Abstract
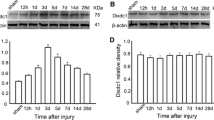
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) initiates a complex series of neurochemical and signaling changes that leads to neuronal dysfunction and over-reactive astrocytes. There is increasing evidence that CRM1 mediated P27Kip1, which is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases complexes, nuclear export-dependent or -independent Jab1/CSN5, and cytoplasmic degradation in cells. Up to now, the function of CRM1 in central nervous system (CNS) is still with limited acquaintance. In our study, to investigate whether CRM1 is involved in CNS lesion, we performed a TBI model in adult rats. Western blot and RT-PCR analysis revealed that the level of protein and mRNA of CRM1 increased in ipsilateral brain cortex in comparison to the contralateral. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence double labeling indicated that CRM1 was shutting into nucleus around the wound, and increased CRM1 co-localized with P27Kip1. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxy-UTP-nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining suggested that CRM1 was involved in neuronal apoptosis after brain injury. We also investigated co-localization of CRM1 and active-caspase-3 in the ipsilateral brain cortex. In addition, the expression patterns of Bax and active-caspase-3 were parallel with that of CRM1. Based on our data, we suggested that CRM1 might play an important role in neuronal apoptosis following TBI, and might provide a basis for the further study on its role in regulating the expression of P27Kip1 and cell cycle re-entry in TBI.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TBI:
-
Traumatic brain injury
- CRM1:
-
Chromosomal region maintenance 1
- P-P27Ser10:
-
Phosphorylation of P27Kip1 on serine 10
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated-dUTP nick end labeling
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride filter
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- NeuN:
-
Neuronal nuclei
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- CDK:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- SCF:
-
Skp1/Cul-1/F box protein
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- KPC:
-
Kip1 ubiquitination-promoting complex
- LMB:
-
Leptomycin B
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer solution
- GILZ:
-
Glucocorticoid-induced Leucine Zipper
- JNK:
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- VEEV:
-
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus
References
Atasheva S, Fish A, Fornerod M, Frolova EI (2010) Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus capsid protein forms a tetrameric complex with CRM1 and importin alpha/beta that obstructs nuclear pore complex function. J Virol 84:4158–4171
Becker EB, Bonni A (2004) Cell cycle regulation of neuronal apoptosis in development and disease. Prog Neurobiol 72:1–25
Boehm M, Yoshimoto T, Crook MF, Nallamshetty S, True A, Nabel GJ, Nabel EG (2002) A growth factor-dependent nuclear kinase phosphorylates p27(Kip1) and regulates cell cycle progression. EMBO J 21:3390–3401
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M (1999) SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol 1:193–199
Chen AJ, D’Esposito M (2010) Traumatic brain injury: from bench to bedside [corrected] to society. Neuron 66:11–14
Chiu WT, Huang SJ, Tsai SH, Lin JW, Tsai MD, Lin TJ, Huang WC (2007) The impact of time, legislation, and geography on the epidemiology of traumatic brain injury. J Clin Neurosci 14:930–935
Clavel S, Siffroi-Fernandez S, Coldefy AS, Boulukos K, Pisani DF, Derijard B (2010) Regulation of the intracellular localization of Foxo3a by stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol 30:470–480
Connor MK, Kotchetkov R, Cariou S, Resch A, Lupetti R, Beniston RG, Melchior F, Hengst L, Slingerland JM (2003) CRM1/Ran-mediated nuclear export of p27(Kip1) involves a nuclear export signal and links p27 export and proteolysis. Mol Biol Cell 14:201–213
Coronado VG, Xu L, Basavaraju SV, McGuire LC, Wald MM, Faul MD, Guzman BR, Hemphill JD (2011) Surveillance for traumatic brain injury-related deaths—United States, 1997–2007. MMWR Surveill Summ 60:1–32
Fornerod M, Ohno M, Yoshida M, Mattaj IW (1997) CRM1 is an export receptor for leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Cell 90:1051–1060
Foster JS, Fernando RI, Ishida N, Nakayama KI, Wimalasena J (2003) Estrogens down-regulate p27Kip1 in breast cancer cells through Skp2 and through nuclear export mediated by the ERK pathway. J Biol Chem 278:41355–41366
Fukuda M, Asano S, Nakamura T, Adachi M, Yoshida M, Yanagida M, Nishida E (1997) CRM1 is responsible for intracellular transport mediated by the nuclear export signal. Nature 390:308–311
Holloway RG, Quill TE (2010) Treatment decisions after brain injury—tensions among quality, preference, and cost. N Engl J Med 362:1757–1759
Ishida N, Hara T, Kamura T, Yoshida M, Nakayama K, Nakayama KI (2002) Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 on serine 10 is required for its binding to CRM1 and nuclear export. J Biol Chem 277:14355–14358
Johnson EA, Svetlov SI, Pike BR, Tolentino PJ, Shaw G, Wang KK, Hayes RL, Pineda JA (2004) Cell-specific upregulation of survivin after experimental traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 21:1183–1195
Kamura T, Hara T, Matsumoto M, Ishida N, Okumura F, Hatakeyama S, Yoshida M, Nakayama K, Nakayama KI (2004) Cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase KPC regulates proteolysis of p27(Kip1) at G1 phase. Nat Cell Biol 6:1229–1235
Konigsmark BW, Murphy EA (1970) Neuronal populations in the human brain. Nature 228:1335–1336
Kudo N, Wolff B, Sekimoto T, Schreiner EP, Yoneda Y, Yanagida M, Horinouchi S, Yoshida M (1998) Leptomycin B inhibition of signal-mediated nuclear export by direct binding to CRM1. Exp Cell Res 242:540–547
Latre de Late P, Pepin A, Assaf-Vandecasteele H, Espinasse C, Nicolas V, Asselin-Labat ML, Bertoglio J, Pallardy M, Biola-Vidamment A (2010) Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) promotes the nuclear exclusion of FOXO3 in a Crm1-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 285:5594–5605
Liu Y, Wang Y, Cheng C, Chen Y, Shi S, Qin J, Xiao F, Zhou D, Lu M, Lu Q, Shen A (2010) A relationship between p27(kip1) and Skp2 after adult brain injury: Implications for glial proliferation. J Neurotrauma 27:361–371
Loane DJ, Byrnes KR (2010) Role of microglia in neurotrauma. Neurotherapeutics 7:366–377
Logan A, Frautschy SA, Gonzalez AM, Baird A (1992) A time course for the focal elevation of synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor and one of its high-affinity receptors (flg) following a localized cortical brain injury. J Neurosci 12:3828–3837
Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (2008) Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol 7:728–741
Maegele M, Engel D, Bouillon B, Lefering R, Fach H, Raum M, Buchheister B, Schaefer U, Klug N, Neugebauer E (2007) Incidence and outcome of traumatic brain injury in an urban area in Western Europe over 10 years. Eur Surg Res 39:372–379
Martins ET, Linhares MN, Sousa DS, Schroeder HK, Meinerz J, Rigo LA, Bertotti MM, Gullo J, Hohl A, Dal-Pizzol F, Walz R (2009) Mortality in severe traumatic brain injury: a multivariated analysis of 748 Brazilian patients from Florianopolis City. J Trauma 67:85–90
Melchior F, Paschal B, Evans J, Gerace L (1993) Inhibition of nuclear protein import by nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP and identification of the small GTPase Ran/TC4 as an essential transport factor. J Cell Biol 123:1649–1659
Mock C, Joshipura M, Goosen J, Lormand JD, Maier R (2005) Strengthening trauma systems globally: the Essential Trauma Care Project. J Trauma 59:1243–1246
Moore MS, Blobel G (1993) The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature 365:661–663
Muller D, Thieke K, Burgin A, Dickmanns A, Eilers M (2000) Cyclin E-mediated elimination of p27 requires its interaction with the nuclear pore-associated protein mNPAP60. EMBO J 19:2168–2180
Park E, Bell JD, Siddiq IP, Baker AJ (2009) An analysis of regional microvascular loss and recovery following two grades of fluid percussion trauma: a role for hypoxia-inducible factors in traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:575–584
Rivest S (2009) Regulation of innate immune responses in the brain. Nat Rev Immunol 9:429–439
Rodier G, Montagnoli A, Di Marcotullio L, Coulombe P, Draetta GF, Pagano M, Meloche S (2001) p27 cytoplasmic localization is regulated by phosphorylation on Ser10 and is not a prerequisite for its proteolysis. EMBO J 20:6672–6682
Sheaff RJ, Groudine M, Gordon M, Roberts JM, Clurman BE (1997) Cyclin E-CDK2 is a regulator of p27Kip1. Genes Dev 11:1464–1478
Shen A, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zou L, Sun L, Cheng C (2009) Expression of CRM1 in human gliomas and its significance in p27 expression and clinical prognosis. Neurosurgery 65:153–159, discussion 159–160
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1995) Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 9:1149–1163
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13:1501–1512
Smitherman M, Lee K, Swanger J, Kapur R, Clurman BE (2000) Characterization and targeted disruption of murine Nup50, a p27(Kip1)-interacting component of the nuclear pore complex. Mol Cell Biol 20:5631–5642
Stade K, Ford CS, Guthrie C, Weis K (1997) Exportin 1 (Crm1p) is an essential nuclear export factor. Cell 90:1041–1050
Stoica BA, Byrnes KR, Faden AI (2009) Cell cycle activation and CNS injury. Neurotox Res 16:221–237
Sutterluty H, Chatelain E, Marti A, Wirbelauer C, Senften M, Muller U, Krek W (1999) p45SKP2 promotes p27Kip1 degradation and induces S phase in quiescent cells. Nat Cell Biol 1:207–214
Swanson C, Ross J, Jackson PK (2000) Nuclear accumulation of cyclin E/Cdk2 triggers a concentration-dependent switch for the destruction of p27Xic1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:7796–7801
Tomoda K, Kubota Y, Arata Y, Mori S, Maeda M, Tanaka T, Yoshida M, Yoneda-Kato N, Kato JY (2002) The cytoplasmic shuttling and subsequent degradation of p27Kip1 mediated by Jab1/CSN5 and the COP9 signalosome complex. J Biol Chem 277:2302–2310
Tomoda K, Kubota Y, Kato J (1999) Degradation of the cyclin-dependent-kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 is instigated by Jab1. Nature 398:160–165
Tsvetkov LM, Yeh KH, Lee SJ, Sun H, Zhang H (1999) p27(Kip1) ubiquitination and degradation is regulated by the SCF(Skp2) complex through phosphorylated Thr187 in p27. Curr Biol 9:661–664
Vlach J, Hennecke S, Amati B (1997) Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. EMBO J 16:5334–5344
Wu X, Shi W, Zhao W, Shao B, Yuan Q, Li C, Zhang S, Sun B, Wu Q, Chen J (2012) Changes in Pirh2 and p27kip1 expression following traumatic brain injury in adult rats. J Mol Neurosci 46:184–191
Yattoo G, Tabish A (2008) The profile of head injuries and traumatic brain injury deaths in Kashmir. J Trauma Manag Outcomes 2:5
Zhang H, Kobayashi R, Galaktionov K, Beach D (1995) p19Skp1 and p45Skp2 are essential elements of the cyclin A-CDK2 S phase kinase. Cell 82:915–925
Zou F, Xu J, Fu H, Cao J, Mao H, Gong M, Cui G, Zhang Y, Shi W, Chen J (2013) Different functions of HIPK2 and CtBP2 in traumatic brain injury. J Mol Neurosci 49:395–408
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31071288) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Aihong Li and Feihui Zou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, A., Zou, F., Fu, H. et al. Upregulation of CRM1 Relates to Neuronal Apoptosis after Traumatic Brain Injury in Adult Rats. J Mol Neurosci 51, 208–218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9994-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9994-7