Abstract
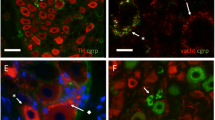
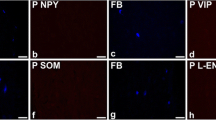
The distribution and chemical coding of neurons supplying urinary bladder in the male pig were studied in the sympathetic chain ganglia, inferior mesenteric ganglia and anterior pelvic ganglia. The combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), neuropeptide Y (NPY), somatostatin (SOM), galanin (GAL), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), nitric oxide synthase (NOS), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), substance P (SP), choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) were applied in the experiment. Bladder-projecting neurons were found in all the ganglia studied. The majority of sympathetic ganglia neurons (inferior mesenteric ganglia and sympathetic chain ganglia) expressed immunoreactivity (IR) to DBH. In sympathetic chain ganglia these neurons simultaneously expressed NPY, GAL or VAChT, while in inferior mesenteric ganglia they contained NPY, SOM and/or GAL. A small number of these bladder-projecting neurons was VAChT-IR and some contained NPY. In the pelvic ganglia bladder-projecting neurons formed two populations: DBH- and VAChT-IR. Some of DBH-IR neurons contained IR to NPY, SOM or GAL, while VAChT-IR neurons were NPY-, SOM- or NOS-IR. The results indicate that sympathetic ganglia contain mainly adrenergic neurons, while pelvic ganglia contain both adrenergic and cholinergic neurons. All these neurons contain typical combinations of neuropeptides.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alm P, Elmer M (1975) Adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the rat urinary bladder. Acta Physiol Scand 94:36–45
Alm P, Uvelius B, Ekstrom J, Holmqvist B, Larsson B, Andersson KE (1995a) Nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in rat parasympathetic, sympathetic and sensory ganglia: a comparative study. Histochem J 27:819–831
Alm P, Zygmunt PK, Iselin C, Larsson B, Uvelius B, Werner S, Andersson KE (1995b) Nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive, adrenergic, cholinergic, and peptidergic nerves of the female rat urinary tract: a comparative study. J Auton Nerv Syst 56:105–114
Brindley GS (1988) Autonmic control of pelvic organs. In: Bannister R (ed) Autonomic failure: a textbook of clinical disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 223–227
Burlinski PJ, Burlinska AM, Gonkowski S, Calka J (2013) Resiniferatoxin and tetrodotoxin induced NPY and TH immunoreactivity changes within the paracervical ganglion neurons supplying the urinary bladder. J Mol Neurosci 49:62–67
Chien CH, Li SH, Shen CL (1991) The ovarian innervation in the dog: a preliminary study for the base for electro-acupuncture. J Auton Nerv Syst 35:185–192
Craggs M, McFarlane J (1999) Neuromodulation of the lower urinary tract. Exp Physiol 84:149–160
Crowe R, Noble J, Robson T, Soediono P, Milroy EJ, Burnstock G (1995) An increase of neuropeptide Y but not nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive nerves in the bladder neck from male patients with bladder neck dyssynergia. J Urol 154:1231–1236
Czaja K, Kaleczyc J, Pidsudko Z, Franke-Radowiecka A, Lakomy M (2001) Distribution of efferent neurones innervating the oviduct in the pig. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 60:243–248
Dail WG (1993) Autonomic inervation of male reproductive genitalia. In: Maggi CA (ed) Nervous control of the urogenital system. Harwood Academic Publ, Chur, Switzerland, pp 69–101
Dail WG, Moll MA, Weber K (1983) Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in penile erectile tissue and in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat. Neuroscience 10:1379–1386
Dail WG, Minorsky N, Moll MA, Manzanares K (1986) The hypogastric nerve pathway to penile erectile tissue: histochemical evidence supporting a vasodilator role. J Auton Nerv Syst 15:341–349
Dalmose AL, Hvistendahl JJ, Olsen LH, Eskild-Jensen A, Djurhuus JC, Swindle MM (2000) Surgically induced urologic models in swine. J Invest Surg 13:133–145
de Groat WC, Booth AM (1993) Synaptic transmission in pelvic ganglia. In: Maggi CA (ed) Nervous control of the urogenital system. Harwood Academic Publishers, Chur, pp 291–347
Dhami D, Mitchell BS (1994) Chemical coding of neurons projecting to pelvic viscera in the male guinea pig: a study by retrograde transport and immunohistochemistry. Histochem J 26:262–270
Downie JW, Champion JA, Nance DM (1984) A quantitative analysis of the afferent and extrinsinc efferent innervation of specyfic regions of the bladder and urethra in the cat. Brain Res Bull 12:735–740
Ekblad E, Hakanson R, Sundler F, Wahlestedt C (1985) Galanin: neuromodulatory and direct contractile effects on smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol 86:241–246
Heym C, Webber R, Horn M, Kummer W (1990) Neuronal pathways in the guinea-pig lumbar sympathetic ganglia as revealed by immunohistochemistry. Histochemistry 93:547–557
Hokfelt T, Elfvin LG, Schultzberg M, Fuxe K, Said S, Mutt V, Goldstein M (1977a) Immunohistochemical evidence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing neurons and nerve fibers in sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience 2:896
Hokfelt T, Elfvin LG, Schultzberg M, Goldstein M, Nilsson G (1977b) On the occurrence of substance P-containing fibers in sympathetic ganglia: immunohistochemical evidence. Brain Res 132:29–41
Hokfelt T, Schultzberg M, Elde R, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Said S, Goldstein M (1978) Peptide neurons in peripheral tissues including the urinary tract: immunohistochemical studies. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 43(Suppl 2):79–89
Houdeau E, Rousseau A, Meusnier C, Prud H, Rousseau JP (1998) Sympathetic innervation of the upper and lower regions of the uterus and cervix in the rat have different origins and routes. J Comp Neurol 399:403–412
Hoyle CH (1994) Non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic control of the urinary bladder. World J Urol 12:233–244
Janig W, McLachlan EM (1987) Organization of lumbar spinal outflow to distal colon and pelvic organs. Physiol Rev 67:1332–1404
Kaleczyc J (1998) Origin and neurochemical characteristics of nerve fibres supplying the mammalian vas deferens. Microsc Res Tech 42:409–422
Kaleczyc J, Timmermans JP, Majewski M, Lakomy M, Scheuermann DW (1995) Distribution and immunohistochemical characteristics of neurons in the porcine caudal mesenteric ganglion projecting to the vas deferens and seminal vesicle. Cell Tissue Res 282:59–68
Kaleczyc J, Sienkiewicz W, Klimczuk M, Czaja K, Lakomy M (2003) Differences in the chemical coding of nerve fibres supplying major populations of neurons between the caudal mesenteric ganglion and anterior pelvic ganglion in the male pig. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 41:201–211
Keast JR (1991) Patterns of co-existence of peptides and differences of nerve fibre types associated with noradrenergic and non-noradrenergic (putative cholinergic) neurons in the major pelvic ganglion of the male rat. Cell Tissue Res 266:405–415
Keast JR (1992) Location and peptide content of pelvic neurons supplying the muscle and lamina propria of the rat vas deferens. J Auton Nerv Syst 40:1–11
Keast JR (1995a) Pelvic ganglia. In: McLachlan EM (ed) Autonomic ganglia. Harwood Academic Publishers, Luxembourg, pp 445–479
Keast JR (1995b) Visualization and immunohistochemical characterization of sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons in the male rat major pelvic ganglion. Neuroscience 66:655–662
Keast JR (2006) Plasticity of pelvic autonomic ganglia and urogenital innervation. Int Rev Cytol 248:141–208
Keast JR, de Groat WC (1989) Immunohistochemical characterization of pelvic neurons which project to the bladder, colon, or penis in rats. J Comp Neurol 288:387–400
Keast JR, Booth AM, de Groat WC (1989) Distribution of neurons in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat which supply the bladder, colon or penis. Cell Tissue Res 256:105–112
Keast JR, Luckensmeyer GB, Schemann M (1995) All pelvic neurons in male rats contain immunoreactivity for the synthetic enzymes of either noradrenaline or acetylcholine. Neurosci Lett 196:209–212
Klimczuk M (2004) Immunohistochemical characteristics of neurons supplying the porcine bulbourethral gland. Pol J Vet Sci 7:129–142
Kummer W (1987) Galanin- and neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivities coexist in paravertebral sympathetic neurones of the cat. Neurosci Lett 78:127–131
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nat 227:680–685
Lakomy M, Häppölä O, Kaleczyc J, Majewski M (1994) Immunohistochemical localization of neuropeptides in the porcine thoraco-lumbar paravertebral ganglia. Anat Histol Embryol 23:12–20
Maggi CA, Meli A (1986) The role of neuropeptides in the regulation of the micturition reflex. J Auton Pharmacol 6:133–162
Majewski M, Heym C (1991) The origin of ovarian neuropeptide Y (NPY)-immunoreactive nerve fibres from the inferior mesenteric ganglion in the pig. Cell Tissue Res 266:591–596
Morris JL (1993) Co-transmission from autonomic vasodilator neurons supplying the guinea pig uterine artery. J Auton Nerv Syst 42:11–21
Morris JL, Gibbins IL (1987) Neuronal colocalization of peptides, catecholamines, and catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes in guinea pig paracervical ganglia. J Neurosci 7:3117–3130
Morris JL, Gibbins IL (1992) Co-transmission and neuromodulation. In: Burnstock G, Hoyle CHV (eds) Autonomic neuroeffector mechanisms. Harwood Academic Publishers, Chur, pp 33–119
Morris JL, Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, Murphy R (1985) Co-localization of neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and dynorphin in non-noradrenergic axons of the guinea pig uterine artery. Neurosci Lett 62:31–37
Morris JL, Gibbins IL, Furness JB (1987) Increased dopamine-beta-hydroxylase-like immunoreactivity in non-noradrenergic axons supplying the guinea-pig uterine artery after 6-hydroxydopamine treatment. J Auton Nerv Syst 21:15–27
Morrison J, Birder L, Craggs M, de Groat WC, Downie J, Drake M, Fowler C, Thor K (2005) Neural control. In: Incontinence. Health Publications, Ltd, Jersey
Papka RE, Traurig HH, Klenn P (1987) Paracervical ganglia of the female rat: histochemistry and immunohistochemistry of neurons, SIF cells, and nerve terminals. Am J Anat 179:243–257
Papka RE, Traurig HH, Schemann M, Collins J, Copelin T, Wilson K (1999) Cholinergic neurons of the pelvic autonomic ganglia and uterus of the female rat: distribution of axons and presence of muscarinic receptors. Cell Tissue Res 296:293–305
Pidsudko Z (2000) Distribution and chemical coding of neurons in the porcine inferior mesenteric ganglion projecting to the urinary bladder trigone. 56. ASGBI/AG/NAV Tripartite Meeting St John’s College Cambridge
Pidsudko Z, Kaleczyc J, Majewski M, Lakomy M, Scheuermann DW, Timmermans JP (2001) Differences in the distribution and chemical coding between neurons in the inferior mesenteric ganglion supplying the colon and rectum in the pig. Cell Tissue Res 303:147–158
Rand MJ (1992) Nitrergic transmission: nitric oxide as a mediator of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neuro-effector transmission. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 19:147–169
Sienkiewicz W (2010) Sources of the porcine testis innervation. Andrologia 42:395–403
Swindle MM, Moody DC, Phillips LD (1992) Swine as a models in biomedical research. Iowa State Univ Press, Ames
Vera PL, Nadelhaft I (1992) Afferent and sympathetic innervation of the dome and the base of the urinary bladder of the female rat. Brain Res Bull 29:651–658
Wang S, Gustafson EL (1998) Galanin receptor subtypes. Drug News Perspect 11:458–468
Wanigasekara Y, Kepper ME, Keast JR (2003) Immunohistochemical characterisation of pelvic autonomic ganglia in male mice. Cell Tissue Res 311:175–185
Wasowicz K (2003) Effect of total or partial uterus extirpation on uterus-projecting neurons in porcine inferior mesenteric ganglion. A. Changes in expression of transmitter-synthesizing enzymes—tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine beta-hydroxylase and choline acetyltransferase. Pol J Vet Sci 6:131–145
Wasowicz K, Majewski M, Lakomy M (1998) Distribution of neurons innervating the uterus of the pig. J Auton Nerv Syst 74:13–22
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank M. Marczak and A. Penkowski for their excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by a grant NN 308 2334 38 from the National Committee for Scientific Research Poland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pidsudko, Z. Immunohistochemical Characteristics and Distribution of Neurons in the Paravertebral, Prevertebral and Pelvic Ganglia Supplying the Urinary Bladder in the Male Pig. J Mol Neurosci 52, 56–70 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0139-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0139-9