Abstract
Background
Although ethanol ablation (EA) is effective, refractory cases have been reported in 5–25% of patients, with a marked decline in efficacy on subsequent reattempt. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) after EA of benign thyroid nodules in patients with incompletely resolved initial clinical problems.
Methods
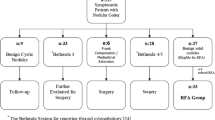
Among 137 patients with 137 benign thyroid nodules who underwent EA, 27 patients (M:F = 5:22; mean age = 38 years, range = 21–60 years) underwent additional RFA if all of the following criteria were fulfilled: (1) complaint of incompletely resolved clinical problems, (2) demonstration of remaining solid component with internal vascularity on 1-month follow-up power Doppler US, and (3) patient desire for additional treatment. After RFA, there was improvement of clinical symptoms and characteristics and volume reduction of the treated nodules as seen on US; complications were evaluated at each follow-up.
Results
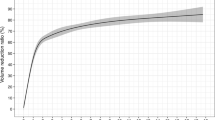
The mean follow-up duration was 21.2 months (range = 6–38 months) after RFA. The mean symptom grading score of 10-cm visual analog scale, the mean cosmetic grading score on a 4-point scale, and the mean volume reduction of thyroid nodules were all significantly decreased from those seen before RFA (2.4–1.1, 3.7–1.5, and 4.2–1.1, respectively) (P < 0.05). There were no major complications.
Conclusions
RFA is an effective and safe method for treating benign thyroid nodules in patients with incompletely resolved clinical problems following EA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennedbaek FN, Hegedus L (2003) Treatment of recurrent thyroid cysts with ethanol: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5773–5777
Cho YS, Lee HK, Ahn IM et al (2000) Sonographically guided ethanol sclerotherapy for benign thyroid cysts: results in 22 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:213–216
Del Prete S, Caraglia M, Russo D et al (2002) Percutaneous ethanol injection efficacy in the treatment of large symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules: ten-year follow-up of a large series. Thyroid 12:815–821
Filetti S, Durante C, Torlontano M (2006) Nonsurgical approaches to the management of thyroid nodules. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2:384–394
Kim DW, Rho MH, Kim HJ et al (2005) Percutaneous ethanol injection for benign cystic thyroid nodules: is aspiration of ethanol-mixed fluid advantageous? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2122–2127
Kim JH, Lee HK, Lee JH et al (2003) Efficacy of sonographically guided percutaneous ethanol injection for treatment of thyroid cysts versus solid thyroid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1723–1726
Lee SJ, Ahn IM (2005) Effectiveness of percutaneous ethanol injection therapy in benign nodular and cystic thyroid diseases: long-term follow-up experience. Endocr J 52:455–462
Monzani F, Lippi F, Goletti O et al (1994) Percutaneous aspiration and ethanol sclerotherapy for thyroid cysts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 78:800–802
Zingrillo M, Torlontano M, Chiarella R et al (1999) Percutaneous ethanol injection may be a definitive treatment for symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules not treatable by surgery: five-year follow-up study. Thyroid 9:763–767
Zingrillo M, Torlontano M, Ghiggi MR et al (1996) Percutaneous ethanol injection of large thyroid cystic nodules. Thyroid 6:403–408
Yasuda K, Ozaki O, Sugino K et al (1992) Treatment of cystic lesions of the thyroid by ethanol instillation. World J Surg 16:958–961
Jeong WK, Baek JH, Rhim H et al (2008) Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 236 patients. Eur Radiol 18:1244–1250
Deandrea M, Limone P, Basso E et al (2008) US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation for the treatment of solid benign hyperfunctioning or compressive thyroid nodules. Ultrasound Med Biol 34:784–791
Owen RP, Silver CE, Ravikumar TS et al (2004) Techniques for radiofrequency ablation of head and neck tumors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:52–56
Baek JH, Jeong HJ, Kim YS et al (2008) Radiofrequency ablation for an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Thyroid 18:675–676
Dupuy DE, Monchik JM, Decrea C et al (2001) Radiofrequency ablation of regional recurrence from well-differentiated thyroid malignancy. Surgery 130:971–977
Monchik JM, Donatini G, Iannuccilli J et al (2006) Radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous ethanol injection treatment for recurrent local and distant well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Ann Surg 244:296–304
Sung JY, Baek JH, Kim YS et al (2008) One-step ethanol ablation of viscous cystic thyroid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191:1730–1733
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Haengil Im (Department of Radiology, Daerim Saint Mary’s Hospital, Seoul) and Bonnie Hami (MA, Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Health System, Cleveland, Ohio) for their editorial assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Kim, Y.S., Lee, D. et al. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Benign Thyroid Nodules in Patients with Incompletely Resolved Clinical Problems after Ethanol Ablation (EA). World J Surg 34, 1488–1493 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0565-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0565-6