Abstract
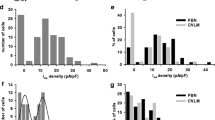
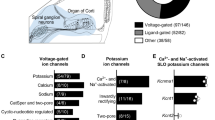
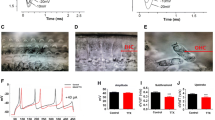
Neurons located in the inferior colliculus (IC) are on the path which processes acoustic information converging from the peripheral auditory system and to be sent through ascending pathways to superior structures. Previous in vitro recordings from early stage animals suggest that voltage-gated K channels underlie distinct neuronal discharge patterns observed in the IC. In this study, using reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction, we show the presence of a voltage-gated K channel family (Kv7/KCNQ) in the central nucleus of the IC (ICc) of the adult guinea pig. Whole-cell recordings from neurons in the nucleus were also made in slices from mature animals, and the action of specific openers and blockers demonstrated on the firing patterns. Our results indicate that mRNA from all members of the Kv7 family of channels are expressed in the ICc, but at different levels, and provide evidence that these channels can modulate neuronal excitability in this nucleus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biervert, C., Schroeder, B. C., Kubisch, C., Berkovic, S. F., Propping, P., Jentsch, T. J., et al. (1998). A potassium channel mutation in neonatal human epilepsy. Science, 279, 403–406. doi:10.1126/science.279.5349.403.
Caminos, E., Garcia-Pino, E., Martinez-Galan, J. R., & Juiz, J. M. (2007). The potassium channel KCNQ5/Kv7.5 is localized in synaptic endings of auditory brainstem nuclei of the rat. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 505, 363–378. doi:10.1002/cne.21497.
Coucke, P. J., Van, H. P., Kelley, P. M., Kunst, H., Schatteman, I., Van, V. D., et al. (1999). Mutations in the KCNQ4 gene are responsible for autosomal dominant deafness in four DFNA2 families. Human Molecular Genetics, 8, 1321–1328. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.7.1321.
Delmas, P., & Brown, D. A. (2005). Pathways modulating neural KCNQ/M (Kv7) potassium channels. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 6, 850–862. doi:10.1038/nrn1785.
Gu, N., Vervaeke, K., Hu, H., & Storm, J. F. (2005). Kv7/KCNQ/M and HCN/h, but not K(Ca)2/SK channels, contribute to the somatic medium after-hyperpolarization and excitability control in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells. The Journal of Physiology, 566, 689–715. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.086835.
Gutman, G. A., et al. (2003). International Union of Pharmacology. XLI. Compendium of voltage-gated ion channels: Potassium channels. Pharmacological Reviews, 55, 583–586. doi:10.1124/pr.55.4.9.
Housley, G. D., & Ashmore, J. F. (1992). Ionic currents of outer hair cells isolated from the guinea-pig cochlea. The Journal of Physiology, 448, 73–98.
Hurley, K. M., Gaboyard, S., Zhong, M., Price, S. D., Wooltorton, J. R., Lysakowski, A., et al. (2006). M-like K+ currents in type I hair cells and calyx afferent endings of the developing rat utricle. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 10253–10269. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2596-06.2006.
Jentsch, T. J. (2000). Neuronal KCNQ potassium channels: Physiology and role in disease. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 1, 21–30. doi:10.1038/35036198.
Kananura, C., Biervert, C., Hechenberger, M., Engels, H., & Steinlein, O. K. (2000). The new voltage gated potassium channel KCNQ5 and neonatal convulsions. Neuroreport, 11, 2063–2067. doi:10.1097/00001756-200006260-00050.
Kharkovets, T., Dedek, K., Maier, H., Schweizer, M., Khimich, D., Nouvian, R., et al. (2006). Mice with altered KCNQ4 K+ channels implicate sensory outer hair cells in human progressive deafness. The EMBO Journal, 25, 642–652. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600951.
Kharkovets, T., Hardelin, J. P., Safieddine, S., Schweizer, M., El-Amraoui, A., Petit, C., et al. (2000). KCNQ4, a K+ channel mutated in a form of dominant deafness, is expressed in the inner ear and the central auditory pathway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 4333–4338. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.8.4333.
Kubisch, C., Schroeder, B. C., Friedrich, T., Lutjohann, B., El-Amraoui, A., Marlin, S., et al. (1999). KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness. Cell, 96, 437–446. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80556-5.
Liang, G. H., Jin, Z., Ulfendahl, M., & Jarlebark, L. (2006). Molecular analyses of KCNQ1–5 potassium channel mRNAs in rat and guinea pig inner ears: Expression, cloning, and alternative splicing. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 126, 346–352. doi:10.1080/00016480500416777.
Liang, G., Moore, E. J., Ulfendahl, M., Rydqvist, B., & Jarlebark, L. (2005). An M-like potassium current in the guinea pig cochlea. ORL; Journal for Oto-Rhino-Laryngology and Its Related Specialties, 67, 75–82. doi:10.1159/000085439.
Marcotti, W., Johnson, S. L., Holley, M. C., & Kros, C. J. (2003). Developmental changes in the expression of potassium currents of embryonic, neonatal and mature mouse inner hair cells. The Journal of Physiology, 548, 383–400. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.034801.
Navarro-Lopez, J. D., Alvarado, J. C., Marquez-Ruiz, J., Escudero, M., Delgado-Garcia, J. M., & Yajeya, J. (2004). A cholinergic synaptically triggered event participates in the generation of persistent activity necessary for eye fixation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 5109–5118. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0235-04.2004.
Neyroud, N., Tesson, F., Denjoy, I., Leibovici, M., Donger, C., Barhanin, J., et al. (1997). A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange–Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nature Genetics, 15, 186–189. doi:10.1038/ng0297-186.
Robbins, J. (2001). KCNQ potassium channels: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 90, 1–19. doi:10.1016/S0163-7258(01)00116-4.
Schenzer, A., Friedrich, T., Pusch, M., Saftig, P., Jentsch, T. J., Grotzinger, J., et al. (2005). Molecular determinants of KCNQ (Kv7) K+ channel sensitivity to the anticonvulsant retigabine. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 5051–5060. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0128-05.2005.
Schroeder, B. C., Hechenberger, M., Weinreich, F., Kubisch, C., & Jentsch, T. J. (2000). KCNQ5, a novel potassium channel broadly expressed in brain, mediates M-type currents. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 24089–24095. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003245200.
Schroeder, B. C., Kubisch, C., Stein, V., & Jentsch, T. J. (1998). Moderate loss of function of cyclic-AMP-modulated KCNQ2/KCNQ3 K+ channels causes epilepsy. Nature, 396, 687–690. doi:10.1038/25367.
Sivaramakrishnan, S., & Oliver, D. L. (2001). Distinct K currents result in physiologically distinct cell types in the inferior colliculus of the rat. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 2861–2877.
Tatulian, L., Delmas, P., Abogadie, F. C., & Brown, D. A. (2001). Activation of expressed KCNQ potassium currents and native neuronal M-type potassium currents by the anti-convulsant drug retigabine. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 5535–5545.
van Rijn, C. M., & Willems-van, B. E. (2003). Synergy between retigabine and GABA in modulating the convulsant site of the GABAA receptor complex. European Journal of Pharmacology, 464, 95–100. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(03)01426-2.
Wang, H. S., Pan, Z., Shi, W., Brown, B. S., Wymore, R. S., Cohen, I. S., et al. (1998). KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel subunits: Molecular correlates of the M-channel. Science, 282, 1890–1893. doi:10.1126/science.282.5395.1890.
Wu, S. H. (2005). Biophysical properties of Inferior colliculus neurons. In J. A. Winer & C. E. Schreiner (Eds.), The inferior colliculus (pp. 282–311). New York: Springer.
Yeung, S. Y., Pucovsky, V., Moffatt, J. D., Saldanha, L., Schwake, M., Ohya, S., et al. (2007). Molecular expression and pharmacological identification of a role for K(v)7 channels in murine vascular reactivity. British Journal of Pharmacology, 151, 758–770. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707284.
Yue, C., & Yaari, Y. (2006). Axo-somatic and apical dendritic Kv7/M channels differentially regulate the intrinsic excitability of adult rat CA1 pyramidal cells. Journal of Neurophysiology, 95, 3480–3495. doi:10.1152/jn.01333.2005.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust, Fundación Martin Escudero, Spanish Government fellows (JCI-2005-1775-25 and CD06/175) and the EU Marie Curie scheme. We would like to thank Dr. Vega-Avelaira for his advice on molecular experiments and Dr. Yajeya and Dr. de la Fuente for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro-López, J., Jiménez-Díaz, L., Géranton, S.M. et al. Electrophysiological and Molecular Analysis of Kv7/KCNQ Potassium Channels in the Inferior Colliculus of Adult Guinea Pig. J Mol Neurosci 37, 263–268 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9130-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9130-2