Abstract
Purpose
Hepatic function is a key prognostic marker in patients with hepatocellular cancer (HCC) and central to patient selection for transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). We investigated the clinical utility of the Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) grade, an emerging prognostic model, in this heterogenous cohort via a meta-analysis of published studies.
Methods
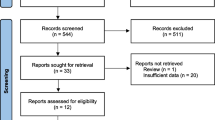
Publications including full text articles and abstracts regarding ALBI grade were sourced by two independent researchers from databases including PubMed, Embase, Medline and Cochrane Library. Studies analysing patients with HCC undergoing TACE treatment were systematically screened utilising the PRISMA tool for data extraction and synthesis, after exclusion of duplicates, irrelevant studies and overlapping cohorts. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS), as determined by ALBI grade and assessed by hazard ratio (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), with analysis of collated data using comprehensive meta-analysis, version 3.0 software.
Results
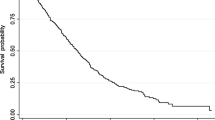
Eight studies were included, with a pooled population of 6538 patients with HCC that underwent TACE treatment. Higher pre-treatment grade was associated with poor OS, with median OS of 12.0 months (P < 0.001) in ALBI grade 3, compared to 33.5 months in ALBI grade 1 (P < 0.001). Significant heterogeneity within each ALBI grade was associated with age and tumour size (P < 0.001) in ALBI grades 1 and 2. In contrast, age and alcohol–related liver disease were significant in the ALBI grade 3 group (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
High pre-treatment ALBI grade is associated with poorer prognosis in patients with HCC undergoing TACE therapy. The ALBI grade demonstrates clinical utility for clinical prognostication and patient selection for TACE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, Al Lami FH, Alam T, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, et al. Global burden of disease cancer collaboration. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(11):1553–68.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Galle PR, Forner A, Llovet JM, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Raoul JL, et al. EASL Clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69:182–236.
Díaz-González Á, Reig M, Bruix J. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Digest Dis. 2016;34(5):597–602.
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Simone P, Filipponi F. Loco-regional interventional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Techniques, outcomes, and future prospects. Transplant Int. 2010;23(7):698–703.
Raoul J-L, Forner A, Bolondi L, Cheung TT, Kloeckner R, de Baere T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;72:28–36.
Raoul J-L, Sangro B, Forner A, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Bolondi L, et al. Evolving strategies for the management of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: available evidence and expert opinion on the use of transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer Treat Rev. 2011;37(3):212–20.
Huo Y, Eslick GD. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization plus radiotherapy compared with chemoembolization alone for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1(6):756–65.
Cabibbo G, Genco C, Marco DV, Barbara M, Enea M, Parisi P, et al. Predicting survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolisation. Aliment Pharm Therap. 2011;34(2):196–204.
Pietrosi G, Miraglia R, Luca A, Vizzini GB, Fili D, Riccardo V, et al. Arterial chemoembolization/embolization and early complications after hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: a safe standardized protocol in selected patients with child class A and B cirrhosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(7):896–902.
Lo C, Ngan H, Tso W, Liu CL, Lam CM, Poon TRP, et al. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35(5):1164–71.
Llovet JM, Real M, Montaña X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9319):1734–9.
Takayasu K, Arii S, Kudo M, Ichida T, Matsui O, Izumi N, et al. Superselective transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Validation of treatment algorithm proposed by Japanese guidelines. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):886–92.
Burrel M, Reig M, Forner A, Barrufet M, de Lope CR, Tremosini S, et al. Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) using drug eluting beads. Implications for clinical practice and trial design. J Hepatol. 2012;56(6):1330–5.
Adhoute X, Pénaranda G, Raoul J, Edeline J, Blanc JF, Pol B, et al. Barcelona clinic liver cancer nomogram and others staging/scoring systems in a French hepatocellular carcinoma cohort. World J Gastroentero. 2017;23(14):2545–55.
Guarino M, Tortora R, Stefano G, Coppola C, Morisco F, Megna AS, et al. Adherence to Barcelona clinic liver cancer guidelines in field practice: Results of Progetto Epatocarcinoma Campania. J Gastroen Hepatol. 2018;33(5):1123–30.
Wallace MC, Huang Y, Preen DB, Garas G, Adams LA, MacQuillan G, et al. HKLC Triages more hepatocellular carcinoma patients to curative therapies compared to BCLC and is associated with better survival. Digest Dis Sci. 2017;62(8):2182–92.
Tovoli F, Negrini G, Bolondi L. Comparative analysis of current guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic Oncol. 2016;3(2):119–36.
Kudo M, Trevisani F, Abou-Alfa GK, Rimassa L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapeutic guidelines and medical treatment. Liver Cancer. 2017;6(1):16–26.
Kudo M. Heterogeneity and subclassification of barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B. Liver Cancer. 2016;5(2):91–6.
Bolondi L, Burroughs A, Dufour J-F, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Raoul JL, et al. Heterogeneity of patients with intermediate (BCLC B) hepatocellular carcinoma: Proposal for a subclassification to facilitate treatment decisions. Semin Liver Dis. 2012;32(04):348–59.
Pinato D, Howell J, Ramaswami R, Sharma Rl. Review article: Delivering precision oncology in intermediate‐stage liver cancer. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(12):1514–23.
Sieghart W, Hucke F, Peck-Radosavljevic M. Transarterial chemoembolization: Modalities, indication, and patient selection. J Hepatol. 2015;62(5):1187–95.
Garwood ER, Fidelman N, Hoch SE, Hoch SE, Kerlan RK, Yao FY. Morbidity and mortality following transarterial liver chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and synthetic hepatic dysfunction. Liver Transplant. 2013;19(2):164–73.
Kloeckner R, Pitton MB, Dueber C, Schmidtmann I, Galle PR, Koch S, et al. Validation of clinical scoring systems ART and ABCR after transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(1):94–102.
Brown DB, Fundakowski CE, Lisker-Melman M, Crippin JS, Pigram TK, Chapman W, et al. Comparison of MELD and child-pugh scores to predict survival after chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;15(11):1209–18.
Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C, Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach—the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. 2014;33(6):550–8.
Pinato DJ, Sharma R, Allara E, Yen C, Arizumi T, Kubota K, et al. The ALBI grade provides objective hepatic reserve estimation across each BCLC stage of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2017;66(2):338–46.
Jaruvongvanich V, Sempokuya T, Wong L. Is there an optimal staging system or liver reserve model that can predict outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma? J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018;9(4):750–61.
Campani C, Vitale A, Dragoni G, Arena U, Giannin EG, Trevisani F, et al. The ALBI and p-ALBI grades predict survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Digest Liver Dis. 2018;50(1):44.
Kim J, Sinn D, Lee J-H, Hyun D, Cho SK, Shin SW, et al. Novel albumin–bilirubin grade-based risk prediction model for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing chemoembolization. Digest Dis Sci. 2018;63(4):1062–71.
Huo T-I, Liu P-H, Hsu C-Y. ALBI score as a novel tool in staging and treatment planning for hepatocellular carcinoma: is it sufficient. Liver Cancer. 2017;6(4):375–6.
Hiraoka A, Kumada T, Michitaka K, Toyoda H, Tada T, Ueki H, et al. Usefulness of albumin–bilirubin grade for evaluation of prognosis of 2584 Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroen Hepatol. 2016;31(5):1031–6.
Waked I, Berhane S, Toyoda H, Chan SL, Stern N, Palmer D, et al. Transarterial chemo-embolisation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact of liver function and vascular invasion. Brit J Cancer. 2017;116(4):448–54.
Hansmann J, Evers MJ, Bui JT, Lokken RP, Lipnik AJ, Gaba RC, et al. Albumin-bilirubin and platelet-albumin-bilirubin grades accurately predict overall survival in high-risk patients undergoing conventional transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(9):1224-1231.e2.
Hickey R, Mouli S, Kulik L, Desai K, Thornburg B, Ganger D, et al. Independent analysis of albumin-bilirubin grade in a 765-patient cohort treated with transarterial locoregional therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(6):795–802.
Aravind P, Thillai K, Suddle A, Heaton N, Karani J, Kane P, et al. Application of ALBI and PALBI score as prognostic variables in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with transarterial-chemoembolization. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(4_suppl):241–241.
Hiraoka A, Kumada T, Kudo M, Hirooka M, Koizumi Y, Hiasa Y, et al. Hepatic function during repeated TACE procedures and prognosis after introducing sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Multicentre analysis. Digest Dis. 2017;35(6):602–10.
Carling U, Røsok B, Line PD, Dorenberg EJ. ALBI and P-ALBI grade in child-pugh A patients treated with drug eluting embolic chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Radiol. 2018;60(6):702–9.
Liu P, Hsu C, Hsia C, Lee YH, Chiou YY, Huang YH, et al. ALBI and PALBI grade predict survival for HCC across treatment modalities and BCLC stages in the MELD Era. J Gastroen Hepatol. 2017;32(4):879–86.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21:1539–58.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391:1301–14.
Granito A, Bolondi L. Non-transplant therapies for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and child-pugh-turcotte class B cirrhosis. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(2):e101–12.
Chan A, Kumada T, Toyoda H, Tada T, Chong C, Mo F, et al. Integration of albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) score into Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroen Hepatol. 2016;31(7):1300–6.
Piscaglia F, Bolondi L. The intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma stage: Should treatment be expanded? Digest Liver Dis. 2010;42:S258–63.
Toyoda H, Kumada T, Tada T, Yama T, Mizuno K, Sone Y, et al. Differences in the impact of prognostic factors for hepatocellular carcinoma over time. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(12):2438–44.
Lee S, Song M, Kim S, Park M. Comparing various scoring system for predicting overall survival according to treatment modalities in hepatocellular carcinoma focused on Platelet-albumin-bilirubin (PALBI) and albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade: a nationwide cohort study. PLoS One. 2019;14(5): e0216173.
Ho S, Liu, Hsu C, Hsia CY, Lee YH, Lee RC, et al. Prognostic role of noninvasive liver reserve markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization. PLoS One. 2017;12(7).
Prins P, Sharma T, Kim KS, Bhardwaj PV, Collins N, Lu E, et al. Change in liver function as measured by change of child pugh score to predict survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) during the treatment course. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(suppl 4):S310.
Hass HG, Markmann H, Schaffer M, Wellhauber U, Smith U, Denzlinger C. Diagnostic and prognostic aspects of hepatocellular carcinoma – a retrospective analysis in 145 patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol Res. 2017;6(3):2358–64.
Georgiades CS, Liapi E, Frangakis C, Park J, Kim HW, Hong K, et al. Prognostic accuracy of 12 liver staging systems in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17(10):1619–24.
Schellhaas B, Strobel D, Stumpf M, Ganslmayer M, Pfeifer L, Goertz RS, et al. Improvement of clinical management and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma nowadays compared with historical cohorts. Eur J Gastroen Hepat. 2018;30(12):1422–7.
Giannini E, Bucci L, Garuti F, Brunacci M, Lenzi B, Valente M, et al. Patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma need a personalized management: a lesson from clinical practice. Hepatology. 2018;67(5):1784–96.
Giannini EG, Savarino V, Risso D, Di Nolfo MA, Del Poggio P, Benvegnu L, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization in child–pugh class B patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Between the devil and the deep blue sea. Liver Int. 2010;30(6):923–4.
Xu Y, Wang Y, Tan Y, Cheng X, Xu XZ. Prognostic value of pretreatment albumin to bilirubin ratio in patients with hepatocellular cancer. Medicine. 2019;98(2).
Demirtas CO, D’Alessio A, Rimassa L, Sharma R, Pinato DJ. ALBI grade: evidence for an improved model for liver functional estimation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. JHEP Rep: Innov Hepatol. 2021;3(5): 100347.
Cai X-R, Chen Z-H, Liu M-M, Lin JX, Zhang XP, et al. Modified CLIP score with the albumin-bilirubin grade retains prognostic value in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with trans-catheter arterial chemoembolization therapy. J Cancer. 2018;9(13):2380–8.
Ueshima K, Nishida N, Hagiwara S, Aoki T, Minami T, Chishina H, et al. Impact of baseline ALBI grade on the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with lenvatinib: a multicenter study. Cancers. 2019;11(7):952.
Yukimoto A, Hirooka M, Hiraoka A, Michitaka K, Ochi H, Joko K, et al. Using ALBI grade at the start of sorafenib treatment to predict regorafenib treatment candidates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019;49(1):42–7.
Edeline J, Blanc JF, Johnson P, Campillo-Gimenez B, Ross P, Ma YTA. multicentre comparison between child pugh and albumin-bilirubin grades in patients treated with sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2016;36(12):1821–8.
Kim HD, Bang Y, Lee MA, Kim JW, Kim JH, Chon HJ. Regorafenib in patients with advanced Child-Pugh B hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicentre retrospective study. Liver Int. 2020;40(10):2544–52.
Vogel A, Frenette C, Sung MW, Daniele B, Baron AD, Chan SL. Baseline liver function and outcomes in the phase III REFLECT study in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC). JClin Oncol. 2020;38(4_suppl):524–524.
Lee PC, Chao Y, Chen MH, Lan KH, Lee CJ, Lee IC. Predictors of response and survival in immune checkpoint inhibitor-treated unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(1):182.
Chan SL, Miksad R, Cicin I, Chen Y, Klumpen HJ, Kim S. Outcomes based on albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade in the phase III CELESTIAL trial of cabozantinib versus placebo in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann Oncol. 2019;30:ix45–6
Pinato DJ, Kaneko T, Saeed A, Pressiani T, Kaseb A, Wang Y. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular cancer patients with mild to severe liver dysfunction: adjunctive role of the ALBI grade. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(7):1862.
Ni JY, Fang ZT, Sun HL, An C, Huang ZM, Zhang TQ. A nomogram to predict survival of patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(4):2377–90.
Shimose S, Tanaka M, Iwamoto H, Niizeki T, Shirono T, Aino H, et al. Prognostic impact of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with radiofrequency ablation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with TACE alone using decision-tree analysis after propensity grade matching. Hepatol Res. 2019;49(8):919–28.
Gui B, Weiner AA, Nosher J, Lu SE, Foltz GM, Hasan O, et al. Assessment of the albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade as a prognostic indicator for hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with radioembolization. Am J Clin Oncol. 2018;41(9):861–6.
Toyoda H, Lai PB, O’Beirne J, Chong CC, Berhane S, Reeves H, et al. Long-term impact of liver function on curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: application of the ALBI grade. Br J Cancer. 2016;114(7):744–50.
Kudo M. Newly developed modified ALBI grade shows better prognostic and predictive value for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 2022;11:1–8.
Deng M, Ng SWY, Cheung ST, Chong CCN. Clinical application of albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score: the current status. Surgeon. 2020;18(3):178–86.
Vogeler M, Mohr I, Pfeiffenberger J, Sprengel SD, Klauss M, Teufel A, et al. Applicability of scoring systems predicting outcome of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020;146(4):1033–50.
Liu Y, Cheng C, Zhou H, Hu S, Wang H, Xie Q, Lei L, Wang P, Liu G, Hu H. Comparison of modified child-pugh (MCP), albumin-bilirubin (ALBI), and child-pugh (CP) grade for predicting of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Bull Cancer. 2021;108(10):931–9.
Jia KF, Wang H, Yu CL, Yin WL, Zhang XD, Wang F, Sun C, Shen W. ASARA, a prediction model based on child-pugh class in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2022;S1499–3872(22):00015–7.
Campani C, Vitale A, Dragoni G, Arena U, Laffi G, Cillo U, et al. Time-varying mHAP-III is the most accurate predictor of survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization. Liver Cancer. 2021;10(2):126–36.
Hiraoka A, Kumada T, Tsuji K, Takaguchi K, Itobayashi E, Kariyama K, et al. Validation of modified ALBI grade for more detailed assessment of hepatic function in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a multicenter analysis. Liver Cancer. 2019;8(2):121–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GM, AM and SKR contributed to the study design; GM and AM performed systematic review; GDE performed statistical analysis; DJP, HI, AH, TH, PL and PJ provided significant data input; all authors contributed to the drafting and/or review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
As a systematic review and meta-analysis, this study did not require approval by the Institutional Review Board or ethics committee.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12029_2022_832_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1: Factors associated with heterogeneity in patients in each ALBI grade; ALBI grade 1 (A-C), ALBI grade 2 (D-E), ALBI grade 3 (F, G) (PDF 125 KB)
12029_2022_832_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file2: Funnel plot of publications included for analysis in each ALBI grade; ALBI grade 1 (A), ALBI grade 2 (B), ALBI grade 3 (C) (JPG 455 KB)
12029_2022_832_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file3: Forest plots evaluating effect of geographical variations in ALBI grade 1 (A), grade 2 (B), and grade 3 (C) on overall survival (JPG 1083 KB)
12029_2022_832_MOESM4_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary file4: Harrell’s C index and AIC by ALBI grade, Child Pugh grade, BCLC stage, MELD and further sub stratification of Child Pugh grade and BCLC stage by ALBI grade, for each included study (XLSX 32 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, G., Majeed, A., Dev, A. et al. Clinical Utility of Albumin Bilirubin Grade as a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Canc 54, 420–432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-022-00832-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-022-00832-0