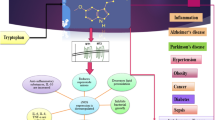
Abstract
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is an interesting example of a 28-amino acid neuropeptide that is abundantly expressed in discrete brain regions/neurons and hence may contribute to brain function. This short review summarizes my own point of view and encompasses 25 years of work and over 100 publications targeting the understanding of VIP production and biological activity. The review starts with our original cloning of the VIP gene, it then continues to discoveries of regulation of VIP synthesis and the establishment of the first VIP transgenic mice. The review ends with the identification of novel VIP analogs that helped decipher VIP’s important role during development, in regulation of the biological clock(s) and diurnal rhythms, sexual activity, learning and memory as well as social behavior, and cancer. This review cites only articles that I have coauthored and gives my own perspective of this exciting ever-growing field.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoston, D. V., Eiden, L. E., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (1991). Spontaneous electrical activity regulates vasoactive intestinal peptide expression in dissociated spinal cord cell cultures. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research, 10, 235–240.
Ashur-Fabian, O., Giladi, E., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (1997). Identification of VIP/PACAP receptors on rat astrocytes using antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 9, 211–222.
Ashur-Fabian, O., Giladi, E., Furman, S., Steingart, R. A., Wollman, Y., Fridkin, M., et al. (2001). Vasoactive intestinal peptide and related molecules induce nitrite accumulation in the extracellular milieu of rat cerebral cortical cultures. Neuroscience Letters, 307, 167–170.
Ashur-Fabian, O., Perl, O., Lilling, G., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (1999). SNV, a lipophilic superactive VIP analog, acts through cGMP to promote neuronal survival. Peptides, 20, 629–633.
Avidor, R., Eilam, R., Malach, R., & Gozes, I. (1989). VIP-mRNA is increased in hypertensive rats. Brain Research, 503, 304–307.
Baldino, F. Jr., Fitzpatrick-McElligott, S., Gozes, I., & Card, J. P. (1989). Localization of VIP and PHI-27 messenger RNA in rat thalamic and cortical neurons. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 1, 199–207.
Bassan, M., Zamostiano, R., Davidson, A., Pinhasov, A., Giladi, E., Perl, O., et al. (1999). Complete sequence of a novel protein containing a femtomolar-activity-dependent neuroprotective peptide. Journal of Neurochemistry, 72, 1283–1293.
Bassan, M., Zamostiano, R., Giladi, E., Davidson, A., Wollman, Y., Pitman, J., et al. (1998). The identification of secreted heat shock 60-like protein from rat glial cells and a human neuroblastoma cell line. Neuroscience Letters, 250, 37–40.
Blondel, O., Collin, C., McCarran, W. J., Zhu, S., Zamostiano, R., Gozes, I., et al. (2000). A glia-derived signal regulating neuronal differentiation. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 8012–8020.
Bodner, M., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (1985). Coding sequences for vasoactive intestinal peptide and PHM-27 peptide are located on two adjacent exons in the human genome. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences United States America, 82, 3548–3551.
Brenneman, D. E., Glazner, G., Hill, J. M., Hauser, J., Davidson, A., & Gozes, I. (1998a). VIP neurotrophism in the central nervous system: multiple effectors and identification of a femtomolar-acting neuroprotective peptide. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 865, 207–212.
Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (1996). A femtomolar-acting neuroprotective peptide. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 97, 2299–2307.
Brenneman, D. E., Hauser, J., Neale, E., Rubinraut, S., Fridkin, M., Davidson, A., et al. (1998b). Activity-dependent neurotrophic factor: structure–activity relationships of femtomolar-acting peptides. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 285, 619–627.
Brenneman, D. E., Hill, J. M., Glazner, G. W., Gozes, I., & Phillips, T. W. (1995). Interleukin-1 alpha and vasoactive intestinal peptide: enigmatic regulation of neuronal survival. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 13, 187–200.
Brenneman, D. E., Hill, J. M., Gozes, I., & Phillips, T. M. (1996). Vasoactive intestinal peptide releases interleukin-1 from astrocytes. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 805, 280–287, discussion 287–289.
Brenneman, D. E., Phillips, T. M., Festoff, B. W., & Gozes, I. (1997). Identity of neurotrophic molecules released from astroglia by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 814, 167–173.
Brenneman, D. E., Phillips, T. M., Hauser, J., Hill, J. M., Spong, C. Y., & Gozes, I. (2003). Complex array of cytokines released by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Neuropeptides, 37, 111–119.
Brenneman, D. E., Schultzberg, M., Bartfai, T., & Gozes, I. (1992). Cytokine regulation of neuronal survival. Journal of Neurochemistry, 58, 454–460.
Card, J. P., Fitzpatrick-McElligott, S., Gozes, I., & Baldino, F. Jr. (1988). Localization of vasopressin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, peptide histidine isoleucine- and somatostatin-mRNA in rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Cell and Tissue Research, 252, 307–315.
Chew, L. J., Burke, Z. D., Morgan, H., Gozes, I., Murphy, D., & Carter, D. A. (1997). Transcription of the vasoactive intestinal peptide gene in response to glucocorticoids: differential regulation of alternative transcripts is modulated by a labile protein in rat anterior pituitary. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 130, 83–91.
Dangoor, D., Biondi, B., Gobbo, M., Vachutinski, Y., Fridkin, M., Gozes, I., et al. (2008). Novel glycosylated VIP analogs: synthesis, biological activity, and metabolic stability. Journal of Peptide Science, 14, 321–328.
Dangoor, D., Giladi, E., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2005). Neuropeptide receptor transcripts are expressed in the rat clitoris and oscillate during the estrus cycle in the rat vagina. Peptides, 26, 2579–2584.
Dangoor, D., Rubinraut, S., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2006). Novel extended and branched N-terminal analogs of VIP. Regulatory Peptides, 137, 42–49.
Dangoor, D., Rubinraut, S., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2007). Novel analogs of VIP with multiple C-terminal domains. Peptides, 28, 1622–1630.
Davidson, A., Moody, T. W., & Gozes, I. (1996). Regulation of VIP gene expression in general. Human lung cancer cells in particular. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 7, 99–110.
Delgado, M., Munoz-Elias, E. J., Kan, Y., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., et al. (1998). Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit tumor necrosis factor alpha transcriptional activation by regulating nuclear factor-kB and cAMP response element-binding protein/c-Jun. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 31427–31436.
Dibbern, D. A. Jr., Glazner, G. W., Gozes, I., Brenneman, D. E., & Hill, J. M. (1997). Inhibition of murine embryonic growth by human immunodeficiency virus envelope protein and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide and activity-dependent neurotrophic factor. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 99, 2837–2841.
Eilam, R., Davidson, A., Gozes, I., & Segal, M. (1999). Locomotor activity causes a rapid up-regulation of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the rat hippocampus. Hippocampus, 9, 534–541.
Gelber, E., Granoth, R., Fridkin, M., Dreznik, Z., Brenneman, D. E., Moody, T. W., et al. (2001). A lipophilic vasoactive intestinal peptide analog enhances the antiproliferative effect of chemotherapeutic agents on cancer cell lines. Cancer, 92, 2172–2180.
Giladi, E., Hill, J. M., Dresner, E., Stack, C. M., & Gozes, I. (2007). Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) regulates activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) expression in vivo. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 33, 278–283.
Giladi, E., Shani, Y., & Gozes, I. (1990). The complete structure of the rat VIP gene. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research, 7, 261–267.
Glazer, R., & Gozes, I. (1994). Diurnal oscillation in vasoactive intestinal peptide gene expression independent of environmental light entraining. Brain Research, 644, 164–167.
Glowa, J. R., Panlilio, L. V., Brenneman, D. E., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., & Hill, J. M. (1992). Learning impairment following intracerebral administration of the HIV envelope protein gp120 or a VIP antagonist. Brain Research, 570, 49–53.
Gozes, I. (2007a). The role of vasoactive intestinal peptide in neuroprotection: Professor Illana Gozes is interviewed by Emma Quigley. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 11, 733–736.
Gozes, I. (2007b). Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein: from gene to drug candidate. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 114, 146–154.
Gozes, I., Avidor, R., Biegon, A., & Baldino, F. Jr. (1989a). Lactation elevates vasoactive intestinal peptide messenger ribonucleic acid in rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Endocrinology, 124, 181–186.
Gozes, I., Avidor, R., Giladi, E., Shani, Y., McEwen, B. S., Dussaillant, M., et al. (1994b). Adrenalectomy decreases vasoactive intestinal peptide mRNA levels in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Neuroscience Letters, 167, 24–28.
Gozes, I., Avidor, R., Yahav, Y., Katznelson, D., Croce, C. M., & Huebner, K. (1987b). The gene encoding vasoactive intestinal peptide is located on human chromosome 6p21–-6qter. Human Genetics, 75, 41–44.
Gozes, I., Bachar, M., Bardea, A., Davidson, A., Rubinraut, S., & Fridkin, M. (1998a). Protection against developmental deficiencies by a lipophilic VIP analogue. Neurochemical Research, 23, 689–693.
Gozes, I., Bachar, M., Bardea, A., Davidson, A., Rubinraut, S., Fridkin, M., et al. (1997). Protection against developmental retardation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by a fatty neuropeptide: implications for early treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurobiology, 33, 329–342.
Gozes, I., Bardea, A., Reshef, A., Zamostiano, R., Zhukovsky, S., Rubinraut, S., et al. (1996a). Neuroprotective strategy for Alzheimer disease: intranasal administration of a fatty neuropeptide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93, 427–432.
Gozes, I., Bodner, M., Shani, Y., & Fridkin, M. (1984a). Detection of mRNAs containing regulatory peptide coding sequences using synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 26, 147–156.
Gozes, I., Bodner, M., Shani, Y., & Fridkin, M. (1986). Structure and expression of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) gene in a human tumor. Peptides, 7(Suppl 1), 1–6.
Gozes, I., Bodner, M., Shwartz, H., Shani, Y., & Fridkin, M. (1984b). Studies toward the biosynthesis of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Peptides, 5, 161–166.
Gozes, I., & Brenneman, D. E. (1989). VIP: molecular biology and neurobiological function. Molecular Neurobiology, 3, 201–236.
Gozes, I., & Brenneman, D. E. (1993). Neuropeptides as growth and differentiation factors in general and VIP in particular. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 4, 1–9.
Gozes, I., & Brenneman, D. E. (1996). Activity-dependent neurotrophic factor (ADNF). An extracellular neuroprotective chaperonin? Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 7, 235–244.
Gozes, Y., Brenneman, D. E., Fridkin, M., Asofsky, R., & Gozes, I. (1991c). A VIP antagonist distinguishes VIP receptors on spinal cord cells and lymphocytes. Brain Research, 540, 319–321.
Gozes, I., & Fridkin, M. (1992). A fatty neuropeptide. Potential drug for noninvasive impotence treatment in a rat model. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 90, 810–814.
Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., & Brenneman, D. E. (1995a). A VIP hybrid antagonist: from developmental neurobiology to clinical applications. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 15, 675–687.
Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., Hill, J. M., & Brenneman, D. E. (1999a). Pharmaceutical VIP: prospects and problems. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 6, 1019–1034.
Gozes, I., & Furman, S. (2003). VIP and drug design. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 9, 483–494.
Gozes, I., & Furman, S. (2004). Clinical endocrinology and metabolism. Potential clinical applications of vasoactive intestinal peptide: a selected update. Best Practice and Research. Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 18, 623–640.
Gozes I., Glowa J., Brenneman D. E., McCune S. K., Lee E. & Westphal H. (1993). Learning and sexual deficiencies in transgenic mice carrying a chimeric vasoactive intestinal peptide gene. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 4, 185–193.
Gozes, I., Lilling, G., Davidson, A., Bardea, A., Reshef, A., Glazer, R., et al. (1996b). Development of VIP agonists and antagonists with tissue and receptor specificity: effects on behavioral maturation, sexual function, and the biologic clock. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 805, 159–169, discussion 169–171.
Gozes, I., Lilling, G., Glazer, R., Ticher, A., Ashkenazi, I. E., Davidson, A., et al. (1995b). Superactive lipophilic peptides discriminate multiple vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 273, 161–167.
Gozes, I., McCune, S. K., Jacobson, L., Warren, D., Moody, T. W., Fridkin, M., et al. (1991b). An antagonist to vasoactive intestinal peptide affects cellular functions in the central nervous system. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 257, 959–966.
Gozes, I., Meltzer, E., Rubinrout, S., Brenneman, D. E., & Fridkin, M. (1989b). Vasoactive intestinal peptide potentiates sexual behavior: inhibition by novel antagonist. Endocrinology, 125, 2945–2949.
Gozes, I., Milner, R. J., Liu, F. T., Johnson, E., Battenberg, E. L., Katz, D. H., et al. (1983b). Monoclonal antibodies against vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: studies of structure and related antigens. Journal of Neurochemistry, 41, 549–555.
Gozes, I., Morimoto, B. H., Tiong, J., Fox, A., Sutherland, K., Dangoor, D., et al. (2005). NAP: research and development of a peptide derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP). CNS Drug Reviews, 11, 353–368.
Gozes, Y., Moskowitz, M. A., Strom, T. B., & Gozes, I. (1982). Conditioned media from activated lymphocytes maintain sympathetic neurons in culture. Brain Research, 282, 93–97.
Gozes, I., Nakai, H., Byers, M., Avidor, R., Weinstein, Y., Shani, Y., & Shows, T. B. (1987c). Sequential expression in the nervous system of c-myb and VIP genes, located in human chromosomal region 6q24. Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics, 13, 305–313.
Gozes, I., O’Connor, D. T., & Bloom, F. E. (1983a). A possible high molecular weight precursor to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide sequestered into pheochromocytoma chromaffin granules. Regulatory Peptide, 6, 111–119.
Gozes, I., Perl, O., Giladi, E., Davidson, A., Ashur-Fabian, O., Rubinraut, S., et al. (1999b). Mapping the active site in vasoactive intestinal peptide to a core of four amino acids: neuroprotective drug design. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 4143–4148.
Gozes, I., Perl, O., Zamostiano, R., Rubinraut, S., Fridkin, M., Shochat, L., et al. (1998b). Multiple actions of a hybrid PACAP antagonist: neuronal cell killing and inhibition of sperm motility. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 865, 266–273.
Gozes, I., Reshef, A., Salah, D., Rubinraut, S., & Fridkin, M. (1994a). Stearyl-norleucine-vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP): a novel VIP analog for noninvasive impotence treatment. Endocrinology, 134, 2121–2125.
Gozes, I., Schachter, P., Shani, Y., & Giladi, E. (1988). Vasoactive intestinal peptide gene expression from embryos to aging rats. Neuroendocrinology, 47, 27–31.
Gozes, I., & Shani, Y. (1986). Hypothalamic vasoactive intestinal peptide messenger ribonucleic acid is increased in lactating rats. Endocrinology, 119, 2497–2501.
Gozes, I., Shani, Y., Kiu, B., & Burbach, J. P. H. (1991a). Diurnal variation in vasoactive intestinal peptide messenger RNA in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience Research Communications, 5, 83–86.
Gozes, I., Shani, Y., & Rostene, W. H. (1987a). Developmental expression of the VIP-gene in brain and intestine. Brain Research, 388, 137–148.
Gozes, I., & Tsafriri, A. (1986). Detection of vasoactive intestinal peptide-encoding messenger ribonucleic acid in the rat ovaries. Endocrinology, 119, 2606–2610.
Gozes, I., Werner, H., Fawzi, M., Abdelatty, A., Shani, Y., Fridkin, M., & Koch, Y. (1989c). Estrogen regulation of vasoactive intestinal peptide mRNA in rat hypothalamus. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 1, 55–61.
Granoth, R., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2000a). VIP and the potent analog, stearyl-Nle(17)-VIP, induce proliferation of keratinocytes. FEBS Letters, 475, 78–83.
Granoth, R., Fridkin, M., Rubinraut, S., & Gozes, I. (2000b). VIP-derived sequences modified by N-terminal stearyl moiety induce cell death: the human keratinocyte as a model. FEBS Letters, 475, 71–77.
Gressens, P., Besse, L., Robberecht, P., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., & Evrard, P. (1999). Neuroprotection of the developing brain by systemic administration of vasoactive intestinal peptide derivatives. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 288, 1207–1213.
Gressens, P., Hill, J. M., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., & Brenneman, D. E. (1993). Growth factor function of vasoactive intestinal peptide in whole cultured mouse embryos. Nature, 362, 155–158.
Gressens, P., Hill, J. M., Paindaveine, B., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., & Brenneman, D. E. (1994). Severe microcephaly induced by blockade of vasoactive intestinal peptide function in the primitive neuroepithelium of the mouse. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 94, 2020–2027.
Gressens, P., Marret, S., Hill, J. M., Brenneman, D. E., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., et al. (1997). Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents excitotoxic cell death in the murine developing brain. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 100, 390–397.
Harmar, A. J., Arimura, A., Gozes, I., Journot, L., Laburthe, M., Pisegna, J. R., et al. (1998). International Union of Pharmacology. XVIII. Nomenclature of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Pharmacological Reviews, 50, 265–270.
Hill, J. M., Glazner, G. W., Lee, S. J., Gozes, I., Gressens, P., & Brenneman, D. E. (1999b). Vasoactive intestinal peptide regulates embryonic growth through the action of activity-dependent neurotrophic factor. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 897, 92–100.
Hill, J. M., Gozes, I., Hill, J. L., Fridkin, M., & Brenneman, D. E. (1991). Vasoactive intestinal peptide antagonist retards the development of neonatal behaviors in the rat. Peptides, 12, 187–192.
Hill, J. M., Hauser, J. M., Sheppard, L. M., Abebe, D., Spivak-Pohis, I., Kushnir, M., et al. (2007). Blockage of VIP during mouse embryogenesis modifies adult behavior and results in permanent changes in brain chemistry. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 31, 183–200.
Hill, J. M., Lee, S. J., Dibbern, D. A. Jr., Fridkin, M., Gozes, I., & Brenneman, D. E. (1999a). Pharmacologically distinct vasoactive intestinal peptide binding sites: CNS localization and role in embryonic growth. Neuroscience, 93, 783–791.
Hill, J. M., Mervis, R. F., Politi, J., McCune, S. K., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., et al. (1994). Blockade of VIP during neonatal development induces neuronal damage and increases VIP and VIP receptors in brain. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 739, 211–225.
Holtzman, R. L., Malach, R., & Gozes, I. (1989). Disruption of the optic pathway during development affects vasoactive intestinal peptide mRNA expression. New Biologist, 1, 215–221.
Kim, W. K., Kan, Y., Ganea, D., Hart, R. P., Gozes, I., & Jonakait, G. M. (2000). Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in injured spinal cord and in activated microglia via a cAMP-dependent pathway. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 3622–3630.
Levy, A., Gal, R., Granoth, R., Dreznik, Z., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2002). In vitro and in vivo treatment of colon cancer by VIP antagonists. Regulatory Peptides, 109, 127–133.
Lilling, G., Wollman, Y., Goldstein, M. N., Rubinraut, S., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., et al. (1994). Inhibition of human neuroblastoma growth by a specific VIP antagonist. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 5, 231–239.
Moody, T. W., & Gozes, I. (2007). Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors: a molecular target in breast and lung cancer. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 13, 1099–1104.
Moody, T. W., Jensen, R. T., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2002). (N-stearyl, norleucine17)VIPhybrid is a broad spectrum vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor antagonist. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 18, 29–35.
Moody, T. W., Leyton, J., Chan, D., Brenneman, D. C., Fridkin, M., Gelber, E., et al. (2001). VIP receptor antagonists and chemotherapeutic drugs inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer and Research Treatment, 68, 55–64.
Moody, T. W., Leyton, J., Coelho, T., Jakowlew, S., Takahashi, K., Jameison, F., et al. (1997). (Stearyl, Norleucine17)VIP hybrid antagonizes VIP receptors on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Life Science, 61, 1657–1666.
Moody, T. W., Leyton, J., Gozes, I., Lang, L., & Eckelman, W. C. (1998). VIP and breast cancer. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 865, 290–296.
Moody, T. W., Walters, J., Casibang, M., Zia, F., & Gozes, Y. (2000). VPAC1 receptors and lung cancer. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 921, 26–32.
Moody, T. W., Zia, F., Draoui, M., Brenneman, D. E., Fridkin, M., Davidson, A., et al. (1993). A vasoactive intestinal peptide antagonist inhibits non-small cell lung cancer growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90, 4345–4349.
Nowak, J. Z., Sedkowska, P., Zawilska, J. B., Gozes, I., & Brenneman, D. E. (2003). Antagonism of VIP-stimulated cyclic AMP formation in chick brain. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 20, 163–172.
Offen, D., Sherki, Y., Melamed, E., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (2000). Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) prevents neurotoxicity in neuronal cultures: relevance to neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Research, 854, 257–262.
Pilzer, I., & Gozes, I. (2006a). VIP provides cellular protection through a specific splice variant of the PACAP receptor: a new neuroprotection target. Peptides, 27, 2867–2876.
Pilzer, I., & Gozes, I. (2006b). A splice variant to PACAP receptor that is involved in spermatogenesis is expressed in astrocytes. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1070, 484–490.
Rostene, W., Montagne, M. N., Dussaillant, M., & Gozes, I. I. (1997). Steroid Regulation of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP). Stress, 2, 79–90.
Servoss, S. J., Lee, S. J., Gibney, G., Gozes, I., Brenneman, D. E., & Hill, J. M. (2001). IGF-I as a mediator of VIP/activity-dependent neurotrophic factor-stimulated embryonic growth. Endocrinology, 142, 3348–3353.
Sigalov, E., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (2000). VIP-Related protection against lodoacetate toxicity in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: a model for ischemic/hypoxic injury. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 15, 147–154.
Steingart, R. A., Heldenberg, E., Pinhasov, A., Brenneman, D. E., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2002). A vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor analog alters the expression of homeobox genes. Life Science, 71, 2543–2552.
Steingart, R. A., Solomon, B., Brenneman, D. E., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (2000). VIP and peptides related to activity-dependent neurotrophic factor protect PC12 cells against oxidative stress. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 15, 137–145.
Wang, H. Y., Jiang, X., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., & Ganea, D. (1999). Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits cytokine production in T lymphocytes through cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent mechanisms. Regulatory Peptides, 84, 55–67.
Werner, H., Koch, Y., Fridkin, M., Fahrenkrug, J., & Gozes, I. (1985). High levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide in human milk. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 133, 228–232.
White, D. M., Walker, S., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (2000). CREB contributes to the increased neurite outgrowth of sensory neurons induced by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and activity-dependent neurotrophic factor. Brain Research, 868, 31–38.
Wollman, Y., Blumberg, S., Spungin, A., Brenneman, D. E., Fridkin, M., Wollman, J., et al. (2002). The increased proliferation of cultured neuroblastoma cells treated with vasoactive intestinal peptide is enhanced by simultaneous inhibition of neutral endopeptidase. Regulatory Peptides, 108, 175–177.
Wollman, Y., Lilling, G., Goldstein, M. N., Fridkin, M., & Gozes, I. (1993). Vasoactive intestinal peptide: a growth promoter in neuroblastoma cells. Brain Research, 624, 339–341.
Wu, J. Y., Henins, K. A., Gressens, P., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., et al. (1997). Neurobehavioral development of neonatal mice following blockade of VIP during the early embryonic period. Peptides, 18, 1131–1137.
Zamostiano, R., Pinhasov, A., Bassan, M., Perl, O., Steingart, R. A., Atlas, R., et al. (1999). A femtomolar-acting neuroprotective peptide induces increased levels of heat shock protein 60 in rat cortical neurons: a potential neuroprotective mechanism. Neuroscience Letters, 264, 9–12.
Zawilska, J. B., Dejda, A., Niewiadomski, P., Gozes, I., & Nowak, J. Z. (2005). Receptors for VIP and PACAP in guinea pig cerebral cortex: effects on cyclic AMP synthesis and characterization by 125I-VIP binding. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 25, 215–224.
Zia, H., Hida, T., Jakowlew, S., Birrer, M., Gozes, Y., Reubi, J. C., et al. (1996). Breast cancer growth is inhibited by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) hybrid, a synthetic VIP receptor antagonist. Cancer Research, 56, 3486–3489.
Zia, H., Leyton, J., Casibang, M., Hau, V., Brenneman, D., Fridkin, M., et al. (2000). (N-stearyl, norleucine17) VIP hybrid inhibits the growth of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Life Science, 66, 379–387.
Zupan, V., Hill, J. M., Brenneman, D. E., Gozes, I., Fridkin, M., Robberecht, P., et al. (1998). Involvement of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide II vasoactive intestinal peptide 2 receptor in mouse neocortical astrocytogenesis. Journal of Neurochemistry, 70, 2165–2173.
Zusev, M., & Gozes, I. (2004). Differential regulation of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein in rat astrocytes by VIP and PACAP. Regulatory Peptides, 123, 33–41.
Acknowledgment
I thank my former student and current colleague and friend Dr. Sharon Furman Assaf for critical reading of this manuscript. VIP studies over the years were supported by the BSF, Bergmann Memorial Award, Neufeld Award, ISF, ISOA, NICHD and NCI intramural, Fogarty Scholar Program, the NIH-TAU student exchange program in Women Health, Fujimoto Pharmaceutical Corp., Bayer, Israel Cancer Research Fund, Tel Aviv University Cancer Center, Johnson & Johnson (COSAT), and the Lily and Avraham Gildor Chair for the Investigation of Growth Factors. Studies were made possible by excellent worldwide collaborations and dedicated staff members, students and postdoctoral fellows (>50) over a quarter of a century. Special thanks are to my long-time friends and colleagues that traveled with me in the VIP field over many years and I will mention just a few, Dr. Yehoshua Gozes, Dr. Douglas E. Brenneman, Dr. Joanna M. Hill, Dr. Terry W. Moody, Dr. Mati Fridkin, Dr. Eliezer Giladi, Dr. Inbar Pilzer, and Dr. David Dangoor. I am currently serving as the incumbent of the Lily and Avraham Gildor Chair for the Investigation of Growth Factors, the Director of the Adams Super Center for Brain Studies, the LEG fMRI Institute and the Elton Laboratory for Molecular Neuroendocrinology at Tel Aviv University. I also serve as the Chief Scientific Officer of Allon Therapeutics Inc (www.allontherapeutics.com).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gozes, I. VIP, From Gene to Behavior and Back: Summarizing my 25 Years of Research. J Mol Neurosci 36, 115–124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9105-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9105-3