal expression and role in somatostatin signaling. J Neurochem 66:147–152
Lima IVA, Bastos LFS, Filho ML, Fiebich BL, Oliveira ACP (2012) Role of prostaglandins in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Mediat Inflamm 2012:1–13
Liu R, Liu IY, Bi X, Thompson RF, Doctrow SR, Malfroy B et al (2001) Reversal of age-related learning deficits and brain oxidative stress in mice with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:8526–8531
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Madrigal JLM, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Lorenzo P, Fernandez AP, Rodrigo J et al (2003) Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 accounts for restraint stress-induced oxidative status in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1579–1588
Mangialasche F, Polidori MC, Monastero R, Ercolani S, Camarda C, Cecchetti R et al (2009) Biomarkers of oxidative and nitrosative damage in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Aging Res Rev 8:285–305
Mao P (2012) Oxidative stress and its clinical applications in dementia. J Neurodegener Dis 1–15
Mao P, Reddy PH (2011) Aging and amyloid beta-induced oxidative DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for early intervention and therapeutics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:1359–1370
Matsumoto Y, Yamaguchi T, Watanabe S, Yamamoto T (2004) Involvement of arachidonic acid cascade in working memory impairment induced by interleukin-1 beta. Neuropharmacology 46:1195–1200
Melnikova T, Savonenko A, Wang Q, Liang X, Hand T, Wu L et al (2006) Cycloxygenase-2 activity promotes cognitive deficits but not increased amyloid burden in a model of Alzheimer’s disease in a sex-dimorphic pattern. Neuroscience 141:1149–1162
Miranda MI, Ferreira G, Ramirez-Lugo L, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2003) Role of cholinergic system on the construction of memories: taste memory encoding. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80:211–222
Montine TJ, Sidell KR, Crews BC, Markesbery WR, Marnett LJ, Roberts LJ (1999) Elevated CSF prostaglandin E2 levels in patients with probable AD. Neurology 53:1495–1498
Morris RGM (1984) Development of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rats. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
O’Banion MK (1999) COX-2 and Alzheimer’s disease: potential roles in inflammation and neurodegeneration. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 8:1521–1536
Pasinetti GM, Aisen PS (1998) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is increased in frontal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neuroscience 87:319–324
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, San Diego
Pepicelli O, Fedele E, Bonanno G, Raiteri M, Ajmone-Cat MA, Greco A et al (2002) In vivo activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the rat hippocampus increases prostaglandin E-2 extracellular levels and triggers lipid peroxidation through cyclooxygenase-mediated mechanisms. J Neurochem 81:1028–1034
Popic P, Nalepa I, Mamczarz J, Vetulani J (1994) Retrieval associated cholinergic activity and its inhibition by memory updating. Life Sci 54:1251–1257
Pratico D (2002) Alzheimer’s disease and oxygen radicals: new insights. Biochem Pharmacol 63:563–567
Pratico D (2008) Evidence of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease brain and antioxidant therapy: lights and shadows. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:70–78
Pratico D, Zhukareva V, Yao Y, Uryu K, Funk CD, Lawson JA et al (2004) 12/15-Lipoxygenase is increased in Alzheimer’s disease: possible involvement in brain oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 164:1655–1662
Rai S, Kamat PK, Nath C, Shukla R (2012) A study on neuroinflammation and NMDA receptor function in STZ (ICV) induced memory impaired rats. J Neuroimmunol 254(1–2):1–9
Salkovic-Petrisic M (2008) Amyloid cascade hypothesis: is it true for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Period Biologrum 110:17–25
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Hoyer S (2007) Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: an experimental approach. J Neural Transm 72:217–233
Sarter M, Parikh V (2005) Choline transporters, cholinergic transmission and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:48–56
Shaftel SS, Kyrkanides S, Olschowka JA, Miller JH, Johnson RE, O’Banion MK (2007) Sustained hippocampal IL-1β overexpression mediates chronic neuroinflammation and ameliorates Alzheimer plaque pathology. J Clin Invest 117:1595–1604
Shaftel SS, Griffin WST, O’Banion MK (2008) The role of interleukin-1 in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer disease: an evolving perspective. J Neuroinflammation 5:1–12
Sharma N, Deshmukh R, Bedi KL (2010) SP600125, a competitive inhibitor of JNK attenuates streptozotocin induced neurocognitive deficit and oxidative stress in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:386–394
Sharma V, Bala A, Deshmukh R, Bedi KL, Sharma PL (2012) Neuroprotective effect of RO-20-1724-a phosphodiesterase4 inhibitor against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced cognitive deficit and oxidative stress in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 101:239–245
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Schorer-Apelbaum D, Weinstock M (2007) Ladostigil prevents gliosis, oxidative–nitrative stress and memory deficits induced by intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Neuropharmacology 52:836–843
Singh VP, Patil CS, Kulkarni SK (2006) Anti-inflammatory effect of licofelone against various inflammatory challenges. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 20:65–71
Smith WL, DeWitt DL, Garavito RM (2000) Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem 69:145–182
Song MS, Rauw G, Baker GB, Kar S (2008) Memantine protects rat cortical cultured neurons against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity by attenuating tau phosphorylation. Eur J Neurosci 28:1989–2002
Sonkusare S, Srinivasan K, Kaul C, Ramarao P (2005) Effect of donepezil and lercanidipine on memory impairment induced by intracerebroventricular streptozotocin in rats. Life Sci 77:1–14
Tahirovic I, Sofic E, Sapcanin A (2007) Reduced brain antioxidant capacity in rat models of betacytotoxic-induced impairment induced by interleukin-1 beta. Neuropharmacology 46:1195–1200
Tang SS, Wang XY, Hong H, Long Y, Li YQ, Xiang GQ et al (2013) Leukotriene D4 induces cognitive impairment through enhancement of CysLT1 R-mediated amyloid-β generation in mice. Neuropharmacology 65:182–192
Tuppo EE, Arias HR (2005) The role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:289–305
Wang XL, Su B, Zheng L, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu XW (2009) The role of abnormal mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 109:153–159
Wang XY, Tang SS, Hu M, Long Y, Li YQ, Liao MX et al (2013) Leukotriene D4 induces amyloid-β generation via CysLT(1)R-mediated NF-κB pathways in primary neurons. Neurochem Int 62:340–347
Wickens AP (2001) Ageing and the free radical theory. Respir Physiol 28:379–391
Wills ED (1996) Mechanism of lipid peroxide formation in animal. Biochem J 99:667–676
Wyss-Coray T (2006) Inflammation in Alzheimer disease: driving force, bystander or beneficial response? Nat Med 12:1005–1015
Xiang Z, Ho L, Valdellon J, Borchelt D, Kelley K, Spielman L et al (2002) Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and cell cycle activity in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Neurobiol Aging 23(3):327–334
Yao Y, Clark CM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Pratico D (2005) Elevation of 12/15 lipoxygenase products in AD and mild cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 58:623–626
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Mr. Parveeen Garg, Chairman, ISF College of Pharmacy, Moga (Punjab), for his praiseworthy inspiration and financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Sharma, S., Prashar, A. et al. Effect of Licofelone—A Dual COX/5-LOX Inhibitor in Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin-Induced Behavioral and Biochemical Abnormalities in Rats. J Mol Neurosci 55, 749–759 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0414-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0414-4