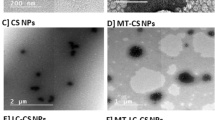
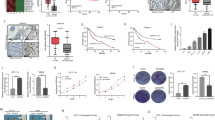
Abstract
Cancer, the leading cause of death worldwide, has witnessed significant advancements in treatment through targeted therapies. Among the proto-oncogenes prevalent in human cancers, KRAS stands out, and recent research has focused on long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) as regulators of miRNAs targeting the KRAS oncogene. This study specifically explores lncRNAs involved in the KRAS pathway in colorectal cancer (CRC). To investigate this, researchers employed iron oxide nanoparticles coated with glucose and conjugated with Oleuropein (Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein NPs) to evaluate their impact on candidate lncRNAs associated with KRAS pathway deregulation. The study utilized TCGA data to identify genes affected by KRAS mutation and lncRNAs linked to KRAS in CRC. Enrichr and MsigDB databases helped identify relevant pathways. Genes with a correlation coefficient above 0.5 and a P-value less than 0.01 with candidate lncRNAs were selected. MTT and flow cytometry assays determined the anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein NPs on CRC cells (SW480) and normal cells (HEK293). The findings showed that increased expression of FEZF1-AS1, GAS6-AS1, and LINC00920 correlated with mutated KRAS, and co-expressed genes were significantly involved in hypoxia, KRAS signaling, DNA repair, and IL-2/STAT5 signaling pathways. Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein NPs exhibited higher toxicity toward cancer cells, with IC50 values of 92 μg/ml for SW480 and 281 μg/ml for HEK293. Flow cytometry analysis revealed a substantial increase in necrotic and apoptotic cells when treated with Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein, along with down-regulation of GAS6-AS1, LINC00920, and FEZF1-AS1 lncRNAs in treated cells. In conclusion, this study highlights the therapeutic potential of Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein on colon cancer cells in vitro. The identification of lncRNAs involved in the KRAS pathway provides insights into the underlying mechanisms and offers avenues for further research in targeted cancer therapies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Mishra J, Drummond J, Quazi SH, Karanki SS, Shaw JJ, Chen B, Kumar N (2013) Prospective of colon cancer treatments and scope for combinatorial approach to enhanced cancer cell apoptosis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 86(3):232–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2012.09.014
Gavas S, Quazi S, Karpiński TM (2021) Nanoparticles for cancer therapy: current progress and challenges. Nanoscale Res Lett 16(1):173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-021-03628-6
Soetaert F, Korangath P, Serantes D, Fiering S, Ivkov R (2020) Cancer therapy with iron oxide nanoparticles: agents of thermal and immune therapies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 163:65–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.025
Shamshoum H, Vlavcheski F, Tsiani E (2017) Anticancer effects of oleuropein. Biofactors 43(4):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1366
Sepporta MV, Fuccelli R, Rosignoli P, Ricci G, Servili M, Fabiani R (2016) Oleuropein prevents azoxymethane-induced colon crypt dysplasia and leukocytes DNA damage in a/J mice. J Med Food 19(10):983–989. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2016.0026
Giner E, Recio MC, Ríos JL, Cerdá-Nicolás JM, Giner RM (2016) Chemopreventive effect of oleuropein in colitis-associated colorectal cancer in c57bl/6 mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 60(2):242–255
Knickelbein K, Zhang L (2015) Mutant KRAS as a critical determinant of the therapeutic response of colorectal cancer. Genes & diseases 2(1):4–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2014.10.002
Pathak N, Chitikela S, Malik PS (2021) Recent advances in lung cancer genomics: application in targeted therapy. Advances in Genetics, 108, 201-275. Pathak, N., Chitikela, S. and Malik, P.S., 2021. Recent advances in lung cancer genomics: application in targeted therapy. Adv Genet 108:201–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.adgen.2021.08.004
Habibi A, Sadat Shandiz SA, Salehzadeh A, Moradi-Shoeili Z (2020) Novel pyridinecarboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone conjugated magnetite nanoparticulates (MNPs) promote apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells. JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry 25:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-019-01728-4
Fekri Kohan S, Zamani H, Salehzadeh A (2023) Antibacterial potential and cytotoxic activity of iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with thymol (Fe3O4@ Glu-Thymol) on breast cancer cells and investigating the expression of BAX, CASP8, and BCL-2 genes. BioMetals 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00516-7
Hosseinkhah M, Ghasemian R, Shokrollahi F, Mojdehi SR, Noveiri MJS, Hedayati M et al (2021) Cytotoxic potential of nickel oxide nanoparticles functionalized with glutamic acid and conjugated with thiosemicarbazide (NiO@ Glu/TSC) against human gastric cancer cells. J Clust Sci 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02124-2
Kumari R, Saini AK, Kumar A, Saini RV (2020) Apoptosis induction in lung and prostate cancer cells through silver nanoparticles synthesized from Pinus roxburghii bioactive fraction. JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry 25(1):23–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-019-01729-3
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Emami N, Farhadian M, Solaimany Nazar AR, Tangestaninejad S (2023) Adsorption of cefixime and lamotrigine on HKUST-1/ZIF-8 nanocomposite: isotherms, kinetics models and mechanism. Int J Environ Sci Technol 20(2):1645–1672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04679-7
Aliyari MA, Salami M, Hosseini E, Emam-Djomeh Z, Karboune S, Waglay A (2021) Biophysical, rheological, and functional properties of complex of sodium caseinate and olive leaf aqueous polyphenolic extract obtained using ultrasound-assisted extraction. Food Biophysics 16:325–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-021-09671-1
Lowry GV, Hill RJ, Harper S, Rawle AF, Hendren CO, Klaessig F et al (2016) Guidance to improve the scientific value of zeta-potential measurements in nanoEHS. Environmental Science: Nano 3(5):953–965. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EN00136J
Rami JM, Patel CD, Patel CM, Patel MV (2021) Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of some synthesized metal oxide nanoparticles. Materials Today: Proceedings 43:655–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.554
Akbarizadeh MR, Naderifar M, Mousazadeh F, Zafarnia N, Sarani M (2022) Cytotoxic activity and magnetic behavior of green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles on brain glioblastoma cells. Nanomedicine Research Journal 7(1):99–106. https://doi.org/10.22034/nmrj.2022.01.010
Ortiz-Ortiz KJ, Ríos-Motta R, Marín-Centeno H, Cruz-Correa M, Ortiz AP (2016) Factors associated with late stage at diagnosis among Puerto Rico’s government health plan colorectal cancer patients: a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res 16(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1590-4
Hauser AK, Mitov MI, Daley EF, McGarry RC, Anderson KW, Hilt JZ (2016) Targeted iron oxide nanoparticles for the enhancement of radiation therapy. Biomaterials 105:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.07.032
Apopa PL, Qian Y, Shao R, Guo NL, Schwegler-Berry D, Pacurari M et al (2009) Iron oxide nanoparticles induce human microvascular endothelial cell permeability through reactive oxygen species production and microtubule remodeling. Particle and fibre toxicology 6(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-6-1
Notarnicola M, Pisanti S, Tutino V, Bocale D, Rotelli MT, Gentile A et al (2011) Effects of olive oil polyphenols on fatty acid synthase gene expression and activity in human colorectal cancer cells. Genes Nutr 6(1):63–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-010-0177-7
Yan CM, Chai EQ, Cai HY, Miao GY, Ma W (2015) Oleuropein induces apoptosis via activation of caspases and suppression of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway in HepG2 human hepatoma cell line. Mol Med Rep 11(6):4617–4624. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3266
Acquaviva R, Di Giacomo C, Sorrenti V, Galvano F, Santangelo R, Cardile V et al (2012) Antiproliferative effect of oleuropein in prostate cell lines. Int J Oncol 41(1):31–38. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2012.1428
Yan L, Raj P, Yao W, Ying H (2019) Glucose metabolism in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 11(10):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101460
Alarifi S, Ali D, Alkahtani S, Alhader MS (2014) Iron oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress, DNA damage, and caspase activation in the human breast cancer cell line. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:416–424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101460
Paunovic J, Vucevic D, Radosavljevic T, Mandić-Rajčević S, Pantic I (2020) Iron-based nanoparticles and their potential toxicity: focus on oxidative stress and apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact 316:108935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108935
Kettler K, Veltman K, Van de Meent D, Van Wezel A, Hendriks AJ (2014) Cellular uptake of nanoparticles as determined by particle properties, experimental conditions, and cell type. Environ Toxicol Chem 33(3):481–492. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2470
Zhu G, Pei L, Xia H, Tang Q, Bi F (2021) Role of oncogenic KRAS in the prognosis, diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer 20(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01441-4
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shirvani-Farsani Z, Hussen BM, Taheri M, Jalili Khoshnoud R (2022) Emerging role of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of KRAS. Cancer Cell Int 22(1):68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02486-1
Chen N, Guo D, Xu Q, Yang M, Wang D, Peng M et al (2016) Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 facilitates cell proliferation and migration in colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget 7(10):11271. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7168
Zhang P, Dong Q, Zhu H, Li S, Shi L, Chen X (2019) Long non-coding antisense RNA GAS6-AS1 supports gastric cancer progression via increasing GAS6 expression. Gene 696:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.079
Chen Q, Zhou L, Ma D, Hou J, Lin Y, Wu J, Tao M (2022) LncRNA GAS6-AS1 facilitates tumorigenesis and metastasis of colorectal cancer by regulating TRIM14 through miR-370-3p/miR-1296-5p and FUS. J Transl Med 20(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03550-0
Wang Y, Lu JH, Wu QN, Jin Y, Wang DS, Chen YX et al (2019) LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer 18(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1105-0
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to Mr. Mohamad Mahdevar for his help in bioinformatics section.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S., M. Z. and M.P. :Conceptualization. A.S., M. Z. and M.P.:Methodology. A.S. and M.P. :Formal analysis and investigation. A.S., Z. M.N. and M.P.: Writing Original Draft Preparation. Z. M.N. :Resources. A.S., M. Z. and M.P.:Supervision
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahdavi Niyaki, Z., Salehzadeh, A., Peymani, M. et al. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein Nanoparticles in Targeting KRAS Pathway-Regulating lncRNAs in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 3073–3085 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03892-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03892-w