Abstract
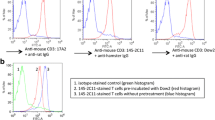
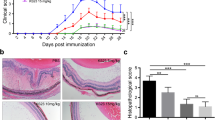
The purpose of the study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory efficiency of vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). EAU was induced in female C57BL/6J mice immunized with interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein peptide. Vorinostat or the control treatment, phosphate-buffered saline, was administrated orally from 3 days before immunization until euthanasia at day 21 after immunization. The clinical and histopathological scores of mice were graded, and the integrity of the blood–retinal barrier was examined by Evans blue staining. T helper cell subsets were measured by flow cytometry, and the macrophage functions were evaluated with immunohistochemistry staining and immunofluorescence assays. The mRNA levels of tight junction proteins were measured by qRT-PCR. The expression levels of intraocular cytokines and transcription factors were examined by western blotting. Vorinostat relieved both clinical and histopathological manifestations of EAU in our mouse model, and the BRB integrity was maintained in vorinostat-treated mice, which had less vasculature leakage and higher mRNA and protein expressions of tight junction proteins than controls. Moreover, vorinostat repressed Th1 and Th17 cells and increased Th0 and Treg cells. Additionally, the INF-γ and IL-17A expression levels were significantly decreased, while the IL-10 level was increased by vorinostat treatment. Furthermore, due to the reduced TNF-α level, the macrophage activity was considerably inhibited in EAU mice. Finally, transcription factors, including STAT1, STAT3, and p65, were greatly suppressed by vorinostat treatment. Our data suggest that vorinostat might be a potential anti-inflammatory agent in the management of uveitis and other autoimmune inflammatory diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, R. K., Silver, P. B., & Caspi, R. R. (2012). Rodent models of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Methods in Molecular Biology, 900, 443–469.
Amadi-Obi, A., Yu, C. R., Liu, X., Mahdi, R. M., Clarke, G. L., Nussenblatt, R. B., et al. (2007). TH17 cells contribute to uveitis and scleritis and are expanded by IL-2 and inhibited by IL-27/STAT1. Nature Medicine, 13(6), 711–718.
Bosisio, D., Vulcano, M., Del Prete, A., Sironi, M., Salvi, V., Salogni, L., et al. (2008). Blocking TH17-polarizing cytokines by histone deacetylase inhibitors in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 84(6), 1540–1548.
Bousquet, E., Camelo, S., Leroux les Jardins, G., Goldenberg, B., Naud, M. C., Besson-Lescure, B., et al. (2011). Protective effect of intravitreal administration of tresperimus, an immunosuppressive drug, on experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 52(8), 5414–5423.
Butler, L. M., Agus, D. B., Scher, H. I., Higgins, B., Rose, A., Cordon-Cardo, C., et al. (2000). Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Research, 60(18), 5165–5170.
Caspi, R. R. (1999). Immune mechanisms in uveitis. Springer Seminars in Immunopathology, 21(2), 113–124.
Caspi, R. R. (2010). A look at autoimmunity and inflammation in the eye. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 120(9), 3073–3083.
Choi, S., & Reddy, P. (2011). HDAC inhibition and graft versus host disease. Molecular Medicine, 17(5–6), 404–416.
Copland, D. A., Liu, J., Schewitz-Bowers, L. P., Brinkmann, V., Anderson, K., Nicholson, L. B., & Dick, A. D. (2012). Therapeutic dosing of fingolimod (FTY720) prevents cell infiltration, rapidly suppresses ocular inflammation, and maintains the blood-ocular barrier. The American Journal of Pathology, 180(2), 672–681.
de Kozak, Y., Omri, B., Smith, J. R., Naud, M. C., Thillaye-Goldenberg, B., & Crisanti, P. (2007). Protein kinase Czeta (PKCzeta) regulates ocular inflammation and apoptosis in endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU): Signaling molecules involved in EIU resolution by PKCzeta inhibitor and interleukin-13. The American Journal of Pathology, 170(4), 1241–1257.
Dick, A. D. (2000). Immune mechanisms of uveitis: Insights into disease pathogenesis and treatment. International Ophthalmology Clinics, 40(2), 1–18.
Dinarello, C. A., Fossati, G., & Mascagni, P. (2011). Histone deacetylase inhibitors for treating a spectrum of diseases not related to cancer. Molecular Medicine, 17(5–6), 333–352.
Erickson, K. K., Sundstrom, J. M., & Antonetti, D. A. (2007). Vascular permeability in ocular disease and the role of tight junctions. Angiogenesis, 10(2), 103–117.
Fan, H., Liu, Z., & Jiang, S. (2011). Th17 and regulatory T cell subsets in diseases and clinical application. International Immunopharmacology, 11(5), 533–535.
Gálvez, J. (2014). Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of human IBD. ISRN Inflammation, 25(2014), 928461.
Ge, Z., Da, Y., Xue, Z., Zhang, K., Zhuang, H., Peng, M., et al. (2013). Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses dendritic cell function and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Experimental Neurology, 241, 56–66.
Grajewski, R. S., Silver, P. B., Agarwal, R. K., Su, S. B., Chan, C. C., Liou, G. I., & Caspi, R. R. (2006). Endogenous IRBP can be dispensable for generation of natural CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells that protect from IRBP-induced retinal autoimmunity. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 203(4), 851–856.
Hayden, M. S., & Ghosh, S. (2012). NF-κB, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes & Development, 26(3), 203–234.
Horai, R., & Caspi, R. R. (2011). Cytokines in autoimmune uveitis. Journal of Interferon and Cytokine Research, 31(10), 733–744.
Jiang, G., Sun, D., Yang, H., Lu, Q., Kaplan, H. J., & Shao, H. (2014). HMGB1 is an early and critical mediator in an animal model of uveitis induced by IRBP-specific T cells. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 95(4), 599–607.
Klaassen, I., Van Noorden, C. J., & Schlingemann, R. O. (2013). Molecular basis of the inner blood–retinal barrier and its breakdown in diabetic macular edema and other pathological conditions. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 34, 19–48.
Leng, C., Gries, M., Ziegler, J., Lokshin, A., Mascagni, P., Lentzsch, S., & Mapara, M. Y. (2006). Reduction of graft-versus-host disease by histone deacetylase inhibitor suberonylanilide hydroxamic acid is associated with modulation of inflammatory cytokine milieu and involves inhibition of STAT1. Experimental Hematology, 34(6), 776–787.
Li, G., Yuan, L., Ren, X., Nian, H., Zhang, L., Han, Z. C., et al. (2013). The effect of mesenchymal stem cells on dynamic changes of T cell subsets in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 173(1), 28–37.
Licciardi, P. V., & Karagiannis, T. C. (2012). Regulation of immune responses by histone deacetylase inhibitors. ISRN Hematology, 2012, 690901.
Miller, J. W., Le Couter, J., Strauss, E. C., & Ferrara, N. (2013). Vascular endothelial growth factor a in intraocular vascular disease. Ophthalmology, 120(1), 106–114.
Mora, J. R., & von Andrian, U. H. (2006). T-cell homing specificity and plasticity: New concepts and future challenges. Trends in Immunology, 27(5), 235–243.
Prete, M., Dammacco, R., Fatone, M. C., & Racanelli, V. (2015). Autoimmune uveitis: Clinical, pathogenetic, and therapeutic features. Clinical and Experimental Medicine. doi:10.1007/s10238-015-0345-6.
Romagnani, S., Maggi, E., Liotta, F., Cosmi, L., & Annunziato, F. (2009). Properties and origin of human Th17 cells. Molecular Immunology, 47(1), 3–7.
Selmi, C. (2014). Diagnosis and classification of autoimmune uveitis. Autoimmunity Reviews, 13(4–5), 591–594.
Servat, J. J., Mears, K. A., Black, E. H., & Huang, J. J. (2012). Biological agents for the treatment of uveitis. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 12(3), 311–328.
Tian, L., Lei, B., Shao, J., Wei, L., Kijlstra, A., & Yang, P. (2012). AAV2-mediated combined subretinal delivery of IFN-α and IL-4 reduces the severity of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. PLoS One, 7(6), e37995.
Ververis, K., & Karagiannis, T. C. (2011). Potential non-oncological applications of histone deacetylase inhibitors. American Journal of Translational Research, 3(5), 454–467.
Wang, L., de Zoeten, E. F., Greene, M. I., & Hancock, W. W. (2009a). Immunomodulatory effects of deacetylase inhibitors: Therapeutic targeting of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 8(12), 969–981.
Wang, L., Tao, R., & Hancock, W. W. (2009b). Using histone deacetylase inhibitors to enhance Foxp3(+) regulatory T-cell function and induce allograft tolerance. Immunology and Cell Biology, 87(3), 195–202.
Wang, R. X., Yu, C. R., Mahdi, R. M., & Egwuagu, C. E. (2012). Novel IL27p28/IL12p40 cytokine suppressed experimental autoimmune uveitis by inhibiting autoreactive Th1/Th17 cells and promoting expansion of regulatory T cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(43), 36012–36021.
Woan, K. V., Sahakian, E., Sotomayor, E. M., Seto, E., & Villagra, A. (2012). Modulation of antigen presenting cells by HDAC inhibitors: Implications in autoimmunity and cancer. Immunology and Cell Biology, 90(1), 55–65.
Yadav, U. C., Shoeb, M., Srivastava, S. K., & Ramana, K. V. (2011). Amelioration of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by aldose reductase inhibition in Lewis rats. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 52(11), 8033–8041.
Yoshimura, T., Benny, O., Bazinet, L., & D’Amato, R. J. (2013). Suppression of autoimmune retinal inflammation by an antiangiogenic drug. PLoS One, 8(6), e66219.
Yu, C. R., Mahdi, R. R., Oh, H. M., Amadi-Obi, A., Levy-Clarke, G., Burton, J., et al. (2011). Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS1) inhibits lymphocyte recruitment into the retina and protects SOCS1 transgenic rats and mice from ocular inflammation. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 52(9), 6978–6986.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 81371038 and 91442124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, S., Meng, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Vorinostat Modulates the Imbalance of T Cell Subsets, Suppresses Macrophage Activity, and Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Uveoretinitis. Neuromol Med 18, 134–145 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8383-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8383-0