Abstract
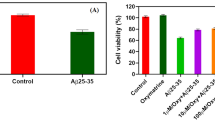
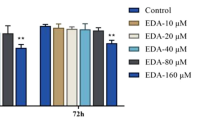
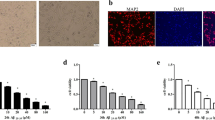
Oxidative damage is an important mediator of Alzheimer’s disease (AD); hence, antioxidant therapy is a potential treatment for AD. Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, has been shown to have neuroprotective properties. The study aimed to examine the effects of edaravone on indicators of Aβ25-35-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells. PC12 cells were treated with 20, 40, or 80 μM edaravone before treatment with 30 μM Aβ25-35. After treatment, the following assessments were performed: cell viability and aggregation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial peroxidation, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and apoptosis. Aggregation, lactate dehydrogenase activity, malondialdehyde concentrations, mitochondrial peroxidation, ROS levels, and apoptosis were significantly increased in Aβ25-35-treated cells but decreased in the treatment with edaravone 40 and 80 μM. In contrast, intracellular glutathione and superoxide dismutase concentrations were significantly decreased in Aβ25-35-treated cells but increased in the treatment with edaravone 40 and 80 μM. Edaravone ameliorates oxidative damage associated with Aβ25-35 treatment in PC12 cells. Our findings support the continued investigation of edaravone as a potential treatment for AD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bains JS, Shaw CA (1997) Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 25:335–358
Boothby LA, Doering PL (2005) Vitamin C and vitamin E for Alzheimer's disease. Ann Pharmacother 39:2073–2080
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 3:186–191
Chang Z, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Wei G (2011) Interactions of Abeta25-35 beta-barrel-like oligomers with anionic lipid bilayer and resulting membrane leakage: an all-atom molecular dynamics study. J Phys Chem B 115:1165–1174
Chen H, Wang S, Ding JH, Hu G (2008) Edaravone protects against MPP+ -induced cytotoxicity in rat primary cultured astrocytes via inhibition of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J Neurochem 106:2345–2352
Dong H, Mao S, Wei J et al (2012) Tanshinone IIA protects PC12 cells from beta-amyloid(25-35)-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 39:6495–6503
Fan J, Zhang N, Yin G et al (2012) Edaravone protects cortical neurons from apoptosis by inhibiting the translocation of BAX and increasing the interaction between 14-3-3 and p-BAD. Int J Neurosci 122(11):665–674. doi:10.3109/00207454.2012.707714
Galante D, Corsaro A, Florio T et al (2012) Differential toxicity, conformation and morphology of typical initial aggregation states of Abeta1-42 and Abetapy3-42 beta-amyloids. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:2085–2093
Huang Y, Mucke L (2012) Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 148:1204–1222
Kaminsky YG, Marlatt MW, Smith MA, Kosenko EA (2010) Subcellular and metabolic examination of amyloid-beta peptides in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis: evidence for Abeta(25-35). Exp Neurol 221:26–37
Lee HP, Zhu X, Casadesus G et al (2010) Antioxidant approaches for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Expert Rev Neurother 10:1201–1208
Maier CM, Chan PH (2002) Role of superoxide dismutases in oxidative damage and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscientist 8:323–334
Mangialasche F, Polidori MC, Monastero R et al (2009) Biomarkers of oxidative and nitrosative damage in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Ageing Res Rev 8:285–305
Martínez E, Navarro A, Ordóñez C, Del Valle E, Tolivia J (2012) Amyloid-beta25-35 induces apolipoprotein D synthesis and growth arrest in HT22 hippocampal cells. J Alzheimers Dis 30:233–244
Mattson MP (2006) Neuronal life-and-death signaling, apoptosis, and neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1997–2006
Millucci L, Ghezzi L, Bernardini G, Santucci A (2010) Conformations and biological activities of amyloid beta peptide 25-35. Curr Protein Pept Sci 11:54–67
Murphy MP, Smith RA (2007) Targeting antioxidants to mitochondria by conjugation to lipophilic cations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:629–656
Pike CJ, Overman MJ, Cotman CW (1995) Amino-terminal deletions enhance aggregation of beta-amyloid peptides in vitro. J Biol Chem 270:23895–23898
Reddy PH (2006) Amyloid precursor protein-mediated free radicals and oxidative damage: implications for the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 96:1–13
Reddy PH (2007) Mitochondrial dysfunction in aging and Alzheimer's disease: strategies to protect neurons. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:1647–1658
Ross CA, Poirier MA (2004) Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med 10(Suppl):S10–S17
Shibata K, Hashimoto T, Nobe K, Hasumi K, Honda K (2011) Neuroprotective mechanisms of SMTP-7 in cerebral infarction model in mice. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 384:103–108
Song Y, Li M, Li JC, Wei EQ (2006) Edaravone protects PC12 cells from ischemic-like injury via attenuating the damage to mitochondria. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 7:749–756
Uzun S, Kozumplik O, Folnegović-Smalc V (2011) Alzheimer's dementia: current data review. Coll Antropol 35:1333–1337
Wang GH, Jiang ZL, Li YC et al (2011) Free-radical scavenger edaravone treatment confers neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 28:2123–2134
Xiong N, Xiong J, Khare G et al (2011) Edaravone guards dopamine neurons in a rotenone model for Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 6:e20677
Yamamura M, Miyamoto Y, Mitsuno M et al (2010) Edaravone reduces mitochondrial damage due to reperfusion injury following leg ischemia in rats. Int J Angiol 19:e129–e131
Yoshida H, Yanai H, Namiki Y, Fukatsu-Sasaki K, Furutani N, Tada N (2006) Neuroprotective effects of edaravone: a novel free radical scavenger in cerebrovascular injury. CNS Drug Rev 12:9–20
Yu M, Li S, Leng W, Chen H, Wu Y, Yan L (2010) Protective effects of MCl-186 on oxidative damage in a cell model of Alzheimer's disease. Neural Regen Res 5:1226–1230
Zhou Y, Li W, Xu L, Chen L (2011) In Salvia miltiorrhiza, phenolic acids possess protective properties against amyloid beta-induced cytotoxicity, and tanshinones act as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 31:443–452
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Shaanxi Science Research Project, China (no. 2010K16-08-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Gl., Zhang, Wg., Du, Y. et al. Edaravone Ameliorates Oxidative Damage Associated with Aβ25-35 Treatment in PC12 Cells. J Mol Neurosci 50, 494–503 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9973-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9973-z