Abstract
Impaired salt and water absorption is a hallmark of diarrhea in IBD. In the present study, the therapeutic effect of continuous anti-TNFα treatment on the progression of inflammation and colonic transport dysfunction during chronic dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis was investigated. Chronic colitis was induced by three DSS exposure cycles. Mice received TNFα monoclonal antibody treatment twice weekly after the end of the first 5-day DSS drinking period. Mice developed chronic DSS-induced colitis characterized by a typical immune cell infiltration composed of CD3+ T cells and CD68+ macrophages, both expressing high levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα, a loss of NHE3 and PDZK1 in the brush border region of the absorptive enterocyte and a decrease of colonic fluid absorption in vivo, measured by colonic single pass perfusion. Concomitant anti-TNFα treatment resulted in a significant reduction of mucosal immune cell infiltration and expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα. It also resulted in a normalization of NHE3-mediated fluid absorption and a restoration of NHE3 and PDZK1 location in the apical and subapical region of the enterocytes. Here, we show for the first time that in this chemically induced murine colitis model, anti-TNFα treatment significantly decreased inflammatory activity, improved mucosal integrity and restored transport function despite an ongoing inflammatory insult. Anti-TNFα treatment may therefore be beneficial in patients with IBD even in spite of an absence of complete mucosal healing.
Key messages
-
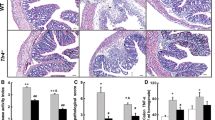
Chronic DSS treatment caused a loss of NHE3 and PDZK1 in the brush border region of the absorptive enterocyte and decreases colonic fluid absorption.
-
In DSS-induced colitis, anti-TNFα treatment reduced mucosal immune cell infiltration and expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα.
-
In DSS-induced colitis, anti-TNFα treatment normalized NHE3-mediated fluid absorption and restored NHE3 and PDZK1 location in the enterocytes.
-
In DSS-induced colitis, anti-TNFα treatment decreased inflammatory activity, improved mucosal integrity, and restored transport function.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSS:
-
Dextran sulfate sodium
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IL-1ß:
-
Interleukin-1 beta
- NHE3:
-
Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3
- PDZK1:
-
PDZ domain-containing 1
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
de Souza HS, Fiocchi C (2016) Immunopathogenesis of IBD: current state of the art. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13(1):13–27
Neurath MF (2014) Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14(5):329–342
Neurath MF (2017) Current and emerging therapeutic targets for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(5):269–278
Geboes K, Rutgeerts P, Opdenakker G, Olson A, Patel K, Wagner CL, Marano CW (2005) Endoscopic and histologic evidence of persistent mucosal healing and correlation with clinical improvement following sustained infliximab treatment for Crohn’s disease. Curr Med Res Opin 21(11):1741–1754
Moss AC (2014) The meaning of low-grade inflammation in clinically quiescent inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 30(4):365–369
Field M (2003) Intestinal ion transport and the pathophysiology of diarrhea. J Clin Invest 111(7):931–943
Gareau MG, Barrett KE (2013) Fluid and electrolyte secretion in the inflamed gut: novel targets for treatment of inflammation-induced diarrhea. Curr Opin Pharmacol 13(6):895–899
Seidler U, Lenzen H, Cinar A, Tessema T, Bleich A, Riederer B (2006) Molecular mechanisms of disturbed electrolyte transport in intestinal inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1072(1):262–275
Donowitz M, Li X (2007) Regulatory binding partners and complexes of NHE3. Physiol Rev 87(3):825–872
Schultheis PJ, Clarke LL, Meneton P, Miller ML, Soleimani M, Gawenis LR, Riddle TM, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Wang T, Giebisch G, Aronson PS, Lorenz JN, Shull GE (1998) Renal and intestinal absorptive defects in mice lacking the NHE3 Na+/H+ exchanger. Nat Genet 19(3):282–285
Lamprecht G, Seidler U (2006) The emerging role of PDZ adapter proteins for regulation of intestinal ion transport. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291(5):G766–G777
Seidler U, Singh A, Chen M, Cinar A, Bachmann O, Zheng W, Wang J, Yeruva S, Riederer B (2009) Knockout mouse models for intestinal electrolyte transporters and regulatory PDZ adaptors: new insights into cystic fibrosis, secretory diarrhoea and fructose-induced hypertension. Exp Physiol 94(2):175–179
Seidler U, Singh AK, Cinar A, Chen M, Hillesheim J, Hogema B, Riederer B (2009) The role of the NHERF family of PDZ scaffolding proteins in the regulation of salt and water transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165(1):249–260
Lenzen H, Lünnemann M, Bleich A, Manns MP, Seidler U, Jörns A (2012) Downregulation of the NHE3-binding PDZ-adaptor protein PDZK1 expression during cytokine-induced inflammation in interleukin-10-deficient mice. PLoS One 7(7):e40657
Yeruva S, Farkas K, Hubricht J, Rode K, Riederer B, Bachmann O, Cinar A, Rakonczay Z, Molnar T, Nagy F et al (2010) Preserved Na(+)/H(+) exchanger isoform 3 expression and localization, but decreased NHE3 function indicate regulatory sodium transport defect in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16(7):1149–1161
Farkas K, Yeruva S, Rakonczay Z Jr, Ludolph L, Molnar T, Nagy F, Szepes Z, Schnur A, Wittmann T, Hubricht J et al (2011) New therapeutic targets in ulcerative colitis: the importance of ion transporters in the human colon. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(4):884–898
Yeruva S, Chodisetti G, Luo M, Chen M, Cinar A, Ludolph L, Lünnemann M, Goldstein J, Singh AK, Riederer B, Bachmann O, Bleich A, Gereke M, Bruder D, Hagen S, He P, Yun C, Seidler U (2015) Evidence for a causal link between adaptor protein PDZK1 downregulation and Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE3 dysfunction in human and murine colitis. Pflügers Arch 467(8):1795–1807
Luo M, Yeruva S, Liu Y, Chodisetti G, Riederer B, Menon MB, Tachibana K, Doi T, Seidler UE (2017) IL-1beta-induced downregulation of the multifunctional PDZ adaptor PDZK1 is attenuated by ERK inhibition, RXRalpha, or PPARalpha stimulation in enterocytes. Front Physiol 8(1):61
Chassaing B, Aitken JD, Malleshappa M, Vijay-Kumar M (2014) Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr Protoc Immunol 104(1):Unit-15.25
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ (1993) Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Investig 69(2):238–249
Eichele DD, Kharbanda KK (2017) Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: an indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 23(33):6016–6029
Whittem CG, Williams AD, Williams CS (2010) Murine colitis modeling using dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/1652
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K, Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S, Neurath MF (2017) Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat Protoc 12(7):1295–1309
Berg DJ, Davidson N, Kuhn R, Muller W, Menon S, Holland G, Thompson-Snipes L, Leach MW, Rennick D (1996) Enterocolitis and colon cancer in interleukin-10-deficient mice are associated with aberrant cytokine production and CD4(+) TH1-like responses. J Clin Invest 98(4):1010–1020
Arndt T, Wedekind D, Weiss H, Tiedge M, Lenzen S, Hedrich HJ, Jörns A (2009) Prevention of spontaneous immune-mediated diabetes development in the LEW.1AR1-iddm rat by selective CD8+ T cell transfer is associated with a cytokine shift in the pancreas-draining lymph nodes. Diabetologia 52(7):1381–1390
Xia W, Yu Q, Riederer B, Singh AK, Engelhardt R, Yeruva S, Song P, Tian DA, Soleiman M, Seidler U (2014) The distinct roles of anion transporters Slc26a3 (DRA) and Slc26a6 (PAT-1) in fluid and electrolyte absorption in the murine small intestine. Pflügers Arch 466(8):1541–1556
Sjöblom M, Nylander O (2007) Isoflurane-induced acidosis depresses basal and PGE(2)-stimulated duodenal bicarbonate secretion in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292(3):G899–G904
Turnberg LA, Bieberdorf FA, Morawski SG, Fordtran JS (1970) Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J Clin Invest 49(3):557–567
Chen M, Sultan A, Cinar A, Yeruva S, Riederer B, Singh AK, Li J, Bonhagen J, Chen G, Yun C, Donowitz M, Hogema B, deJonge H, Seidler U (2010) Loss of PDZ-adaptor protein NHERF2 affects membrane localization and cGMP- and [Ca2+]- but not cAMP-dependent regulation of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in murine intestine. J Physiol 588(24):5049–5063
Hegan PS, Giral H, Levi M, Mooseker MS (2012) Myosin VI is required for maintenance of brush border structure, composition, and membrane trafficking functions in the intestinal epithelial cell. Cytoskeleton 69(4):235–251
Chen T, Hubbard A, Murtazina R, Price J, Yang J, Cha B, Sarker R, Donowitz M (2014) Myosin VI mediates the movement of NHE3 down the microvillus in intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 127(16):3535–3545
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Lemann M (2011) Review article: remission rates achievable by current therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33(8):870–879
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Reinisch W, Colombel JF, Mantzaris GJ, Kornbluth A, Diamond R, Rutgeerts P, Tang LK, Cornillie FJ, Sandborn WJ (2014) Clinical disease activity, C-reactive protein normalisation and mucosal healing in Crohn’s disease in the SONIC trial. Gut 63(1):88–95
Sandle GI, Hayslett JP, Binder HJ (1986) Effect of glucocorticoids on rectal transport in normal subjects and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 27(3):309–316
Bergann T, Zeissig S, Fromm A, Richter JF, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2009) Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergize to induce absorption by the epithelial sodium channel in the colon. Gastroenterology 136(3):933–942
Oprins JC, Meijer HP, Groot JA (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha potentiates ion secretion induced by muscarinic receptor activation in the human intestinal epithelial cell line HT29cl.19A. Ann N Y Acad Sci 915(3):102–106
Hering NA, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2012) Determinants of colonic barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease and potential therapeutics. J Physiol 590(5):1035–1044
Dinarello CA (2009) Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol 27(1):519–550
Gill RK, Saksena S, Syed IA, Tyagi S, Alrefai WA, Malakooti J, Ramaswamy K, Dudeja PK (2002) Regulation of NHE3 by nitric oxide in Caco-2 cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283(3):G747–G756
Jörns A, Ertekin UG, Arndt T, Terbish T, Wedekind D, Lenzen S (2015) TNF-alpha antibody therapy in combination with the T-cell-specific antibody anti-TCR reverses the diabetic metabolic state in the LEW.1AR1-iddm rat. Diabetes 64(8):2880–2891
Siddique I, Hasan F, Khan I (2009) Suppression of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform-3 in human inflammatory bowel disease: lack of reversal by 5′-aminosalicylate treatment. Scand J Gastroenterol 44(1):56–64
Sullivan S, Alex P, Dassopoulos T, Zachos NC, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Donowitz M, Brant SR, Cuffari C, Harris ML, Datta LW, Conklin L, Chen Y, Li X (2009) Downregulation of sodium transporters and NHERF proteins in IBD patients and mouse colitis models: potential contributors to IBD-associated diarrhea. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15(2):261–274
Turnberg LA, Fordtran JS, Carter NW, Rector FC Jr (1970) Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest 49(3):548–556
Lohi H, Makela S, Pulkkinen K, Hoglund P, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Puolakkainen P, Kere J (2002) Upregulation of CFTR expression but not SLC26A3 and SLC9A3 in ulcerative colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283(3):G567–G575
Yang H, Jiang W, Furth EE, Wen X, Katz JP, Sellon RK, Silberg DG, Antalis TM, Schweinfest CW, Wu GD (1998) Intestinal inflammation reduces expression of DRA, a transporter responsible for congenital chloride diarrhea. Am J Phys 275(6 Pt 1):G1445–G1453
Xiao F, Juric M, Li J, Riederer B, Yeruva S, Singh AK, Zheng L, Glage S, Kollias G, Dudeja P, Tian DA, Xu G, Zhu J, Bachmann O, Seidler U (2012) Loss of downregulated in adenoma (DRA) impairs mucosal HCO3(−) secretion in murine ileocolonic inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis 18(1):101–111
Juric M, Xiao F, Amasheh S, May O, Wahl K, Bantel H, Manns MP, Seidler U, Bachmann O (2013) Increased epithelial permeability is the primary cause for bicarbonate loss in inflamed murine colon. Inflamm Bowel Dis 19(5):904–911
Hillesheim J, Riederer B, Tuo B, Chen M, Manns M, Biber J, Yun C, Kocher O, Seidler U (2007) Down regulation of small intestinal ion transport in PDZK1- (CAP70/NHERF3) deficient mice. Pflügers Arch 454(4):575–586
Zachos NC, Li X, Kovbasnjuk O, Hogema B, Sarker R, Lee LJ, Li M, de Jonge H, Donowitz M (2009) NHERF3 (PDZK1) contributes to basal and calcium inhibition of NHE3 activity in Caco-2BBe cells. J Biol Chem 284(35):23708–23718
Cinar A, Chen M, Riederer B, Bachmann O, Wiemann M, Manns M, Kocher O, Seidler U (2007) NHE3 inhibition by cAMP and Ca2+ is abolished in PDZ-domain protein PDZK1-deficient murine enterocytes. J Physiol 581(3):1235–1246
Kato Y, Sai Y, Yoshida K, Watanabe C, Hirata T, Tsuji A (2005) PDZK1 directly regulates the function of organic cation/carnitine transporter OCTN2. Mol Pharmacol 67(3):734–743
Kocher O, Comella N, Gilchrist A, Pal R, Tognazzi K, Brown LF, Knoll JH (1999) PDZK1, a novel PDZ domain-containing protein up-regulated in carcinomas and mapped to chromosome 1q21, interacts with cMOAT (MRP2), the multidrug resistance-associated protein. Lab Investig 79(9):1161–1170
Sugiura T, Shimizu T, Kijima A, Minakata S, Kato Y (2011) PDZ adaptors: their regulation of epithelial transporters and involvement in human diseases. J Pharm Sci 100(9):3620–3635
LaLonde DP, Garbett D, Bretscher A (2010) A regulated complex of the scaffolding proteins PDZK1 and EBP50 with ezrin contribute to microvillar organization. Mol Biol Cell 21(9):1519–1529
Malmberg EK, Pelaseyed T, Petersson AC, Seidler UE, De Jonge H, Riordan JR, Hansson GC (2008) The C-terminus of the transmembrane mucin MUC17 binds to the scaffold protein PDZK1 that stably localizes it to the enterocyte apical membrane in the small intestine. Biochem J 410(2):283–289
Pelaseyed T, Bergström JH, Gustafsson JK, Ermund A, Birchenough GM, Schutte A, van der Post S, Svensson F, Rodriguez-Pineiro AM, Nyström EE et al (2014) The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol Rev 260(1):8–20
Martin L, Koczera P, Zechendorf E, Schuerholz T (2016) The endothelial glycocalyx: new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in sepsis. Biomed Res Int 2016(2016):3758278
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Brigitte Riederer for fruitful discussions and valuable advice. The excellent technical assistance of D. Lischke and R. Strauss is gratefully acknowledged.
Source of funding
This work has been supported in part by funding from the “Ellen-Schmidt-Habilitation” program of the Equal Opportunities Office of the Hannover Medical School (to H.L.), grants from the German Research Council (SE460/19-1 and 21-1 to U.S.) and (JO395/2-2 to A.J.) and a grant from the Lower Saxony Ministry of Science and Culture (VW-Vorab to U.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL, US, and AJ were involved in the design of the study, acquisition, and interpretation of data and drafting the article. JQ was involved in acquisition and analysis of data and revising the article critically for important intellectual content. MPM provided key support in interpretation of data and revising the article for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were performed according to the national and institutional guidelines and were approved by the Local Institutional Animal Care and Research Advisory Committee at the Hannover Medical School and authorized by the local government for the regulation of animal welfare (Niedersächsisches Landesamt für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit, LAVES, No 33.12-42502-04-14/1641).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
Time course of the experiments, showing the three DSS cycles and anti-TNFα treatment. Control and DSS-treated mice received a corresponding number of IgG i.p. injections of an identical volume (100 μL) instead of anti-TNFα injections. (PNG 85 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lenzen, H., Qian, J., Manns, M.P. et al. Restoration of mucosal integrity and epithelial transport function by concomitant anti-TNFα treatment in chronic DSS-induced colitis. J Mol Med 96, 831–843 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1658-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1658-1