Abstract
Biologic medications are an expanding field of therapeutics for various medical conditions including cancer and inflammatory diseases. Due to their targeted approach to therapy, biologics can be less toxic than traditional systemic medications. However, as use becomes more widespread, adverse effects from biologic administration have also become apparent. Immune-related adverse events are a common mechanism by which biologics can cause on-target immune-related toxicities and both immediate and delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions can be mediated by cytokine release or antibody mediated reactions, while delayed-type hypersensitivity is most often caused by serum sickness-like reactions. Additionally, biologics used for treatment of cancer using checkpoint blockade and rheumatologic disease using cytokine blockade can result in autoimmunity. Finally, when inflammatory cytokines are targeted for treatment of autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease, the host immune defense can be compromised predisposing to secondary immunodeficiency. This review will discuss the mechanisms of these reactions and discuss examples of biologics implicated in each of these adverse events.

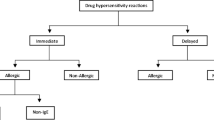
Adapted from Picard et al. [12]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corominas M, Gastaminza G, Lobera T (2014) Hypersensitivity reactions to biological drugs. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 24:212–25; quiz 1p following 25
Purcell RT, Lockey RF (2008) Immunologic responses to therapeutic biologic agents. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 18:335–342
Khan DA (2016) Hypersensitivity and immunologic reactions to biologics: opportunities for the allergist. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 117:115–120
Kohler G, Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256:495–497
Brennan PJ, Rodriguez Bouza T, Hsu FI, Sloane DE, Castells MC (2009) Hypersensitivity reactions to mAbs: 105 desensitizations in 23 patients, from evaluation to treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:1259–1266
Pichler WJ (2019) Immune pathomechanism and classification of drug hypersensitivity. Allergy 74:1457–1471
Pichler WJ (2006) Adverse side-effects to biological agents. Allergy 61:912–920
Mori F, Saretta F, Bianchi A, Crisafulli G, Caimmi S, Liotti L et al (2020) Hypersensitivity reactions to monoclonal antibodies in children. Medicina (Kaunas) 56
Vultaggio A, Castells MC (2014) Hypersensitivity reactions to biologic agents. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 34(615–32):ix
Isabwe GAC, Garcia Neuer M, de Las Vecillas Sanchez L, Lynch DM, Marquis K, Castells M (2018) Hypersensitivity reactions to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: Phenotypes and endotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 142:159–70 e2
Galvao VR, Castells MC (2015) Hypersensitivity to biological agents-updated diagnosis, management, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 3:175–85; quiz 86
Picard M, Galvao VR (2017) Current knowledge and management of hypersensitivity reactions to monoclonal antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 5:600–609
Bremmer M, Deng A, Gaspari AA (2009) A mechanism-based classification of dermatologic reactions to biologic agents used in the treatment of cutaneous disease: Part 2. Dermatitis 20:243–256
Bremmer M, Deng A, Gaspari AA (2009) A mechanism-based classification of dermatologic reactions to biologic agents used in the treatment of cutaneous disease: Part 1. Dermatitis 20:182–192
Puxeddu I, Giori L, Rocchi V, Bazzichi L, Bombardieri S, Tavoni A et al (2012) Hypersensitivity reactions during treatment with infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 108:123–124
Broyles AD, Banerji A, Barmettler S, Biggs CM, Blumenthal K, Brennan PJ et al (2020) Practical guidance for the evaluation and management of drug hypersensitivity: specific drugs. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 8:S16–S116
Cheifetz A, Smedley M, Martin S, Reiter M, Leone G, Mayer L et al (2003) The incidence and management of infusion reactions to infliximab: a large center experience. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1315–1324
Akarsu A, Soyer O, Sekerel BE (2020) Hypersensitivity reactions to biologicals: from bench to bedside. Curr Treat Options Allergy 7:71–83
Baldo BA (2013) Adverse events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy: Focus on hypersensitivity responses. Oncoimmunology 2:e26333
Wong JT, Long A (2017) Rituximab hypersensitivity: evaluation, desensitization, and potential mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 5:1564–1571
van Vollenhoven RF, Emery P, Bingham CO, 3rd, Keystone EC, Fleischmann RM, Furst DE et al (2013) Long-term safety of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: 9.5-year follow-up of the global clinical trial programme with a focus on adverse events of interest in RA patients. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1496–502
Jung JW, Kang HR, Lee SH, Cho SH (2014) The incidence and risk factors of infusion-related reactions to rituximab for treating B cell malignancies in a single tertiary hospital. Oncology 86:127–134
Checkley LA, Kristofek L, Kile S, Bolgar W (2019) Incidence and Management of Infusion Reactions to Infliximab in an Alternate Care Setting. Dig Dis Sci 64:855–862
Choquette D, Faraawi R, Chow A, Rodrigues J, Bensen WJ, Nantel F (2015) Incidence and management of infusion reactions to infliximab in a prospective real-world community registry. J Rheumatol 42:1105–1111
Lichtenstein L, Ron Y, Kivity S, Ben-Horin S, Israeli E, Fraser GM et al (2015) Infliximab-Related Infusion Reactions: Systematic Review. J Crohns Colitis 9:806–815
Cook-Bruns N (2001) Retrospective analysis of the safety of Herceptin immunotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. Oncology 61(Suppl 2):58–66
Thompson LM, Eckmann K, Boster BL, Hess KR, Michaud LB, Esteva FJ et al (2014) Incidence, risk factors, and management of infusion-related reactions in breast cancer patients receiving trastuzumab. Oncologist 19:228–234
Pratt KP (2018) Anti-drug antibodies: emerging approaches to predict, reduce or reverse biotherapeutic immunogenicity. Antibodies (Basel) 7
Chung CH, Mirakhur B, Chan E, Le QT, Berlin J, Morse M et al (2008) Cetuximab-induced anaphylaxis and IgE specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. N Engl J Med 358:1109–1117
Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Rispens T, Verploegen S, van der Palen-Merkus T, Stapel S, Workman LJ et al (2011) Anti-galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose IgE from allergic patients does not bind alpha-galactosylated glycans on intact therapeutic antibody Fc domains. Nat Biotechnol 29:574-6
Finkelman FD, Khodoun MV, Strait R (2016) Human IgE-independent systemic anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137:1674–1680
Matucci A, Pratesi S, Petroni G, Nencini F, Virgili G, Milla M et al (2013) Allergological in vitro and in vivo evaluation of patients with hypersensitivity reactions to infliximab. Clin Exp Allergy 43:659–664
Mourad AA, Boktor MN, Yilmaz-Demirdag Y, Bahna SL (2015) Adverse reactions to infliximab and the outcome of desensitization. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 115:143–146
Cox L, Platts-Mills TA, Finegold I, Schwartz LB, Simons FE, Wallace DV et al (2007) American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force Report on omalizumab-associated anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:1373–1377
Cox L, Lieberman P, Wallace D, Simons FE, Finegold I, Platts-Mills T et al (2011) American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Omalizumab-Associated Anaphylaxis Joint Task Force follow-up report. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:210–212
Price KS, Hamilton RG (2007) Anaphylactoid reactions in two patients after omalizumab administration after successful long-term therapy. Allergy Asthma Proc 28:313–319
Owens G, Petrov A (2011) Successful desensitization of three patients with hypersensitivity reactions to omalizumab. Curr Drug Saf 6:339–342
Fouda GE, Bavbek S (2020) Rituximab hypersensitivity: from clinical presentation to management. Front Pharmacol 11:572863
Sloane D, Govindarajulu U, Harrow-Mortelliti J, Barry W, Hsu FI, Hong D et al (2016) Safety, costs, and efficacy of rapid drug desensitizations to chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 4:497–504
Hong DI, Dioun AF (2014) Indications, protocols, and outcomes of drug desensitizations for chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies in adults and children. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2:13–9; quiz 20
Dilley MA, Lee JP, Platt CD, Broyles AD (2016) Rituximab desensitization in pediatric patients: results of a case series. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol 29:91–94
Munoz-Cano R, Carnes J, Sanchez-Lopez J, Saiz A, Bartra J, Lopez-Matas MA et al (2010) Biological agents: new drugs, old problems. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:394–395
Hellwig K, Schimrigk S, Fischer M, Haghikia A, Muller T, Chan A et al (2008) Allergic and nonallergic delayed infusion reactions during natalizumab therapy. Arch Neurol 65:656–658
Calabresi PA, Giovannoni G, Confavreux C, Galetta SL, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M et al (2007) The incidence and significance of anti-natalizumab antibodies: results from AFFIRM and SENTINEL. Neurology 69:1391–1403
Camacho-Halili M, George R, Gottesman M, Davis-Lorton M (2011) An approach to natalizumab hypersensitivity: a case series of induction of tolerance. Mult Scler 17:250–253
Bignardi D, Ribizzi G, Voltolini S, Serrati C, Troise C (2012) Successful desensitization to natalizumab in a skin test–positive patient: a case report. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol 44:26–29
Ribizzi G, Bignardi D, Farinini D, Sassos D, Gentile R, Arecco D et al (2013) Desensitization to natalizumab: clinical and immunological observations. Mult Scler 19:376–377
Perez-Rodriguez E, Hernandez-Perez MA, Martinez-Tadeo JA (2017) Successful desensitization to natalizumab using a 1-solution protocol. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 118:113–114
Hansel K, Bianchi L, Tramontana M, Balato A, Scala E, Brozzi J et al (2019) Immediate local and systemic hypersensitivity due to etanercept and adalimumab. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 7:726–727
Baert F, Noman M, Vermeire S, Van Assche G, G DH, Carbonez A et al (2003) Influence of immunogenicity on the long-term efficacy of infliximab in Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med 348:601–8
O’Meara S, Nanda KS, Moss AC (2014) Antibodies to infliximab and risk of infusion reactions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20:1–6
Maneiro JR, Salgado E, Gomez-Reino JJ (2013) Immunogenicity of monoclonal antibodies against tumor necrosis factor used in chronic immune-mediated Inflammatory conditions: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med 173:1416–1428
Bavbek S, Ataman S, Akinci A, Castells M (2015) Rapid subcutaneous desensitization for the management of local and systemic hypersensitivity reactions to etanercept and adalimumab in 12 patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 3:629–632
O’Neil BH, Allen R, Spigel DR, Stinchcombe TE, Moore DT, Berlin JD et al (2007) High incidence of cetuximab-related infusion reactions in Tennessee and North Carolina and the association with atopic history. J Clin Oncol 25:3644–3648
Commins SP, Satinover SM, Hosen J, Mozena J, Borish L, Lewis BD et al (2009) Delayed anaphylaxis, angioedema, or urticaria after consumption of red meat in patients with IgE antibodies specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:426–433
Chitnavis M, Stein DJ, Commins S, Schuyler AJ, Behm B (2017) First-dose anaphylaxis to infliximab: a case of mammalian meat allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 5:1425–1426
Jerath MR, Kwan M, Kannarkat M, Mirakhur B, Carey L, Valgus J et al (2009) A desensitization protocol for the mAb cetuximab. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:260–262
Murdaca G, Spano F, Puppo F (2013) Selective TNF-alpha inhibitor-induced injection site reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf 12:187–193
Chen CB, Wu MY, Ng CY, Lu CW, Wu J, Kao PH et al (2018) Severe cutaneous adverse reactions induced by targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies. Cancer Manag Res 10:1259–1273
Bulur I, Keseroglu HO, Saracoglu ZN, Gonul M (2015) Symmetrical drug-related intertriginous and flexural exanthema (Baboon syndrome) associated with infliximab. J Dermatol Case Rep 9:12–14
Castells M (2017) Drug hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis in cancer and chronic inflammatory diseases: the role of desensitizations. Front Immunol 8:1472
Gamarra RM, McGraw SD, Drelichman VS, Maas LC (2006) Serum sickness-like reactions in patients receiving intravenous infliximab. J Emerg Med 30:41–44
Karmacharya P, Poudel DR, Pathak R, Donato AA, Ghimire S, Giri S et al (2015) Rituximab-induced serum sickness: A systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 45:334–340
Bayer G, Agier MS, Lioger B, Lepelley M, Zenut M, Lanoue MC et al (2019) Rituximab-induced serum sickness is more frequent in autoimmune diseases as compared to hematological malignancies: A French nationwide study. Eur J Intern Med 67:59–64
Barakat L, Torres MJ, Phillips EJ, Caminati M, Chang YS, Caimmi D et al (2020) Biological treatments in allergy: prescribing patterns and management of hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract
Dreyfus DH, Randolph CC (2006) Characterization of an anaphylactoid reaction to omalizumab. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 96:624–627
Pilette C, Coppens N, Houssiau FA, Rodenstein DO (2007) Severe serum sickness-like syndrome after omalizumab therapy for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:972–973
Eapen A, Kloepfer KM (2018) Serum sickness-like reaction in a pediatric patient using omalizumab for chronic spontaneous urticaria. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 29:449–450
Molderings GJ, Dumoulin FL, Homann J, Sido B, Textor J, Mucke M et al (2020) Adrenal insufficiency is a contraindication for omalizumab therapy in mast cell activation disease: risk for serum sickness. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393:1573–1580
Her M, Kavanaugh A (2016) Alterations in immune function with biologic therapies for autoimmune disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137:19–27
Ribas A, Wolchok JD (2018) Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 359:1350–1355
Ramos-Casals M (2020) Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Dis Primers 21
Hu J-R, Florido R, Lipson EJ, Naidoo J, Ardehali R, Tocchetti CG et al (2019) Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cardiovasc Res 115:854–868
Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD (2018) Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N Engl J Med 378:158–168
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK et al (2018) Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 378:1277–1290
Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R, Zurawski B, Kim S-W, Carcereny Costa E et al (2019) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 381:2020–2031
Ramos-Casals M, Brahmer JR, Callahan MK, Flores-Chavez A, Keegan N, Khamashta MA et al (2020) Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Dis Primers 6:38
Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, Hodi FS, Min L, Krop IE et al (2018) Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 4:173
Johnson DB, Jakubovic BD, Sibaud V, Sise ME (2020) Balancing cancer immunotherapy efficacy and toxicity. J Allergy Clin Immunol: In Pract 8:2898–906.
Akturk HK, Kahramangil D, Sarwal A, Hoffecker L, Murad MH, Michels AW (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced Type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med 36:1075–1081
Shivaji UN, Jeffery L, Gui X, Smith SCL, Ahmad OF, Akbar A et al (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated gastrointestinal and hepatic adverse events and their management. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 12:1756284819884196
Salem J-E, Manouchehri A, Moey M, Lebrun-Vignes B, Bastarache L, Pariente A et al (2018) Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: an observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study. Lancet Oncol 19:1579–1589
Johnson DB, Manouchehri A, Haugh AM, Quach HT, Balko JM, Lebrun-Vignes B et al (2019) Neurologic toxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a pharmacovigilance study. J Immunother Cancer 7:134
Wang DY, Salem J-E, Cohen JV, Chandra S, Menzer C, Ye F et al (2018) Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 4:1721
Darnell EP, Mooradian MJ, Baruch EN, Yilmaz M, Reynolds KL (2020) Immune-related adverse events (irAEs): diagnosis, management, and clinical pearls. Curr Oncol Rep 22:39
Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, Atkins MB, Brassil KJ, Caterino JM et al (2018) Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol 36:1714–1768
Dolladille C, Ederhy S, Sassier M, Cautela J, Thuny F, Cohen AA et al (2020) Immune checkpoint inhibitor rechallenge after immune-related adverse events in patients with cancer. JAMA Oncol 6:865–871
Eggermont AMM, Kicinski M, Blank CU, Mandala M, Long GV, Atkinson V et al (2020) Association between immune-related adverse events and recurrence-free survival among patients with stage III melanoma randomized to receive pembrolizumab or placebo: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 6:519–527
Fujii T, Colen RR, Bilen MA, Hess KR, Hajjar J, Suarez-Almazor ME et al (2018) Incidence of immune-related adverse events and its association with treatment outcomes: the MD Anderson Cancer Center experience. Invest New Drugs 36:638–646
Cortellini A, Buti S, Agostinelli V, Bersanelli M (2019) A systematic review on the emerging association between the occurrence of immune-related adverse events and clinical outcomes with checkpoint inhibitors in advanced cancer patients. Semin Oncol 46:362–371
Perez-De-Lis M, Retamozo S, Flores-Chavez A, Kostov B, Perez-Alvarez R, Brito-Zeron P et al (2017) Autoimmune diseases induced by biological agents. A review of 12,731 cases (BIOGEAS Registry). Expert Opin Drug Saf 16:1255–71
Her M, Kavanaugh A (2016) Alterations in immune function with biologic therapies for autoimmune disease. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 137:19–27
Conrad C, Di Domizio J, Mylonas A, Belkhodja C, Demaria O, Navarini AA et al (2018) TNF blockade induces a dysregulated type I interferon response without autoimmunity in paradoxical psoriasis. Nat Commun 9:25
Guerra I, Perez-Jeldres T, Iborra M, Algaba A, Monfort D, Calvet X et al (2016) Incidence, clinical characteristics, and management of psoriasis induced by anti-TNF therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a nationwide cohort study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 22:894–901
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcon GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR et al (2012) Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64:2677–2686
Borchers AT, Leibushor N, Cheema GS, Naguwa SM, Gershwin ME (2011) Immune-mediated adverse effects of biologicals used in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. J Autoimmun 37:273–288
Perez-Alvarez R, Pérez-de-Lis M, Ramos-Casals M (2013) Biologics-induced autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 25:56–64
Sokumbi O, Wetter DA, Makol A, Warrington KJ (2012) Vasculitis associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. Mayo Clin Proc 87:739–745
Shivaji UN, Jeffery L, Gui X, Smith SCL, Ahmad OF, Akbar A et al (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated gastrointestinal and hepatic adverse events and their management. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 12:175628481988419
Atiqi S, Hooijberg F, Loeff FC, Rispens T, Wolbink GJ (2020) Immunogenicity of TNF-Inhibitors Front Immunol 11:312
Bartelds GM, Krieckaert CL, Nurmohamed MT, van Schouwenburg PA, Lems WF, Twisk JW et al (2011) Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA 305:1460–1468
Moots RJ, Xavier RM, Mok CC, Rahman MU, Tsai W-C, Al-Maini MH et al (2017) The impact of anti-drug antibodies on drug concentrations and clinical outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab: Results from a multinational, real-world clinical practice, non-interventional study. PLoS One 12:e0175207
Strand V, Balsa A, Al-Saleh J, Barile-Fabris L, Horiuchi T, Takeuchi T et al (2017) Immunogenicity of biologics in chronic inflammatory diseases: a systematic review. BioDrugs 31:299–316
Singh JA, Wells GA, Christensen R, Tanjong Ghogomu E, Maxwell L, Macdonald JK et al (2011) Adverse effects of biologics: a network meta-analysis and Cochrane overview. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD008794
Henrickson SE, Ruffner MA, Kwan M (2016) Unintended immunological consequences of biologic therapy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 16:46
Davis BP, Ballas Z (2017) Biologic response modifiers: indications, implications, and insights. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139:1445–1456
Kalliolias GD, Ivashkiv LB (2016) TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:49–62
Keystone EC (2011) Does anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy affect risk of serious infection and cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis?: a review of longterm data. J Rheumatol 38:1552–1562
Garcia-Doval I, Cohen AD, Cazzaniga S, Feldhamer I, Addis A, Carretero G et al (2017) Risk of serious infections, cutaneous bacterial infections, and granulomatous infections in patients with psoriasis treated with anti–tumor necrosis factor agents versus classic therapies: Prospective meta-analysis of Psonet registries. J Am Acad Dermatol 76:299–308
Dixon WG, Watson K, Lunt M, Hyrich KL, Silman AJ, Symmons DP et al (2006) Rates of serious infection, including site-specific and bacterial intracellular infection, in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Arthritis Rheum 54:2368–2376
Keystone EC (2011) Does anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy affect risk of serious infection and cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis?: a review of longterm data. J Rheumatol 38:1552–1562
Curtis JR, Patkar N, Xie A, Martin C, Allison JJ, Saag M et al (2007) Risk of serious bacterial infections among rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to tumor necrosis factor α antagonists. Arthritis Rheum 56:1125–1133
Dinarello CA, Simon A, van der Meer JWM (2012) Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 11:633–652
Mantovani A, Dinarello CA, Molgora M, Garlanda C (2019) Interleukin-1 and related cytokines in the regulation of inflammation and immunity. Immunity 50:778–795
Evavold CL, Kagan JC (2019) Inflammasomes: threat-assessment organelles of the innate immune system. Immunity 51:609–624
Beukelman T, Xie F, Baddley JW, Chen L, Mannion ML, Saag KG et al (2016) The risk of hospitalized infection following initiation of biologic agents versus methotrexate in the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 18:210
Salliot C, Dougados M, Gossec L (2009) Risk of serious infections during rituximab, abatacept and anakinra treatments for rheumatoid arthritis: meta-analyses of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis 68:25–32
Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C et al (2017) Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med 377:1119–1131
Rose-John S, Winthrop K, Calabrese L (2017) The role of IL-6 in host defence against infections: immunobiology and clinical implications. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13:399–409
Kang S, Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T (2019) Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity 50:1007–1023
Schaper F, Rose-John S (2015) Interleukin-6: biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26:475–487
Stone JH, Tuckwell K, Dimonaco S, Klearman M, Aringer M, Blockmans D et al (2017) Trial of Tocilizumab in Giant-Cell Arteritis. N Engl J Med 377:317–328
van Rhee F, Wong RS, Munshi N, Rossi JF, Ke XY, Fossa A et al (2014) Siltuximab for multicentric Castleman’s disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 15:966–974
Garbers C, Heink S, Korn T, Rose-John S (2018) Interleukin-6: designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17:395–412
Schiff MH, Kremer JM, Jahreis A, Vernon E, Isaacs JD, van Vollenhoven RF (2011) Integrated safety in tocilizumab clinical trials. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R141
Morel J, Constantin A, Baron G, Dernis E, Flipo RM, Rist S et al (2017) Risk factors of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab in the French Registry REGATE. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56:1746–1754
Pawar A, Desai RJ, Solomon DH, Santiago Ortiz AJ, Gale S, Bao M et al (2019) Risk of serious infections in tocilizumab versus other biologic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multidatabase cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 78:456–464
Rutherford AI, Patarata E, Subesinghe S, Hyrich KL, Galloway JB (2018) Opportunistic infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to biologic therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 57:997–1001
Koike T, Harigai M, Inokuma S, Ishiguro N, Ryu J, Takeuchi T et al (2014) Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab: postmarketing surveillance of 7901 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. J Rheumatol 41:15–23
Socié G, Caby-Tosi MP, Marantz JL, Cole A, Bedrosian CL, Gasteyger C et al (2019) Eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome: 10-year pharmacovigilance analysis. Br J Haematol 185:297–310
McNamara LA, Topaz N, Wang X, Hariri S, Fox L, MacNeil JR (2017) High risk for invasive meningococcal disease among patients receiving eculizumab (Soliris) despite receipt of meningococcal vaccine. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 66:734–737
Crew PE, Abara WE, McCulley L, Waldron PE, Kirkcaldy RD, Weston EJ et al (2019) Disseminated gonococcal infections in patients receiving eculizumab: a case series. Clin Infect Dis 69:596–600
Matucci A, Maggi E, Vultaggio A (2014) Cellular and humoral immune responses during tuberculosis infection: useful knowledge in the era of biological agents. J Rheumatol Suppl 91:17–23
Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC et al (2016) 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:1–26
Cao BL, Qasem A, Sharp RC, Abdelli LS, Naser SA (2018) Systematic review and meta-analysis on the association of tuberculosis in Crohn’s disease patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors (Anti-TNFalpha). World J Gastroenterol 24:2764–2775
Zhang Z, Fan W, Yang G, Xu Z, Wang J, Cheng Q et al (2017) Risk of tuberculosis in patients treated with TNF-alpha antagonists: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 7:e012567
Sands BE, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, O’Brien CD, Zhang H, Johanns J et al (2019) Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 381:1201–1214
Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, Gasink C, Jacobstein D, Lang Y, Friedman JR et al (2016) Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med 375:1946–1960
Gottlieb A, Menter A, Mendelsohn A, Shen Y-K, Li S, Guzzo C et al (2009) Ustekinumab, a human interleukin 12/23 monoclonal antibody, for psoriatic arthritis: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. 373:8
Vignali DA, Kuchroo VK (2012) IL-12 family cytokines: immunological playmakers. Nat Immunol 13:722–728
Papp KA, Griffiths CE, Gordon K, Lebwohl M, Szapary PO, Wasfi Y et al (2013) Long-term safety of ustekinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: final results from 5 years of follow-up. Br J Dermatol 168:844–854
Major EO (2010) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients on immunomodulatory therapies. Annu Rev Med 61:35–47
Misbah SA (2017) Progressive multi-focal leucoencephalopathy-driven from rarity to clinical mainstream by iatrogenic immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol 188:342–352
Card T, Xu J, Liang H, Bhayat F (2018) What is the risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn′s disease Treated With Vedolizumab? Inflamm Bowel Dis 24:953–959
Berger JR, Fox RJ (2016) Reassessing the risk of natalizumab-associated PML. J Neurovirol 22:533–535
Teng MW, Bowman EP, McElwee JJ, Smyth MJ, Casanova JL, Cooper AM et al (2015) IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines: from discovery to targeted therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Nat Med 21:719–729
Srinivas C, Odsbu I, Linder M (2020) Risk of common infections among individuals with psoriasis in Sweden: a nationwide cohort study comparing secukinumab to ustekinumab. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 29:1562–1569
Li X, Bechara R, Zhao J, McGeachy MJ, Gaffen SL (2019) IL-17 receptor-based signaling and implications for disease. Nat Immunol 20:1594–1602
Zwicky P, Unger S, Becher B (2020) Targeting interleukin-17 in chronic inflammatory disease: a clinical perspective. J Exp Med 217
Meroni PL, Zavaglia D, Girmenia C (2018) Vaccinations in adults with rheumatoid arthritis in an era of new disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36:317–328
Furer V, Rondaan C, Heijstek MW, Agmon-Levin N, van Assen S, Bijl M et al (2020) 2019 update of EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 79:39–52
Bingham CO 3rd, Looney RJ, Deodhar A, Halsey N, Greenwald M, Codding C et al (2010) Immunization responses in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with rituximab: results from a controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum 62:64–74
Alvarez-Cuesta E, Madrigal-Burgaleta R, Angel-Pereira D, Urena-Tavera A, Zamora-Verduga M, Lopez-Gonzalez P et al (2015) Delving into cornerstones of hypersensitivity to antineoplastic and biological agents: value of diagnostic tools prior to desensitization. Allergy 70:784–794
Lieberman P, Rahmaoui A, Wong DA (2010) The safety and interpretability of skin tests with omalizumab. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 105:493–495
Funding
SAS is supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, through Grant T32AI007062.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JLW, SAS, and MK performed literature search and wrote the article. JLW and SAS contributed equally to the article as co-first authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldron, J.L., Schworer, S.A. & Kwan, M. Hypersensitivity and Immune-related Adverse Events in Biologic Therapy. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 62, 413–431 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-021-08879-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-021-08879-w