Abstract
Background
Gastric cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related death. Determining molecular and histopathologic tumor features, which may contribute to the development or progression of gastric cancer, can improve the prognosis. Expression patterns of DNA repair proteins such as MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 that are associated with microsatellite instability (MSI) are some of the markers that are useful in predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer.
Purpose
The purpose was to determine the immunohistochemical expression pattern of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 in tumor specimens of Iranian gastric carcinoma patients.
Methods
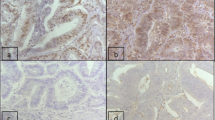
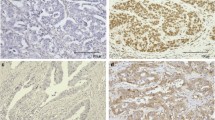
In this prospective cohort, 186 consecutive patients with gastric cancer, attending Taleghani Hospital, were enrolled. The immunohistochemical expression patterns of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 in tumor specimens among them were determined.
Results
The results of this study demonstrated that 91.4% of our gastric cancer patients were negative for MSI, and 8.6% of them were MSI positive. The positive MSI was seen in 5.9% and 15.7% of male and female subjects, respectively, with a significant difference (P = 0.043). The other variables were not related to MSI results (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
According to the obtained results, the expression of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 in tumor specimens is positive in 8.6% of the total Iranian gastric cancer sample size, which is mainly positive in female subjects. However, it is not related to the location and stage of the tumor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleman MP. Cancer survival: global surveillance will stimulate health policy and improve equity. Lancet. 2014;383(9916):564–73.
Vineis P, Wild CP. Global cancer patterns: causes and prevention. Lancet. 2014;383(9916):549–57.
Zhu L, Li ZH, Wang Y, Zhang CH, Liu Y, Qu X. Microsatellite instability and survival in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015;3:699–705.
Janjigian Y, Sanchez-Vega F, Jonsson P, Chatila WK, Hechtman JF, Geoffrey YK, et al. Genetic predictors of response to systemic therapy in esophagogastric cancer. Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2017:1.
Bae YS, Kim H, Noh SH, Kim H. Usefulness of immunohistochemistry for microsatellite instability screening in gastric cancer. Gut Liver. 2015;9(5):629–35.
Lee HS, Choi SI, Lee HK, Kim HS, Yang HK, Kang GH, Kim YI, Lee BL, Kim WH Distinct clinical features and outcomes of gastric cancers with microsatellite instability
Chiaravalli AM, Furlan D, Facco C, Tibiletti MG, Dionigi A, Casati B, et al. Immunohistochemical pattern of hMSH2/hMLH1 in familial and sporadic colorectal, gastric, endometrial and ovarian carcinomas with instability in microsatellite sequences. Virchows Arch. 2001;438(1):39–48.
Baek MJ, Kang H, Kim SE, Park JH, Lee JS, Paik YK, et al. Expression of hMLH1 is inactivated in the gastric adenomas with enhanced microsatellite instability. Br J Cancer. 2001;85(8):1147–52.
Beghelli S, de Manzoni G, Barbi S, Tomezzoli A, Roviello F, Di Gregorio C, et al. Microsatellite instability in gastric cancer is associated with better prognosis in only stage II cancers. Surgery. 2006;139(3):347–56.
Falchetti M, Saieva C, Lupi R, Masala G, Rizzolo P, Zanna I, et al. Gastric cancer with high-level microsatellite instability: target gene mutations, clinicopathologic features, and long-term survival. Hum Pathol. 2008;39(6):925–32.
Seo HM, Chang YS, Joo SH, Kim YW, Park YK, Hong SW, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and outcomes of gastric cancers with the MSH-H phenotype. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99(3):143–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salari, S., Ghadyani, M., Karimi, M. et al. Immunohistochemical Expression Pattern of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 in Tumor Specimen of Iranian Gastric Carcinoma Patients. J Gastrointest Canc 53, 192–196 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-020-00566-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-020-00566-x