Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to compare efficacy and safety of minimally invasive therapies such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), ethanol ablation (EA), and laser ablation (LA) for thyroid nodules through network meta-analysis (NMA).
Methods
This study searched PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and The Cochrane Library databases to collect randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or cohort studies comparing efficacy and safety of different minimally invasive therapies for thyroid nodules. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was implemented to assess quality of included cohort studies, and Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool was utilized to evaluate quality of included RCTs. Eligible studies contained at least one of the following clinical outcome measures: volume reduction rate (VRR), symptom score, cosmetic score, nodule regrowth rate, and complication rate. STATA software was utilized for NMA.
Results
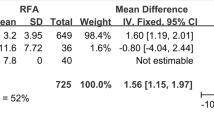
Sixteen eligible studies (4 RCTs, 11 retrospective cohort studies, 1 prospective cohort study) involved 4094 patients. NMA results revealed that RFA group had the highest VRR at 1 months and 12 months. There were no significant differences in symptom scores and cosmetic scores among all treatment methods, with the lowest symptom scores and cosmetic scores in RFA group. LA group had a significantly higher nodule regrowth rate than RFA and MWA groups, with the lowest in RFA group. There were no significant differences in complication rate among all treatment methods.
Conclusion
RFA had the highest VRR for thyroid nodules, and it excelled in symptom scores, cosmetic scores, and nodule regrowth rates.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.A. Cipriani, M.G. White, P. Angelos, R.H. Grogan, Large cytologically benign thyroid nodules do not have high rates of malignancy or false-negative rates and clinical observation should be considered: A meta-analysis. Thyroid 28, 1595–1608 (2018)
R.E. Weiss, J. Lado-Abeal, Thyroid nodules: diagnosis and therapy. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 14, 46–52 (2002)
E.K. Alexander, S. Hurwitz, J.P. Heering, C.B. Benson, M.C. Frates, P.M. Doubilet et al. Natural history of benign solid and cystic thyroid nodules. Ann. Intern Med. 138, 315–318 (2003)
C. Durante, G. Grani, L. Lamartina, S. Filetti, S.J. Mandel, D.S. Cooper, The diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: A review. JAMA 319, 914–924 (2018)
K. Kariyama, A. Wakuta, M. Nishimura, M. Kishida, A. Oonishi, A. Ohyama et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 89(Suppl 2), 19–26 (2015)
M. Barral, A. Auperin, A. Hakime, V. Cartier, V. Tacher, Y. Otmezguine et al. Percutaneous thermal ablation of breast cancer metastases in oligometastatic patients. Cardiovasc Interv. Radio. 39, 885–893 (2016)
S. Chheang, F. Abtin, A. Guteirrez, S. Genshaft, R. Suh, Imaging features following thermal ablation of lung malignancies. Semin Interv. Radio. 30, 157–168 (2013)
Z. Cheng, P. Liang, Advances in ultrasound-guided thermal ablation for symptomatic benign thyroid nodules. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med 29, 1123–1129 (2020)
A.P. Mainini, C. Monaco, L.C. Pescatori, C. De Angelis, F. Sardanelli, L.M. Sconfienza et al. Image-guided thermal ablation of benign thyroid nodules. J. Ultrasound 20, 11–22 (2017)
N.M. Iniguez-Ariza, R.A. Lee, N.M. Singh-Ospina, M.N. Stan, M.R. Castro, Ethanol ablation for the treatment of cystic and predominantly cystic thyroid nodules. Mayo Clin. Proc. 93, 1009–1017 (2018)
A. Chorti, V. Bontinis, G. Tzikos, A. Bontinis, A. Ioannidis, A. Michalopoulos et al. Minimally invasive treatments of benign thyroid nodules: a network meta-analysis of short-term outcomes. Thyroid 33, 950–964 (2023)
F.N. Bennedbaek, L. Hegedus, Treatment of recurrent thyroid cysts with ethanol: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 5773–5777 (2003)
S. Del Prete, M. Caraglia, D. Russo, G. Vitale, G. Giuberti, M. Marra et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection efficacy in the treatment of large symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules: ten-year follow-up of a large series. Thyroid 12, 815–821 (2002)
J.H. Kim, H.K. Lee, J.H. Lee, I.M. Ahn, C.G. Choi, Efficacy of sonographically guided percutaneous ethanol injection for treatment of thyroid cysts versus solid thyroid nodules. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 180, 1723–1726 (2003)
K. Yasuda, O. Ozaki, K. Sugino, T. Yamashita, K. Toshima, K. Ito et al. Treatment of cystic lesions of the thyroid by ethanol instillation. World J. Surg. 16, 958–961 (1992)
Y.S. Cho, H.K. Lee, I.M. Ahn, S.M. Lim, D.H. Kim, C.G. Choi et al. Sonographically guided ethanol sclerotherapy for benign thyroid cysts: results in 22 patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 174, 213–216 (2000)
F. Monzani, F. Lippi, O. Goletti, P. Del Guerra, N. Caraccio, P.V. Lippolis et al. Percutaneous aspiration and ethanol sclerotherapy for thyroid cysts. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 78, 800–802 (1994)
M. Zingrillo, M. Torlontano, R. Chiarella, M.R. Ghiggi, V. Nirchio, M. Bisceglia et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection may be a definitive treatment for symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules not treatable by surgery: five-year follow-up study. Thyroid 9, 763–767 (1999)
G. Verde, E. Papini, C.M. Pacella, C. Gallotti, S. Delpiano, S. Strada et al. Ultrasound guided percutaneous ethanol injection in the treatment of cystic thyroid nodules. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 41, 719–724 (1994)
S.J. Lee, I.M. Ahn, Effectiveness of percutaneous ethanol injection therapy in benign nodular and cystic thyroid diseases: long-term follow-up experience. Endocr. J. 52, 455–462 (2005)
F.N. Bennedbaek, L.K. Nielsen, L. Hegedus, Effect of percutaneous ethanol injection therapy versus suppressive doses of L-thyroxine on benign solitary solid cold thyroid nodules: a randomized trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 830–835 (1998)
J.H. Lee, Y.S. Kim, D. Lee, H. Choi, H. Yoo, J.H. Baek, Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of benign thyroid nodules in patients with incompletely resolved clinical problems after ethanol ablation (EA). World J. Surg. 34, 1488–1493 (2010)
C.K. Baldwin, M.B. Natter, K.N. Patel, S.P. Hodak, Minimally invasive techniques for the management of thyroid nodules. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 51, 323–349 (2022)
T. Cui, C. Jin, D. Jiao, D. Teng, G. Sui, Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation for benign thyroid nodules and papillary thyroid microcarcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radio. 118, 58–64 (2019)
M. Ahmed, C.L. Brace, F.T. Lee Jr, S.N. Goldberg, Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 258, 351–369 (2011)
E.M. Knavel, C.L. Brace, Tumor ablation: common modalities and general practices. Tech. Vasc. Inter. Radio. 16, 192–200 (2013)
J.H. Shin, J.H. Baek, E.J. Ha, J.H. Lee, Radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules: basic principles and clinical application. Int J. Endocrinol. 2012, 919650 (2012)
J.P. Ritz, K.S. Lehmann, U. Zurbuchen, V. Knappe, T. Schumann, H.J. Buhr et al. Ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of laser-induced thermotherapy for nodular thyroid disease. Lasers Surg. Med 41, 479–486 (2009)
S.N. Goldberg, G.S. Gazelle, S.L. Dawson, W.J. Rittman, P.R. Mueller, D.I. Rosenthal, Tissue ablation with radiofrequency: effect of probe size, gauge, duration, and temperature on lesion volume. Acad. Radio. 2, 399–404 (1995)
G. Mauri, L. Cova, C.G. Monaco, L.M. Sconfienza, S. Corbetta, S. Benedini et al. Benign thyroid nodules treatment using percutaneous laser ablation (PLA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA). Int J. Hyperth. 33, 295–299 (2017)
J.S. Sim, J.H. Baek, Long-term outcomes following thermal ablation of benign thyroid nodules as an alternative to surgery: The importance of controlling regrowth. Endocrinol. Metab. (Seoul.) 34, 117–123 (2019)
W.K. Jeong, J.H. Baek, H. Rhim, Y.S. Kim, M.S. Kwak, H.J. Jeong et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 236 patients. Eur. Radio. 18, 1244–1250 (2008)
Y.S. Kim, H. Rhim, K. Tae, D.W. Park, S.T. Kim, Radiofrequency ablation of benign cold thyroid nodules: Initial clinical experience. Thyroid 16, 361–367 (2006)
H.K. Lim, J.H. Baek, J.H. Lee, W.B. Kim, T.Y. Kim, Y.K. Shong et al. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation for treating locoregional recurrence from papillary thyroid cancer. Eur. Radio. 25, 163–170 (2015)
H. Jin, J. Fan, K. Liao, Z. He, W. Li, M. Cui, A propensity score matching study between ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation and conventional thyroidectomy for benign thyroid nodules treatment. Int. J. Hyperth. 35, 232–238 (2018)
J.H. Baek, E.J. Ha, Y.J. Choi, J.Y. Sung, J.K. Kim, Y.K. Shong, Radiofrequency versus ethanol ablation for treating predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: A randomized clinical trial. Korean J. Radio. 16, 1332–1340 (2015)
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Health Commission (No. 2022018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., Di, L., Yu, X. et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of different minimally invasive therapies for thyroid nodules: A network meta-analysis. Endocrine (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-024-03782-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-024-03782-8