Abstract
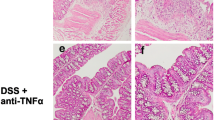
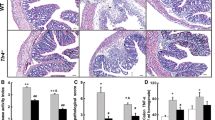
VIP is highly expressed in the colon and regulates motility, vasodilatation, and sphincter relaxation. However, its role in the development and progress of colitis is still controversial. Our aim was to determine the participation of VIP on dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colonic mucosal inflammation using VIP−/− and WT mice treated with VIP antagonists. Colitis was induced in 32 adult VIP−/− and 14 age-matched WT litter-mates by giving 2.5 % DSS in the drinking water. DSS-treated WT mice were injected daily with VIP antagonists, VIPHyb (n = 22), PG 97–269 (n = 9), or vehicle (n = 31). After euthanasia, colons were examined; colonic cytokines mRNA were quantified. VIP−/− mice were remarkably resistant to DSS-induced colitis compared to WT. Similarly, DSS-treated WT mice injected with VIPHyb (1 μM) or PG 97–269 (1 nM) had significantly reduced clinical signs of colitis. Furthermore, colonic expression of IL-1ϐ, TNF-α, and IL-6 was significantly lower in VIP−/− and VIPHyb or PG 97–269 compared to vehicle-treated WT. Genetic deletion of VIP or pharmacological inhibition of VIP receptors resulted in resistance to colitis. These data demonstrate a pro-inflammatory role for VIP in murine colitis and suggest that VIP antagonists may be an effective clinical treatment for human inflammatory bowel diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad C, Martinez C, Juarranz MG et al (2003) Therapeutic effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid mice model of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 124:961–971
Abad C, Gomariz RP, Waschek JA (2006) Neuropeptide mimetics and antagonists in the treatment of inflammatory disease: focus on VIP and PACAP. Curr Top Med Chem 6:151–163
Abad C, Tan YV, Lopez R et al (2010) Vasoactive intestinal peptide loss leads to impaired CNS parenchymal T-cell infiltration and resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:19555–19560
Abad C, Tan YV, Cheung-Lau G, Nobuta H, Waschek JA (2012) VIP deficient mice exhibit resistance to lipopolysaccharide induced endotoxemia with an intrinsic defect in proinflammatory cellular responses. PLoS One 7:e36922
Alex P, Zachos NC, Nguyen T et al (2009) Distinct cytokine patterns identified from multiplex profiles of murine DSS and TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:341–352
Andersen O, Fahrenkrug J, Wikkelsø C, Johansson BB (1984) VIP in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Peptides 5:435–437
Ballinger A (2008) Adverse effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the colon. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10:485–489
Banks MR, Farthing MJ, Robberecht P, Burleigh DE (2005) Antisecretory actions of a novel vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) antagonist in human and rat small intestine. Br J Pharmacol 144:994–1001
Belai A, Boulos PB, Robson T, Burnstock G (1997) Neurochemical coding in the small intestine of patients with Crohn’s disease. Gut 40:767–774
Boyer L, Sidpra D, Jevon G, Buchan AM, Jacobson K (2007) Differential responses of VIPergic and nitrergic neurons in paediatric patients with Crohn’s disease. Auton Neurosci 134:106–114
Brandtzaeg P, Oktedalen O, Kierulf P, Opstad PK (1989) Elevated VIP and endotoxin plasma levels in human gram-negative septic shock. Regul Pept 24:37–44
Colwell CS, Michel S, Itri J et al (2003) Disrupted circadian rhythms in VIP- and PHI-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:R939–R949
Delgado M, Martinez C, Johnson MC, Gomariz RP, Ganea D (1996) Differential expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors 1 and 2 (VIP-R1 and VIP-R2) mRNA in murine lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol 68:27–38
Delgado M, Pozo D, Martinez C et al (1999a) Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit endotoxin-induced TNF-alpha production by macrophages: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Immunol 162:2358–2367
Delgado M, Martinez C, Leceta J, Gomariz RP (1999b) Vasoactive intestinal peptide in thymus: synthesis, receptors and biological actions. Neuroimmunomodulation 6:97–107
Delgado M, Pozo D, Ganea D (2004a) The significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation. Pharmacol Rev 56:249–290
Delgado M, Gonzalez-Rey E, Ganea D (2004b) VIP/PACAP preferentially attract Th2 effectors through differential regulation of chemokine production by dendritic cells. FASEB J 18:1453–1455
Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H et al (1998) Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol 114:385–391
Gonzalez-Rey E, Fernandez-Martin A, Chorny A et al (2006) Therapeutic effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: down-regulation of inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Am J Pathol 168:1179–1188
Gozes Y, Brenneman DE, Fridkin M, Asofsky R, Gozes I (1991) A VIP antagonist distinguishes VIP receptors on spinal cord cells and lymphocytes. Brain Res 540:319–321
Grimm MC, Newman R, Hassim Z et al (2003) Cutting edge: vasoactive intestinal peptide acts as a potent suppressor of inflammation in vivo by trans-deactivating chemokine receptors. J Immunol 17:4990–4994
Gross KJ, Pothoulakis C (2007) Role of neuropeptides in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13:918–932
Harmar AJ, Fahrenkrug J, Gozes I et al (2012) Pharmacology and functions of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide: IUPHAR review 1. Br J Pharmacol 166:4–17
Johnston JA, Taubb DD, Lloyd AR, Conlon K, Oppenheim JJ, Kevlin DJ (1994) Human T lymphocyte chemotaxis and adhesion induced by VIP. J Immunol 153:1762–1768
Juarranz Y, Gutiérrez-Cañas I, Santiago B, Carrión M, Pablos JL, Gomariz RP (2008) Differential expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide and its functional receptors in human osteoarthritic and rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 58:1086–1095
Margolis KG, Gershon MD (2009) Neuropeptides and inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 25:503–511
Melgar S, Karlsson A, Michaëlsson E (2005) Acute colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium progresses to chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice: correlation between symptoms and inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G1328–G1338
Melgar S, Karlsson L, Rehnström E et al (2008) Validation of murine dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis using four therapeutic agents for human inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol 8:836–844
Moody TW, Jensen RT, Fridkin M, Gozes I (2002) (N-stearyl, norleucine17)VIPhybrid is a broad spectrum vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor antagonist. J Mol Neurosci 18:29–35
Moody TW, Zia F, Draoui M et al (2003) A vasoactive intestinal peptide antagonist inhibits non-small cell lung cancer growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:4345–4349
Newman R, Cuan N, Hampartzoumian T, Connor SJ, Lloyd AR, Grimm MC (2005) Vasoactive intestinal peptide impairs leucocyte migration but fails to modify experimental murine colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 139:411–420
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R (1990) A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702
Ottaway CA, Lewis DL, Asa SL (1987) Vasoactive intestinal peptide-containing nerves in Peyer’s patches. Brain Behav Immun 1:148–158
Perrier C, Rutgeerts P (2012) New drug therapies on the horizon for IBD. Dig Dis 30(Suppl 1):100–105
Perše M, Cerar A (2012) Dextran sodium sulphate colitis mouse model: traps and tricks. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:718617
Reshef R, Varkel J, Shiller M, Loberant N (1992) Systemic effects of rectally administered corticosteroids. Isr J Med Sci 28:98–100
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Törnwall J, Uusitalo H, Hukkanen M, Sorsa T, Konttinen YT (1994) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and its binding sites in labial salivary glands in Sjögren’s syndrome and in normal controls. Clin Exp Rheumatol 12:287–292
Truelove SC (1960) Systemic and local corticosteroid therapy in ulcerative colitis. Br Med J 1:464–467
Von der Weid PY, Rehal S, Dyrda P et al (2012) Mechanisms of VIP-induced inhibition of the lymphatic vessel pump. J Physiol 590:2677–2691
Wang JM, McVicar DW, Oppenheim JJ, Kelvin DJ (1993) Identification of RANTES receptors on human monocytic cells: competition for binding and desensitization by homologous chemotactic cytokines. J Exp Med 177:699–705
Waschek J (2013) VIP and PACAP: neuropeptide modulators of CNS inflammation, injury and repair. Br J Pharmacol 169:512–523
Yadav M, Huang MC, Goetzl EJ (2011) VPAC1 (vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptor type 1) G protein-coupled receptor mediation of VIP enhancement of murine experimental colitis. Cell Immunol 267:124–132
Yukawa T, Oshitani N, Yamagami H, Watanabe K, Higuchi K, Arakawa T (2007) Differential expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1 expression in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Med 20:161–167
Zia H, Hida T, Jakowlew S et al (1996) Breast cancer growth is inhibited by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) hybrid, a synthetic VIP receptor antagonist. Cancer Res 56:3486–3489
Zia H, Leyton J, Casibang M et al (2000) (N-stearyl, norleucine17) VIP hybrid inhibits the growth of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Life Sci 66:379–387
Grant Support
Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Review (PG, JP) NIH DK-41301 & RO1 DK-078676 (MM)
Conflict of Interest
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(JPEG 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vu, J.P., Million, M., Larauche, M. et al. Inhibition of Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide (VIP) Induces Resistance to Dextran Sodium Sulfate (DSS)-Induced Colitis in Mice. J Mol Neurosci 52, 37–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0205-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0205-3