Abstract
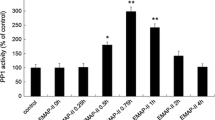
Endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide-II (EMAP-II) increases blood–tumor barrier (BTB) permeability by inducing alterations in the tight junction (TJ) complex between brain endothelial cells. In the present study, an in vitro BTB model was used to search for the interacting and functional cell surface molecule of EMAP-II as well as the signaling pathway involved in the EMAP-II-induced BTB hyperpermeability. Our results revealed that EMAP-II-induced increase in BTB permeability and down-regulation of TJ-related proteins occludin and ZO-1 were associated with its binding to ATP synthase α subunit (α-ATP synthase) on the surface of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs). In addition, we observed that EMAP-II administration activated protein kinase C (PKC) and induced the translocation of PKC from the cytosolic to the membrane fraction of BMECs. The effects of EMAP-II on BTB permeability as well as expression levels of occludin and ZO-1 in BMECs were significantly diminished by H7, the inhibitor of PKC. In summary, these data suggest that EMAP-II increases BTB permeability through α-ATP synthase on the surface of BMECs, and PKC signaling pathway might be involved in this process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arechaga I, Jones PC (2001) Quick guide: ATP synthase. Curr Biol 11(4):R117
Augereau O, Claverol S, Boudes N et al (2005) Identification of tyrosinephosphorylated proteins of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation machinery. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(13):1478–1488
Barnett G, Jakobsen AM, Tas M et al (2000) Prostate adenocarcinoma cells release the novel proinflammatory polypeptide EMAP-II in response to stress. Cancer Res 60(11):2850–2857
Berger AC, Alexander HR, Tang G et al (2000) Endothelial monocyte activating polypeptide II induces endothelial cell apoptosis and may inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res 60(1):70–80
Black KL, Ningaraj NS (2004) Modulation of brain tumor capillaries for enhanced drug delivery selectively to brain tumor. Cancer Control 11(3):165–173
Burwick NR, Wahl ML, Fang J et al (2005) An inhibitor of the F1 subunit of ATP synthase (IF1) modulates the activity of angiostatin on the endothelial cell surface. J Biol Chem 280(3):1740–1745
Chang SY, Park SG, Kim S et al (2002) Interaction of the C-terminal Domain of p43 and the alpha subunit of ATP Synthase. Its functional implication in endothelial cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 277(10):8388–8394
Fleegal MA, Hom S, Borg LK et al (2005) Activation of PKC modulates blood–brain barrier endothelial cell permeability changes induced by hypoxia and posthypoxic reoxyenation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289(5):H2012–H2019
Gloor SM, Wachtel M, Bolliger MF et al (2001) Molecular and cellular permeability control at the blood–brain barrier. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 36(2–3):258–264
Guo M, Wu MH, Korompai F et al (2003) Upregulation of PKC gene and isozymes in cardiovascular tissues during early stages of experimental diabetes. Physiol Genomics 12(2):139–146
Harhaj NS, Antonetti DA (2004) Regulation of tight junctions and loss of barrier function in pathophysiology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(7):1206–1237
Karczewski J, Groot J (2000) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions: III. Tight junction regulation by intracellular messengers: differences in response within and between epithelia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279(4):G660–G665
Liu LB, Xue YX, Liu YH et al (2008) Bradykinin increases blood–tumor barrier permeability by down-regulating the expression levels of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 and rearranging actin cytoskeleton. J Neurosci Res 86(5):1153–1168
Ma T, Xue YX (2010) RhoA-mediated potential regulation of blood–tumor barrier permeability by bradykinin. J Mol Neurosci 42(1):67–73
Newton AC (1997) Regulation of protein kinase C. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9(2):161–167
Opii WO, Nukala VN, Sultana R et al (2007) Proteomic identification of oxidized mitochondrial proteins following experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 24(5):772–789
Qiu LB, Ding GR, Li KC et al (2010) The role of protein kinase C in the opening of blood–brain barrier induced by electromagnetic pulse. Toxicology 273(1–3):29–34
Ron D, Kazanietz MG (1999) New insight into the regulation of protein kinase C and novel phorbol ester receptors. FASEB J 13(13):1658–1676
Schmitz HP, Lorberg A, Heinisch JJ (2002) Regulation of yeast protein kinase C activity by interaction with the small GTPase Rho1p through its aminoterminal HR1 domain. Mol Microbiol 44(3):829–840
Scotet E, Martinez LO, Grant E et al (2005) Tumor recognition following Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell receptor interactions with a surface F1-ATPase-related structure and apolipoprotein A-I. Immunity 22(1):71–80
Shalak V, Guigou L, Kaminska M et al (2007) Characterization of p43 (ARF), a derivative of the p43 component of multiaminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex released during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282(15):10935–10943
Siegal T, Zylber-Katz E (2002) Strategies for increasing drug delivery to the brain: focus on brain lymphoma. Clin Pharmacokinet 41(3):171–186
Slater SJ, Seiz JL, Stagliano BA et al (2001) Interaction of protein kinase C isozysmes with Rho GTPases. Biochemistry 40(14):4437–4445
Stamatovic SM, Dimitrijevic OB, Keep RF et al (2006) Protein kinase Cα-RhoA cross-talk in CCL2-induced alterations in brain endothelial permeability. J Biol Chem 281(13):8379–8388
Wang YB, Peng C, Liu YH (2007) Low dose of bradykinin selectively increases intracellular calcium in glioma cells. J Neurol Sci 258(1–2):44–51
Willis CL, Meske DS, Davis TP (2010) PKC activation modulates reversible increase in cortical blood–brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein expression during hypoxia and posthypoxic reoxyenation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(11):1847–1859
Wolburg H, Lippoldt A (2002) Tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier: development, composition and regulation. Vascul Pharmacol 38(6):323–337
Xie H, Xue YX, Liu LB et al (2010) Endothelial-monocyte-activating polypeptide II increases blood–tumor barrier permeability by down-regulating the expression of tight junction associated proteins. Brain Res 1319:13–20
Xie H, Xue YX, Liu LB et al (2011) Role of RhoA/ROCK signaling in Endothelial- monocyte-activating polypeptide II opening of the blood–tumor barrier. J Mol Neurosci (Accepted)
Yuan SY (2002) Protein kinase signaling in the modulation of microvascular permeability. Vascul Pharmacol 39(4–5):213–223
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81172197, 30872656, 30973079, 81001029, 81072056), the special fund for Scientific Research of Doctor-degree Subjects in Colleges and Universities, (Nos. 20092104110015, 20102104110009) and Shenyang Science and Technology Plan Projects (Nos. F-10-205-1-22, F-10-205-1-37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Liu, Yh., Xue, Yx. et al. Mechanisms for Endothelial Monocyte-Activating Polypeptide-II-Induced Opening of the Blood–Tumor Barrier. J Mol Neurosci 47, 408–417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9657-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9657-5