Abstract
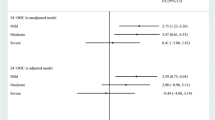
Excess cholesterol is removed from the brain via hydroxylation mediated by cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase (CYP46), which is a mechanism of maintaining cholesterol homeostasis in the brain. The CYP46A1 gene has been suggested as a genetic risk factor for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In this report, we analyzed an intronic CYP46A1 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in 508 sporadic AD patients and 549 controls in a Chinese Han population. Our results indicated that the distribution of CYP46A1 SNP rs754203 genotypes was significantly different in AD patients compared to controls (χ2 = 6.59, P = 0.037). The frequency of at least one of CYP46A1 T allele (C/T or T/T) was higher in AD patients compared to controls (χ2 = 6.58, P = 0.01). The age- and sex-adjusted odds ratio for the risk of AD in carriers of CYP46A1 T allele (C/T + T/T) was 1.69 (95 % confidence interval, 1.12–2.56). We conclude that this intronic polymorphism in CYP46A1 gene is associated with AD in a Chinese Han population, and the CYP46A1 T allele might be a risk factor for AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniades D, Katopodi T, Pappa S, Lampropoulos A, Konsta V, Frydas E, Mpalogiannis S, Hatzistilianou M (2011) The role of reelin gene polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in a Greek population. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 25:351–358
Borroni B, Archetti S, Agosti C, Akkawi N, Brambilla C, Caimi L, Caltagirone C, Di Luca M, Padovani A (2004) Intronic CYP46 polymorphism along with ApoE genotype in sporadic Alzheimer disease: from risk factors to disease modulators. Neurobiol Aging 25:747–751
Campion D, Dumanchin C, Hannequin D, Dubois B, Belliard S, Puel M, Thomas-Anterion C, Michon A, Martin C, Charbonnier F, Raux G, Camuzat A, Penet C, Mesnage V, Martinez M, Clerget-Darpoux F, Brice A, Frebourg T (1999) Early-onset autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease: prevalence, genetic heterogeneity, and mutation spectrum. Am J Hum Genet 65:664–670
Chalmers KA, Culpan D, Kehoe PG, Wilcock GK, Hughes A, Love S (2004) APOE promoter, ACE1 and CYP46 polymorphisms and beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 15:95–98
Combarros O, Infante J, Llorca J, Berciano J (2004) Genetic association of CYP46 and risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cog Disord 18:257–260
Desai P, DeKosky ST, Kamboh MI (2002) Genetic variation in the cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46) gene and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 328:9–12
Fassbender K, Simons M, Bergmann C, Stroick M, Lütjohann D, Keller P, Runz H, Kuhl S, Bertsch T, von Bergmann K, Hennerici M, Beyreuther K, Hartmann T (2001) Simvastatin strongly reduces levels of Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides Abeta 42 and Abeta 40 in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:5856–5861
Fernández Del Pozo V, Alvarez Alvarez M, Fernández Martínez M, Galdós Alcelay L, Gómez Busto F, Peña JA, Alfonso-Sánchez MA, Zarranz Imirizaldu JJ, de Pancorbo MM (2006) Polymorphism in the cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase gene (CYP46A1) associated with the APOEpsilon3 allele increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and of mild cognitive impairment progressing to Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 21:81–87
Golanska E, Hulas-Bigoszewska K, Wojcik I, Rieske P, Styczynska M, Peplonska B, Pfeffer A, Luczywek E, Wasiak B, Gabryelewicz T, Religa D, Chodakowska-Zebrowska M, Barcikowska M, Sobow T, Liberski PP (2005) CYP46: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease or a coincidence? Neurosci Lett 383:105–108
Helisalmi S, Vepsäläinen S, Koivisto AM, Mannermaa A, Iivonen S, Hiltunen M, Kiviniemi V, Soininen H (2006) Association of CYP46 intron 2 polymorphism in Finnish Alzheimer’s disease samples and a global scale summary. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:421–422
Huang Y, Weisgraber KH, Mucke L, Mahley RW (2004) Apolipoprotein E: diversity of cellular origins, structural and biophysical properties, and effects in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 23:189–204
Ingelsson M, Jesneck J, Irizarry MC, Hyman BT, Rebeck GW (2004) Lack of association of the cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46) intron 2 polymorphism with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 367:228–231
Johansson A, Katzov H, Zetterberg H, Feuk L, Johansson B, Bogdanovic N, Andreasen N, Lenhard B, Brookes AJ, Pedersen NL, Blennow K, Prince JA (2004) Variants of CYP46A1 may interact with age and APOE to influence CSF Abeta42 levels in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Genet 114:581–587
Juhász A, Rimanóczy A, Boda K, Vincze G, Szlávik G, Zana M, Bjelik A, Pákáski M, Bódi N, Palotás A, Janka Z, Kálmán J (2005) CYP46 T/C polymorphism is not associated with Alzheimer’s dementia in a population from Hungary. Neurochem Res 30:943–948
Kabbara A, Payet N, Cottel D, Frigard B, Amouyel P, Lambert JC (2004) Exclusion of CYP46 and APOM as candidate genes for Alzheimer’s disease in a French population. Neurosci Lett 363:139–143
Kirsch C, Eckert GP, Koudinov AR, Müller WE (2003) Brain cholesterol, statins and Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacopsychiatry 36(Suppl 2):S113–S119
Kölsch H, Lütjohann D, Jessen F, Popp J, Hentschel F, Kelemen P, Schmitz S, Maier W, Heun R (2009) CYP46A1 variants influence Alzheimer’s disease risk and brain cholesterol metabolism. Eur Psychiatry 24:183–190
Kölsch H, Lütjohann D, Ludwig M, Schulte A, Ptok U, Jessen F, von Bergmann K, Rao ML, Maier W, Heun R (2002) Polymorphism in the cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase gene is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 7:899–902
Li Y, Chu LW, Chen YQ, Cheung BM, Leung RY, Yik PY, Ng KM, Mak W, Jin DY, St George-Hyslop P, Song YQ (2006) Intron 2 (T/C) CYP46 polymorphism is associated with Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22:399–404
Lund EG, Guileyardo JM, Russell DW (1999) cDNA cloning of cholesterol 24-hydroxylase, a mediator of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7238–7243
Lütjohann D, von Bergmann K (2003) 24S-hydroxycholesterol: a marker of brain cholesterol metabolism. Pharmacopsychiatry 36(Suppl 2):S102–S106
Ma SL, Tang NL, Lam LC, Chiu HF (2006) Polymorphisms of the cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46A1) gene and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in a Chinese population. Int Psychogeriatr 18:37–45
Mast N, Norcross R, Andersson U, Shou M, Nakayama K, Bjorkhem I, Pikuleva IA (2003) Broad substrate specificity of human cytochrome P450 46A1 which initiates cholesterol degradation in the brain. Biochemistry 42:14284–14292
Papassotiropoulos A, Lütjohann D, Bagli M, Locatelli S, Jessen F, Rao ML, Maier W, Bjorkhem I, von Bergmann K, Heun R (2000) Plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol: a peripheral indicator of neuronal degeneration and potential state marker for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 11:1959–1962
Papassotiropoulos A, Streffer JR, Tsolaki M, Schmid S, Thal D, Nicosia F, Iakovidou V, Maddalena A, Lütjohann D, Ghebremedhin E, Hegi T, Pasch T, Träxler M, Brühl A, Benussi L, Binetti G, Braak H, Nitsch RM, Hock C (2003) Increased brain beta-amyloid load, phosphorylated tau, and risk of Alzheimer disease associated with an intronic CYP46 polymorphism. Arch Neurol 60:29–35
Palotás A, Kálmán J (2006) Candidate susceptibility genes in Alzheimer’s disease are at high risk for being forgotten—they don’t give peace of mind. Curr Drug Metab 7:273–293
Reiss AB, Siller KA, Rahman MM, Chan ES, Ghiso J, de Leon MJ (2004) Cholesterol in neurologic disorders of the elderly: stroke and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25:977–989
Roses AD (1998) Alzheimer diseases: a model of gene mutations and susceptibility polymorphisms for complex psychiatric diseases. Am J Med Genet 81:49–57
Shibata N, Kawarai T, Lee JH, Lee HS, Shibata E, Sato C, Liang Y, Duara R, Mayeux RP, St George-Hyslop PH, Rogaeva E (2006) Association studies of cholesterol metabolism genes (CH25H, ABCA1 and CH24H) in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 391:142–146
Tedde A, Rotondi M, Cellini E, Bagnoli S, Muratore L, Nacmias B, Sorbi S (2006) Lack of association between the CYP46 gene polymorphism and Italian late-onset sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:773.e1–773.e3
Vega GL, Weiner MF, Lipton AM, Von Bergmann K, Lütjohann D, Moore C, Svetlik D (2003) Reduction in levels of 24S-hydroxycholesterol by statin treatment in patients with Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 60:510–515
Wang B, Zhang C, Zheng W, Lu Z, Zheng C, Yang Z, Wang L, Jin F (2004) Association between a T/C polymorphism in intron 2 of cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase gene and Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese. Neurosci Lett 369:104–107
Wang F, Jia J (2007) Polymorphisms of cholesterol metabolism genes CYP46 and ABCA1 and the risk of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese. Brain Res 25:34–38
Wang LZ, Tian Y, Yu JT, Chen W, Wu ZC, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Tan L (2011) Association between late-onset Alzheimer’s disease and microsatellite polymorphisms in intron II of the human toll-like receptor 2 gene. Neurosci Lett 489:164–167
Yanagisawa K (2002) Cholesterol and pathological processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 70:361–366
Yu JT, Sun YP, Ou JR, Cui WZ, Zhang W, Tan L (2011) No association of toll-like receptor 2 polymorphisms with Alzheimer’s disease in Han Chinese. Neurobiol Aging 32:1924.e1–1924.e3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Xm., Zhang, Zx., Zhang, Jw. et al. An Intronic CYP46A1 Polymorphism Is Associated with Alzheimer Disease in a Chinese Han Population. J Mol Neurosci 47, 514–518 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9778-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9778-5