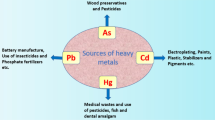
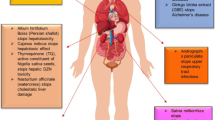
Abstract
Taurine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid derived from cysteine. It is involved in several phenomena such as the regulation of growth and differentiation, osmoregulation, neurohormonal modulation, and lipid metabolism. Taurine is important because of its high levels in several tissues such as the central nervous system (CNS), heart, skeletal muscles, retinal membranes, and platelets. In this report, we present the functional properties of taurine indicating that it has potential effects on various metal toxicities. Therefore, a comprehensive literature review was performed using the Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science databases. According to the search keywords, 61 articles were included in the study. The results indicate that taurine protects tissues against metal toxicity through enhancement of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity, modulation of oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects, involvement in different molecular pathways, and interference with the activity of various enzymes. Taken together, taurine is a natural supplement that presents antitoxic effects against many types of compounds, especially metals, suggesting public consumption of this amino acid as a prophylactic agent against the incidence of metal toxicity.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- Al:
-
Aluminum
- ALAD:
-
δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- ALD:
-
Alendronate
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- As:
-
Arsenic
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ATF-6:
-
Activating transcription factor-6
- AZA:
-
Azathioprine
- BALF:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- Bax:
-
bcl-2-like protein 4
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- BUN:
-
Blood urine nitrogen
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- CK:
-
creatine kinase
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- Cr:
-
Chromium
- Cr:
-
Creatinine
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- DBAN:
-
Dibromoacetonitrile
- DP:
-
Depotentiation
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- EPSP:
-
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
- ERK:
-
Extracellular regulated protein kinases
- FBP:
-
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
- FSH:
-
Follicle stimulating
- G6-PD:
-
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GABA:
-
gamma-Aminobutyric acid
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSH-Px:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSSG:
-
Glutathione disulfide
- GST:
-
Glutathione-S-transferase
- H2O2:
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- HBCD:
-
Hexabromocyclododecane
- Hcy:
-
Homocysteine
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1
- IL-1β:
-
Interlukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin
- INH:
-
Isoniazid
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IRE1α:
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha
- ISO:
-
Isoproterenol
- JNKs:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinases
- KBrO3:
-
Potassium bromate
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- LH:
-
Luteinizing
- LHP:
-
Lipid hydroperoxides
- LOX-1:
-
Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor 1
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- MDH:
-
Malate dehydrogenase
- MCH:
-
Mean cell hemoglobin
- MCHC:
-
Mean cell hemoglobin concentration
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- ME:
-
Malic enzyme
- METH:
-
Methamphetamine
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NAGase:
-
N-acetyl-b-D-glucosaminidase
- NF-кβ:
-
Nuclear factor kappa‐β
- NLRP3:
-
Pyrin domain-containing 3
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NQO:
-
NADPH-quinone oxidoreductase
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PERK:
-
Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase
- PLT:
-
Platelet
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen system
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TOCP:
-
Triorthocresyl phosphate
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- WBC:
-
White blood cells
- ZPP:
-
Zinc protoporphyrin
References
Inam UL et al (2018) Ameliorative effects of taurine against diabetes: a review. Amino Acids 50(5):487–502
Ripps H, Shen W (2012) Review: taurine: a “very essential” amino acid. Mol Vis 18:2673–86
Han X et al (2006) The taurine transporter: mechanisms of regulation. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 187(1–2):61–73
Zulli A (2011) Taurine in cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 14(1):57–60
Yamori Y et al (2010) Taurine in health and diseases: consistent evidence from experimental and epidemiological studies. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S6
L’Amoreaux WJ et al (2010) Taurine regulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cell lines. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S11
Schmidt SY, Berson EL, Hayes KC (1976) Retinal degeneration in cats fed casein I. Taurine deficiency. Invest Ophthalmol 15(1):47–52
Gupta RC (2006) Taurine analogues and taurine transport: therapeutic advantages. Adv Exp Med Biol 583:449–67
Kulthinee S et al (2017) Taurine supplementation ameliorates the adverse effects of perinatal taurine depletion and high sugar intake on cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury of adult female rats. Adv Exp Med Biol 975(Pt 2):741–755
Miyazaki T, Matsuzaki Y (2014) Taurine and liver diseases: a focus on the heterogeneous protective properties of taurine. Amino Acids 46(1):101–10
Sirdah MM (2015) Protective and therapeutic effectiveness of taurine in diabetes mellitus: a rationale for antioxidant supplementation. Diabetes Metab Syndr 9(1):55–64
Lerdweeraphon W et al (2013) Perinatal taurine exposure affects adult oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305(2):R95-7
Ghosh J et al (2009) Taurine prevents arsenic-induced cardiac oxidative stress and apoptotic damage: role of NF-kappa B, p38 and JNK MAPK pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240(1):73–87
Kim C, Cha Y-N (2014) Taurine chloramine produced from taurine under inflammation provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Amino Acids 46(1):89–100
Ommati MM et al (2022) Taurine mitigates the development of pulmonary inflammation, oxidative stress, and histopathological alterations in a rat model of bile duct ligation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology 395(12):1557–1572
Khlifi R, Hamza-Chaffai A (2010) Head and neck cancer due to heavy metal exposure via tobacco smoking and professional exposure: a review. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 248(2):71–88
Gilbert SG (2004) A small dose of toxicology: The health effects of common chemicals. 1st Edition edn. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203461730
Seiler H, Sigel A, Sigel H (1994) Handbook on metals in clinical and analytical chemistry. 1st Edition edn. CRC Press
Egorova KS, Ananikov VP (2017) Toxicity of metal compounds: knowledge and myths. Organometallics 36(21):4071–4090
El-Sayed WM, Al-Kahtani MA, Abdel-Moneim AM (2011) Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of taurine against aluminum-induced acute hepatotoxicity in mice. J Hazard Mater 192(2):880–886
Feng T et al (2016) Combination of DFP and taurine counteracts the aluminum-induced alterations in oxidative stress and ATPase in cortex and blood of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 174(1):142–149
Qiao M et al (2015) Potential protection of taurine on antioxidant system and ATPase in brain and blood of rats exposed to aluminum. Biotechnol Lett 37(8):1579–84
Wenting L et al (2014) Therapeutic effect of taurine against aluminum-induced impairment on learning, memory and brain neurotransmitters in rats. Neurol Sci 35(10):1579–84
Abdulkadir TS et al (2021) Taurine and camel milk modulate neurobehavioral and biochemical changes in aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease in rats. J Alzheimer’s Dis 84(1):291–302
Al Kahtani MA, Abdel-Moneim AM, El-Sayed WM (2014) The influence of taurine pretreatment on aluminum chloride induced nephrotoxicity in Swiss albino mice
Khalaf HA et al (2022) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial injury are critical molecular drivers of AlCl3-induced testicular and epididymal distortion and dysfunction: protective role of taurine. Histochem Cell Biol 158(1):97–121
Zheng Y et al (2017) Protection of taurine against arsenic-induced DNA damage of mice kidneys. Adv Exp Med Biol 975(Pt 2):917–927
Zhang C et al (2017) Taurine normalizes the levels of Se, Cu, Fe in mouse liver and kidney exposed to arsenic subchronically. In: Taurine 10. Springer
Roy A, Manna P, Sil PC (2009) Prophylactic role of taurine on arsenic mediated oxidative renal dysfunction via MAPKs/NF-κ B and mitochondria dependent pathways. Free radic res 43(10):995–1007
Guan H et al (2017) Protection of taurine against impairment in learning and memory in mice exposed to arsenic. Adv Exp Med Biol 975(Pt 1):255–269
Li S et al (2017) Taurine ameliorates arsenic-induced apoptosis in the hippocampus of mice through intrinsic pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol 975(Pt 1):183–192
Das J et al (2009) Arsenic-induced oxidative cerebral disorders: protection by taurine. Drug Chem Toxicol 32(2):93–102
Das J et al (2010) Protective role of taurine against arsenic-induced mitochondria-dependent hepatic apoptosis via the inhibition of PKCdelta-JNK pathway. PLoS One 5(9):e12602
Flora SJ et al (2008) Combined administration of taurine and monoisoamyl DMSA protects arsenic induced oxidative injury in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 1(1):39–45
Li S et al (2017) Taurine protects mouse liver against arsenic-induced apoptosis through JNK pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol 975 Pt 2:855–862. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_67
Pei P et al (2019) Inorganic arsenic induces pyroptosis and pancreatic β cells dysfunction through stimulating the IRE1α/TNF-α pathway and protective effect of taurine. Food Chem Toxicol 125:392–402
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2007) Taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 21(8):1419–28
Wang Z et al (2019) Taurine protected As2O3-induced the activation of hepatic stellate cells through inhibiting PPARα-autophagy pathway. Chem Biol Interact 300:123–130
Gao N et al (2019) Taurine improves low-level inorganic arsenic-induced insulin resistance by activating PPARγ-mTORC2 signalling and inhibiting hepatic autophagy. J Cell Physiol 234(4):5143–5152
Bai J et al (2016) Taurine protects against As2O3-induced autophagy in livers of rat offsprings through PPARγ pathway. Sci Rep 6(1):27733
Bai J et al (2016) Taurine protects against As2O3-induced autophagy in pancreas of rat offsprings through Nrf2/Trx pathway. Biochim 123:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2016.01.002
Qiu T et al (2018) Taurine attenuates arsenic-induced pyroptosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting the autophagic-inflammasomal pathway. Cell Death Dis 9(10):946
Ghosh J et al (2009) Taurine prevents arsenic-induced cardiac oxidative stress and apoptotic damage: Role of NF-κB, p38 and JNK MAPK pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240(1):73–87
Kumar P et al (2009) Ascorbic acid, garlic extract and taurine alleviate cadmium-induced oxidative stress in freshwater catfish (Clarias batrachus). Sci Total Environ 407(18):5024–30
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009) Taurine plays a beneficial role against cadmium-induced oxidative renal dysfunction. Amino Acids 36:417–428
Hwang D-F, Wang L (2001) Effect of taurine on toxicity of cadmium in rats. Toxicol 167(3):173–180
Zheng J et al (2023) Hepatoprotective effects of taurine against cadmium-induced liver injury in female mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 201(3):1368–1376
Hano T et al (2017) Effect of taurine supplementation on hepatic metabolism and alleviation of cadmium toxicity and bioaccumulation in a marine teleost, red sea bream Pagrus major. Fish Physiol Biochem 43(1):137–152
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2008) Amelioration of cadmium-induced cardiac impairment by taurine. Chem Biol Interact 174(2):88–97
Choi K-S et al (2013) Effects of taurine on cadmium exposure in muscle, gill, and bone tissues of Carassius auratus. Nutr Res Pract 7(1):22–25
Abalaka SE et al (2021) Effects of Moringa oleifera leaves extract, vitamin C, and taurine co-exposures on calcium and metallothionein levels, oxidative stress, and gill histopathological changes in Clarias gariepinus exposed to sub-lethal cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(37):52258–52271
Chen N et al (2022) Cadmium induces placental glucocorticoid barrier damage by suppressing the cAMP/PKA/Sp1 pathway and the protective role of taurine. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 440:115938
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2008) Cadmium induced testicular pathophysiology: prophylactic role of taurine. Reprod Toxicol 26(3–4):282–291
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2008) Cadmium-induced neurological disorders: prophylactic role of taurine. J Appl Toxicol 28(8):974–986
Hwang D-F, Wang L, Cheng H (1998) Effect of taurine on toxicity of copper in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 36(3):239–244
Husain N, Mahmood R (2020) Taurine attenuates Cr(VI)-induced cellular and DNA damage: an in vitro study using human erythrocytes and lymphocytes. Amino Acids 52(1):35–53
Boşgelmez II, Söylemezoğlu T, Güvendik G (2008) The protective and antidotal effects of taurine on hexavalent chromium-induced oxidative stress in mice liver tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 125(1):46-58
Boşgelmez İİ, Güvendik G (2019) Beneficial effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine or taurine pre-or post-treatments in the heart, spleen, lung, and testis of hexavalent chromium-exposed mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 190(2):437–445
Boşgelmez II, Güvendik G (2004) Effects of taurine on oxidative stress parameters and chromium levels altered by acute hexavalent chromium exposure in mice kidney tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 102:209–225
Lakshmi Devi S, Anuradha CV (2010) Mitochondrial damage, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in iron-potentiated alcoholic liver fibrosis: amelioration by taurine. Amino Acids 38(3):869-79
Zhang Z et al (2014) Taurine supplementation reduces oxidative stress and protects the liver in an iron-overload murine model. Mol Med Rep 10(5):2255–62
Oudit GY et al (2004) Taurine supplementation reduces oxidative stress and improves cardiovascular function in an iron-overload murine model. Circulation 109(15):1877–1885
Devi SL, Viswanathan P, Anuradha CV (2009) Taurine enhances the metabolism and detoxification of ethanol and prevents hepatic fibrosis in rats treated with iron and alcohol. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 27(1):120–126
Feng X et al (2022) Taurine ameliorates iron overload-induced hepatocyte injury via the Bcl-2/VDAC1-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022
Dawson R et al (2000) Taurine inhibition of metal-stimulated catecholamine oxidation. Neurotox Res 2:1–15
Gürer H et al (2001) Antioxidant effect of taurine against lead-induced oxidative stress. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41(4):397–402
Flora SJ et al (2004) Combined administration of taurine and meso 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid in the treatment of chronic lead intoxication in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 23(4):157–66
Zhu DM et al (2005) Protection by a taurine supplemented diet from lead-induced deficits of long-term potentiation/depotentiation in dentate gyrus of rats in vivo. Neuroscience 134(1):215–24
Neuwirth LS et al (2022) Taurine-derived compounds produce anxiolytic effects in rats following developmental lead exposure. Taurine 12: a conditionally essential amino acid. Springer, pp 445–460
Akande M et al (2014) Taurine mitigates cognitive impairment induced by chronic co-exposure of male Wistar rats to chlorpyrifos and lead acetate. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37(1):315–325
Aglan HS et al (2021) Developmental toxicity of lead in rats after gestational exposure and the protective role of taurine. 35(8):e22816
Ommati MM et al (2023) Taurine improves sperm mitochondrial indices, blunts oxidative stress parameters, and enhances steroidogenesis and kinematics of sperm in lead-exposed mice. Reprod Sci 30(6):1891–1910
Lu C-L et al (2014) Taurine improves the spatial learning and memory ability impaired by sub-chronic manganese exposure. J Biomed Sci 21(1):1–8
Xu Z et al (2010) Effects of MK-801, taurine and dextromethorphan on neurotoxicity caused by manganese in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 26(1):55–60
Ahmadi N et al (2018) Taurine prevents mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and swelling upon interaction with manganese: implication in the treatment of cirrhosis-associated central nervous system complications. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32(11):e22216
Ommati MM et al (2019) Taurine treatment provides neuroprotection in a mouse model of manganism. Biol Trace Elem Res 190(2):384–395
Agha FE et al (2014) Nephroprotective potential of selenium and taurine against mercuric chloride induced nephropathy in rats. Ren Fail 36(5):704–16
Jagadeesan G, Pillai SS (2007) Hepatoprotective effects of taurine against mercury induced toxicity in rat. J Environ Biol 28(4):753
Xu S et al (2015) The neuroprotective effects of taurine against nickel by reducing oxidative stress and maintaining mitochondrial function in cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 590:52–7
Yeh YH et al (2011) Dietary taurine reduces zinc-induced toxicity in male Wistar rats. J Food Sci 76(4):T90–T98
Abdoli N et al (2021) Taurine mitigates bile duct obstruction-associated cholemic nephropathy: effect on oxidative stress and mitochondrial parameters. Clin Exp Hepatol 7(1):30–40
Mousavi K et al (2020) Taurine mitigates cirrhosis-associated heart injury through mitochondrial-dependent and antioxidative mechanisms. Clin Exp Hepatol 6(3):207–219
Niknahad H et al (2023) Cirrhosis-induced oxidative stress in erythrocytes: the therapeutic potential of taurine. Clin Exp Hepatol 9(1):79–93
Ommati MM et al (2023) Taurine improves sperm mitochondrial indices, blunts oxidative stress parameters, and enhances steroidogenesis and kinematics of sperm in lead-exposed mice. Reprod Sci 30(6):1891–1910
Ommati MM et al (2019) Taurine enhances skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in a rat model of resistance training. PharmaNutrition 9:100161
Klotz K et al (2017) The health effects of aluminum exposure. Dtsch Arztebl Int 114(39):653–659
Barabasz W et al (2002) Ecotoxicology of aluminium. Pol J Environ Stud 11(3):199–204
Olaniran AO, Balgobind A, Pillay B (2013) Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil: impact on microbial biodegradation of organic compounds and possible improvement strategies. Int J Mol Sci 14(5):10197–10228
Vardar F, Ünal M (2007) Aluminum toxicity and resistance in higher plants
Shayan M et al (2023) The protective effect of natural or chemical compounds against arsenic-induced neurotoxicity: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Food Chem Toxicol 175:113691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2023.113691
Costa M (2019) Review of arsenic toxicity, speciation and polyadenylation of canonical histones. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 375:1–4
Susan A et al (2019) An overview of plant-based interventions to ameliorate arsenic toxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 109:838–852
Yarmohammadi F et al (2023) Melatonin ameliorates arsenic-induced cardiotoxicity through the regulation of the Sirt1/Nrf2 pathway in rats. Biofactors 49(3):620–635
Yang L et al (2019) Taurine protects against arsenic trioxide-induced insulin resistance via ROS-Autophagy pathway in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 112:50–60
Yang H, Shu Y (2015) Cadmium transporters in the kidney and cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 16(1):1484–94
Rani A et al (2014) Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: a review. International journal of environmental health research 24(4):378–399
Patrick L (2003) Toxic metals and antioxidants: Part II. The role of antioxidants in arsenic and cadmium toxicity. Altern Med Rev 8(2)
Ahmadian R et al (2023) Alpha-mangostin protects PC12 cells against neurotoxicity induced by cadmium and arsenic. Biol Trace Elem Res 201(8):4008–4021
Joseph P (2009) Mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):272–279
Rahimzadeh MR et al (2017) Cadmium toxicity and treatment: an update. Caspian J Intern Med 8(3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.3.135
Balarastaghi S et al (2022) Melatonin improves arsenic-induced hypertension through the inactivation of the Sirt1/autophagy pathway in rat. Biomed Pharmacother 151:113135
Keshavarzi M et al (2019) Hormesis effects of nano-and micro-sized copper oxide. Iran J Pharm Res: IJPR 18(4):2042
Gaetke LM, Chow-Johnson HS, Chow CK (2014) Copper: toxicological relevance and mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 88:1929–1938
Hasan NM, Lutsenko S (2012) Regulation of copper transporters in human cells. Curr Top Membr 69:137–161
Tian X et al (2009) Copper–taurine (CT): a potential organic compound to facilitate infected wound healing. Med Hypotheses 73(6):1048–1050
Costello RB, Dwyer JT, Bailey RL (2016) Chromium supplements for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: limited evidence of effectiveness. Nutr Rev 74(7):455–68
Dayan A, Paine A (2001) Mechanisms of chromium toxicity, carcinogenicity and allergenicity: review of the literature from 1985 to 2000. Hum Exp Toxicol 20(9):439–451
DesMarias TL, Costa M (2019) Mechanisms of chromium-induced toxicity. Curr Opin Toxicol 14:1–7
Hershko C (2007) Mechanism of iron toxicity. Food Nutr Bull 28(4_suppl4): S500-S509
Rouault TA (2016) Mitochondrial iron overload: causes and consequences. Curr Opin Genet Dev 38:31–37
Pasantes-Morales H, Wright C, Gaull G (1985) Taurine protection of lymphoblastoid cells from iron-ascorbate induced damage. Biochem Pharmacol 34(12):2205–2207
Mitra P et al (2017) Clinical and molecular aspects of lead toxicity: an update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 54(7–8):506–528
Nemsadze K et al (2009) Mechanisms of lead-induced poisoning. Georgian Med News 172–173:92–96
Dzugkoev S, Dzugkoeva F, Margieva O (2022) Mechanisms of lead toxicity and their pathogenetic correction. J Evol Biochem Phys 58(3):807–814
Neuwirth LS et al (2019) Early neurodevelopmental exposure to low lead levels induces fronto-executive dysfunctions that are recovered by taurine co-treatment in the rat attention set-shift test: implications for taurine as a psychopharmacotherapy against neurotoxicants. Taurine 11. Springer, pp 821–846
Cruz GB et al (2022) Developmental lead exposure in rats causes sex-dependent changes in neurobiological and anxiety-like behaviors that are improved by taurine co-treatment. Taurine 12: a conditionally essential amino acid. Springer, pp 461–479
Caudle WM (2015) Occupational exposures and parkinsonism. Handb Clin Neurol 131:225–239
Cappelletti S et al (2019) Mercuric chloride poisoning: symptoms, analysis, therapies, and autoptic findings. A review of the literature. Crit Rev Toxicol 49(4):329-341
Yang L et al (2020) Toxicity of mercury: molecular evidence. Chemosphere 245:125586
Das KK et al (2018) Primary concept of nickel toxicity - an overview. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 30(2):141–152
Macomber L, Hausinger RP (2011) Mechanisms of nickel toxicity in microorganisms. Metallomics 3(11):1153–1162
Agnew UM, Slesinger TL (2020) Zinc toxicity
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH contributed to the study conception, design, and supervision of the research. Data collection and analysis were performed by KN and MK. A critical revision of the paper was conducted by BMR. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KN and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naraki, K., Keshavarzi, M., Razavi, B.M. et al. The Protective Effects of Taurine, a Non-essential Amino Acid, Against Metals Toxicities: A Review Article. Biol Trace Elem Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04191-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04191-8