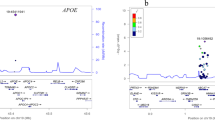
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in older population. Growing evidence of genetic background that predisposes individuals to AD has been reported as the risk factors in recent years. The Department of Medical Genetics and the Immunology Research Centre investigated the distribution of 11 polymorphisms in 160 patients with late onset AD (LOAD) and in 163 healthy controls, using the sequencing technique. All participants were of Turkish Azeri ethnicity. We compared allele and genotype frequencies between the LOAD patients and control subjects using a chi-square or Fisher’s exact test. Alleles and genotypes of APOE, PICALM rs3851179 and rs541458, and the BIN1 gene rs744373 polymorphism were significantly different between LOAD and control groups. The frequencies of the other investigated alleles were similar in the two groups. We also analyzed the association of BIN1, CR1 and PICALM SNPs with LOAD in subgroups stratified by the presence or absence of the APOE ε4 allele. After adjusting for APOE, statistical analysis revealed that the association with PICALM rs541458 and BIN1 rs744373 were only significant among subjects without the APOE ε4 allele.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Barberger-Gateau P, Samieri C, Catherine F, Plourde M (2011) Dietary omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and Alzheimer’s disease: interaction with apolipoprotein E genotype. Curr Alzheimer Res 8(5):479–491
Blacker D, Haines JL, Rodes L et al (1997) ApoE-4 and age at onset of Alzheimer’s disease: the NIMH genetics initiative. Neurology 48:139–147
Corneveaux JJ, Myers AJ, Allen AN et al (2010) Association of CR1, CLU and PICALM with Alzheimer’s disease in a cohort of clinically characterized and neuropathologically verified individuals. Hum Mol Genet 19(16):3295–301
Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, Berg S (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:168–174
Gharesouran J, Rezazadeh M, Ghojazadeh M et al (2013a) Association of CALHM1 gene polymorphism with late onset alzheimer disease. Middle East J Med Genet 2(2):50–54
Gharesouran J, Rezazadeh M, Mohaddes Ardebili SM M et al (2013b) Investigation of five polymorphic DNA markers associated with late onset alzheimer disease. Genetika 45(2):503–514
Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M, Brown J et al (1991) Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 349:704–706
Gozalpour E, Kamali K, Mohammd K et al (2010) Association between Alzheimer’s disease and apolipoprotein E polymorphisms. Iran J Publ Health 39:1–6
Gyungah J, Adam CN, Gary WB (2010) Meta-analysis confirms CR1, CLU, and PICALM as Alzheimer disease risk loci and reveals interactions with APOE genotypes. Arch Neurol 67(12):1473–1484
Harel A, Wu F, Mattson MP, Morris CM, Yao PJ (2008) Evidence for CALM in directing VAMP2 trafficking. Traffic 9:417–429
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and shows evidence for additional susceptibility genes. Nat Genet 41(10):1088–1093
Hostage AC, Choudhury K, Doraiswamy PM et al (2013) Dissecting the gene dose-effects of the APOE e4 and e2 alleles on hippocampal volumes in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 8(2):e54483
Hu X, Pickering E, Liu CY et al (2011) Meta-analysis for genome-wide association study identifies multiple variants at the BIN1 locus associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 6(2):e16616
Jones L, Harold D, Williams J (2010) Genetic evidence for the involvement of lipid metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:754–761
Jun G, Naj AC, Beecham GW, Wang L et al (2010) Meta-analysis confirms CR1, CLU, and PICALM as Alzheimer disease risk loci and reveals interactions with APOE genotypes. Arch Neurol 67:1473–1484
Kamboh MI, Minster RL, Demirci FY (2012a) Association of CLU and PICALM variants with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(3):518–521
Kamboh MI, Demirci FY, Wang X et al (2012b) Genome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Psychiatry 2:e117
Khera R, Das N (2009) Complement receptor 1: disease associations and therapeutic implications. Mol Immunol 46(5):761–772
Koren J, Jinwal UK et al (2009) Chaperone signalling complexes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Mol Med 13(4):619–630
Krych-Goldberg M, Atkinson JP (2001) Structure–function relationships of complement receptor type 1. Immunol Rev 180:112–122
Kuusisto J, Koivisto K, Kervinen K et al (1994) Association of apolipoprotein E phenotypes with late onset Alzheimer’s disease: population based study. BMJ 309(6955):636–638
Kwok JB (2010) Role of epigenetics in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Epigenomics 2(5):671–682
Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1094–1099
Lambert JC, Zelenika D, Hiltunen M et al (2011) Evidence of the association of BIN1 and PICALM with the AD risk in contrasting European populations. Neurobiol Aging 32(4):756.e11–5
Lazarczyk MJ, Hof PR, Bouras C, Giannakopoulos P (2012) Preclinical Alzheimer disease: identification of cases at risk among cognitively intact older individuals. BMC Med 10:127
Lee JH, Cheng R, Barral S et al (2011) Identification of novel loci for Alzheimer disease and replication of CLU, PICALM, and BIN1 in Caribbean Hispanic individuals. Arch Neurol 68(3):320–328
Mahley RW, Rall SC (1988) Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 240:622–630
Masoodi TA, Al Shammari SA, Al-Muammar MN, Alhamdan AA, Talluri VR (2013) Exploration of deleterious single nucleotide polymorphisms in late-onset Alzheimer disease susceptibility genes. Gene 512(2):429–437
Mei Sian C, Sahadevan S (2005) Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: diagnosis and prediction of progression. Lancet Neurol 4:576–579
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43:436–441
Ohara T, Ninomiya T, Hirakawa Y et al (2012) Association study of susceptibility genes for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the Japanese population. Psychiatr Genet 22:290–293
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 362:329–344
Rao AT, Degnan AJ, Levy LM (2014) Genetics of Alzheimer disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(3):457–458
Rogaev EI (1999) Genetic factors and a polygenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Genetika 35(11):1558–1571
Rogaev EI, Sherrington R, Rogaeva EA et al (1995) Familial Alzheimer’s disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene. Nature 376:775–778
Roses AD (1996) Apolipoprotein E alleles as risk factors in Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Med 47:387–400
Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop et al (1993) Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 43:1467–1472
Schmechel DE, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ et al (1993) Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:9649–9653
Seshadri S, Fitzpatrick AL, Ikram MA et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 303(18):1832–1840
Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y et al (1995) Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 375:754–760
Shi H, Belbin O, Medway C et al (2012) Genetic variants influencing human aging from late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Neurobiol Aging 33(8):1849e5–1849e18
Stanford JW (2004) APOE genotype effects on Alzheimer’s disease onset and epidemiology. J Mol Neurosci 23:157–165
Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS, Roses AD (1993) Apolipoprotein E high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:1977–1981
Styczyñska M, Strosznajder JB, Religa D et al (2008) Association between genetic and environmental factors and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol 46(4):249–254
Tan JT, Yu W, Zhang ZC et al (2012) Association of GWAS-linked loci with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in a northern Han Chinese population. Alzheimers Dement 9(5):546–553
Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2013) Bridging integrator 1 (BIN1): form, function, and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 19(10):594–603
Tebar F, Bohlander SK, Sorkin A (1999) Clathrin assembly lymphoid myeloid leukemia (CALM) protein: localization in endocytic-coated pits, interactions with clathrin, and the impact of overexpression on clathrin-mediated traffic. Mol Biol Cell 10:2687–2702
The Dementia Study Group of the Italian Neurological Society (2000) Guidelinesfor the diagnosis of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Ital J Neurol Sci 21:187–194
van Rossum IA, Vos S, Handels R, Visser PJ (2010) Biomarkers as predictors for conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer-type dementia implications for trial design. J Alzheimers Dis 20(3):881–891
Wijsman EW, Nathan DP, Yoonha C et al (2011) Genome-wide association of familial late-onset Alzheimer’s disease replicates BIN1 and CLU and nominates CUGBP2 in interaction with APOE. PLoS Genet 7(2):e1001308
Zawia N, Lahiri DK, Cardozo-Pelaez F (2009) Epigenetics, oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 46(9):1241–1249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jalal Gharesouran and Maryam Rezazadeh have equal contribution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gharesouran, J., Rezazadeh, M., Khorrami, A. et al. Genetic Evidence for the Involvement of Variants at APOE, BIN1, CR1, and PICALM Loci in Risk of Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease and Evaluation for Interactions with APOE Genotypes. J Mol Neurosci 54, 780–786 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0377-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0377-5