Abstract
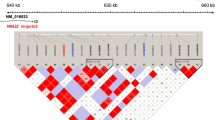
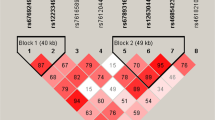
Linkage/linkage-disequilibrium analysis studies, based on positional information and gene function, indicated that ALOX5AP gene was an independent risk factor of cerebral infarction in humans; however, this needs to be verified among different populations. Herein, we verified whether ALOX5AP was a risk factor of cerebral infarction in the Chinese Han population. For this purpose, 547 cerebral infarction patients were enrolled as the case group; the control group comprised 794 healthy, age-matched individuals unrelated to case group and had no history of cerebral infarction/transient ischemic attack. Regarding single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) selection and ALOX5AP genotyping, we selected four SNP loci (SG13S25, SG13S114, SG13S89, and SG13S32) and determined allelic frequencies. Genotyping of SG13S114 and SG13S32 adopted a method of combining real-time quantitative PCR and allele-specific PCR. A linkage-disequilibrium analysis of ALOX5AP was also performed. We found that the allelic frequencies of SG13S25 and SG13S89 were below 5 % and those of SG13S114 and SG13S32 were above 5 %. We did not find any differences between the case and control groups regarding allele, allele types, and haplotype gene frequencies of two SNP loci. The results indicate that the two genetic polymorphisms of ALOX5AP, SG13S114 and SG13S32, are not associated with cerebral infarction in Chinese Han population.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helgadottir, A., Manolescu, A., Thorleifsson, G., et al. (2004). The gene encoding 5-lipoxygenase activating protein confers risk of myocardial infarction and stroke. Nature Genetics, 36, 233–239.
De Caterina, R., & Zampolli, A. (2004). From asthma to atherosclerosis—5-lipoxygenase, leukotrienes, and inflammation. The New England Journal of Medicine, 350, 4–7.
Samuelsson, B., Dahlen, S. E., Lindgren, J. A., Rouzer, C. A., & Serhan, C. N. (1987). Leukotrienes and lipoxins: Structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science, 237, 1171–1176.
Dixon, R. A., Diehl, R. E., Opas, E., et al. (1990). Requirement of a 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein for leukotriene synthesis. Nature, 343, 282–284.
Samuelsson, B. (1983). Leukotrienes: Mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science, 220, 568–575.
Mehrabian, M., Allayee, H., Wong, J., et al. (2002). Identification of 5-lipoxygenase as a major gene contributing to atherosclerosis susceptibility in mice. Circulation Research, 91, 120–126.
Spanbroek, R., Grabner, R., Lotzer, K., et al. (2003). Expanding expression of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway within the arterial wall during human atherogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 1238–1243.
Dwyer, J. H., Allayee, H., Dwyer, K. M., et al. (2004). Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase promoter genotype, dietary arachidonic acid, and atherosclerosis. The New England Journal of Medicine, 350, 29–37.
Aiello, R. J., Bourassa, P. A., Lindsey, S., Weng, W., Freeman, A., & Showell, H. J. (2002). Leukotriene B4 receptor antagonism reduces monocytic foam cells in mice. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 22, 443–449.
Ghazalpour, A., Wang, X., Lusis, A. J., & Mehrabian, M. (2006). Complex inheritance of the 5-lipoxygenase locus influencing atherosclerosis in mice. Genetics, 173, 943–951.
Helgadottir, A., Gretarsdottir, S., St Clair, D., et al. (2005). Association between the gene encoding 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein and stroke replicated in a Scottish population. American Journal of Human Genetics, 76, 505–509.
Meschia, J. F., Brott, T. G., Brown, R. D., Jr, et al. (2005). Phosphodiesterase 4D and 5-lipoxygenase activating protein in ischemic stroke. Annals of Neurology, 58, 351–361.
Lohmussaar, E., Gschwendtner, A., Mueller, J. C., et al. (2005). ALOX5AP gene and the PDE4D gene in a central European population of stroke patients. Stroke, 36, 731–736.
Zee, R. Y. L., Cheng, S., Hegener, H. H., Erlich, H. A., & Ridker, P. M. (2006). Genetic variants of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein, and risk of incident myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke: A nested case–control approach. Stroke, 37, 2007–2011.
Shi, Y. Y., & He, L. (2005). SHEsis, a powerful software platform for analyses of linkage disequilibrium, haplotype construction, and genetic association at polymorphism loci. Cell Research, 15, 97–98.
Sun, H., Wu, H., Zhang, J., et al. (2011). A tagging SNP in ALOX5AP and risk of stroke: A haplotype-based analysis among eastern Chinese Han population. Molecular Biology Reports, 38, 4731–4738.
Acknowledgments
We thank Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau Scientific Research Foundation for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chen Xu and Cao Limei contributed to this work as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Qiang, L., Limei, C. et al. Correlation Between Cerebral Infarction and ALOX5AP Gene Expression. Cell Biochem Biophys 67, 899–904 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9579-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9579-7