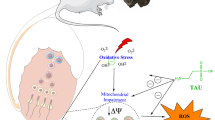
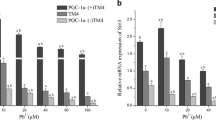
Abstract
Lead (Pb) is a widely distributed toxic heavy metal element known to have strong male reproductive toxicity, which can result in issues such as abnormal count and morphology of sperm. Zinc (Zn) is an essential trace element for the human body that can antagonize the activity of Pb in some physiological environments, and it also possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. However, the specific mechanism of Zn’s antagonism against Pb remains largely unclear. In our study, we conducted research using swine testis cells (ST cells) and confirmed that the half maximal inhibitory concentration of Pb on ST cells was 994.4 μM, and the optimal antagonistic concentration of Zn was 10 μM. Based on this information, we treated ST cells with Pb and Zn and detected related indices such as apoptosis, oxidative stress, and the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway using flow cytometry, DCFH-DA staining, RT-PCR, and Western blot. Our results demonstrated that Pb exposure can generate excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS), disrupt the antioxidant system, upregulate PTEN expression, and inhibit the PI3K/AKT pathway in ST cells. In contrast, Zn significantly inhibited the overproduction of ROS, improved oxidative stress, and decreased PTEN expression, thus protecting the PI3K/AKT pathway compared to Pb-exposed ST cells. Furthermore, we found that Pb exposure exacerbated the expression of genes related to the apoptosis pathway and reduced the expression of anti-apoptotic genes. Furthermore, this situation was significantly improved when co-cultured with Pb and Zn. In summary, our study demonstrated that Zn alleviated Pb-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through the ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis in ST cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data and materials are available on request from the authors.
References
Krzywy I, Krzywy E, Pastuszak-Gabinowska M, Brodkiewicz A (2010) Lead--is there something to be afraid of? Annales Academiae Medicae Stetinensis 56(2):118–128
Wani AL, Ara A, Usmani JA (2016) Lead toxicity: a review. Interdiscip Toxicol 8(2):55–64
Adnan M, Xiao B, Xiao P, Zhao P, Li R, Bibi S (2022) Research progress on heavy metals pollution in the soil of smelting sites in China. Toxics 10(5):231
Li Q, Zhu K, Liu L, Sun X (2021) Pollution-induced food safety problem in China: trends and policies. Front Nutr 8:703832
Kanchelashvili G, Gulbiani L, Dekanosidze A, Kvachantiradze L, Kamkamidze G, Sturua L (2022) Knowledge of Georgian population towards air pollution and health effects of lead contamination. Georgian Med News 322:58–62
Hai DN, Tung LV, Van DK, Binh TT, Phuong HL, Trung ND, Son ND, Giang HT, Hung NM, Khue PM (2018) Lead environmental pollution and childhood lead poisoning at Ban Thi Commune, Bac Kan Province, Vietnam. Biomed Res Int 2018:5156812
Vorvolakos T, Arseniou S, Samakouri M (2016) There is no safe threshold for lead exposure: α literature review. Psychiatriki 27(3):204–214
Childebayeva A, Goodrich JM, Chesterman N, Leon-Velarde F, Rivera-Ch M, Kiyamu M, Brutsaert TD, Bigham AW, Dolinoy DC (2021) Blood lead levels in Peruvian adults are associated with proximity to mining and DNA methylation. Environment International 155:106587
Taylor MP, Isley CF, Glover J (2019) Prevalence of childhood lead poisoning and respiratory disease associated with lead smelter emissions. Environ Int 127:340–352
Hernández-Flores S, Rico-Martínez R (2006) Study of the effects of Pb and Hg toxicity using a chronic toxicity reproductive 5-day test with the freshwater rotifer Lecane quadridentata. Environ Toxicol 21(5):533–540
Elsheikh NAH, Omer NA, Yi-Ru W, Mei-Qian K, Ilyas A, Abdurahim Y, Wang GL (2020) Protective effect of betaine against lead-induced testicular toxicity in male mice. Andrologia 52(7):e13600
Ezejiofor AN, Orisakwe OE (2019) The protective effect of Costus afer Ker Gawl aqueous leaf extract on lead-induced reproductive changes in male albino Wistar rats. JBRA Assist Reprod 23(3):215–224
He X, Wu J, Yuan L, Lin F, Yi J, Li J, Yuan H, Shi J, Yuan T, Zhang S et al (2017) Lead induces apoptosis in mouse TM3 Leydig cells through the Fas/FasL death receptor pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 56:99–105
Łuszczek-Trojnar E, Drąg-Kozak E, Szczerbik P, Socha M, Popek W (2014) Effect of long-term dietary lead exposure on some maturation and reproductive parameters of a female Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio B.). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(4):2465–2478
Zhao D, Zhang X (2018) Selenium antagonizes the lead-induced apoptosis of chicken splenic lymphocytes in vitro by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 182(1):119–129
Yin K, Cui Y, Sun T, Qi X, Zhang Y, Lin H (2020) Antagonistic effect of selenium on lead-induced neutrophil apoptosis in chickens via miR-16-5p targeting of PiK3R1 and IGF1R. Chemosphere 246:125794
Amin I, Hussain I, Rehman MU, Mir BA, Ganaie SA, Ahmad SB, Mir MUR, Shanaz S, Muzamil S, Arafah A et al (2021) Zingerone prevents lead-induced toxicity in liver and kidney tissues by regulating the oxidative damage in Wistar rats. J Food Biochem 45(3):e13241
Aoki M, Fujishita T (2017) Oncogenic Roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 407:153–189
Zhang M, Zhang X (2019) The role of PI3K/AKT/FOXO signaling in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 311(2):83–91
Gagliardi PA, Puliafito A, Primo L (2018) PDK1: At the crossroad of cancer signaling pathways. Semin Cancer Biol 48:27–35
Liu C, Chen K, Wang H, Zhang Y, Duan X, Xue Y, He H, Huang Y, Chen Z, Ren H et al (2020) Gastrin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by a PI3K/Akt/bad-mediated anti-apoptosis signaling. Front Pharmacol 11:540479
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30(2):193–204
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2006) Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/akt survival signal pathways are implicated in neuronal survival after stroke. Mol Neurobiol 34(3):249–270
Miao Z, Miao Z, Wang S, Shi X, Xu S (2021) Quercetin antagonizes imidacloprid-induced mitochondrial apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT in grass carp hepatocytes. Environ Pollut 290:118036
Wang W, Liu Q, Zhang T, Chen L, Li S, Xu S (2020) Glyphosate induces lymphocyte cell dysfunction and apoptosis via regulation of miR-203 targeting of PIK3R1 in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 101:51–57
Luo X, Lin B, Gao Y, Lei X, Wang X, Li Y, Li T (2019) Genipin attenuates mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT pathway in acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol 76:105842
Haddadi N, Lin Y, Travis G, Simpson AM, Nassif NT, McGowan EM (2018) PTEN/PTENP1: 'Regulating the regulator of RTK-dependent PI3K/Akt signalling’, new targets for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer 17(1):37
Gao X, Qin T, Mao J, Zhang J, Fan S, Lu Y, Sun Z, Zhang Q, Song B, Li L (2019) PTENP1/miR-20a/PTEN axis contributes to breast cancer progression by regulating PTEN via PI3K/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):256
Noorolyai S, Shajari N, Baghbani E, Sadreddini S, Baradaran B (2019) The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene 698:120–128
Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Link W, Leal JF (2008) The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8(3):187–198
Papa A, Pandolfi PP (2019) The PTEN-PI3K Axis in Cancer. Biomolecules 9(4):153
Zhou J, Li XY, Liu YJ, Feng J, Wu Y, Shen HM, Lu GD (2022) Full-coverage regulations of autophagy by ROS: from induction to maturation. Autophagy 18(6):1240–1255
Kma L, Baruah TJ (2022) The interplay of ROS and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 69(1):248–264
Gong M, Li Z, Zhang X, Liu B, Luo J, Qin X, Wei Y (2021) PTEN mediates serum deprivation-induced cytotoxicity in H9c2 cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Toxicol In Vitro 73:105131
Fang Y, Yan C, Zhao Q, Xu J, Liu Z, Gao J, Zhu H, Dai Z, Wang D, Tang D (2021) The roles of microbial products in the development of colorectal cancer: a review. Bioengineered 12(1):720–735
Zhang C, Lin T, Nie G, Hu R, Pi S, Wei Z, Wang C, Xing C, Hu G (2021) Cadmium and molybdenum co-induce pyroptosis via ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Environ Pollut 272:116403
Lihui X, Jinming G, Yalin G, Hemeng W, Hao W, Ying C (2022) Albicanol inhibits the toxicity of profenofos to grass carp hepatocytes cells through the ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 120:325–336
Wang L, Wang L, Shi X, Xu S (2020) Chlorpyrifos induces the apoptosis and necroptosis of L8824 cells through the ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis. J Hazard Mater 398:122905
Lihui X, Jinming G, Yalin G, Hemeng W, Hao W, Ying C (2022) Albicanol inhibits the toxicity of profenofos to grass carp hepatocytes cells through the ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 120:325–336
Rahman MM, Hossain KFB, Banik S, Sikder MT, Akter M, Bondad SEC, Rahaman MS, Hosokawa T, Saito T, Kurasaki M (2019) Selenium and zinc protections against metal-(loids)-induced toxicity and disease manifestations: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:146–163
Formigari A, Irato P, Santon A (2007) Zinc, antioxidant systems and metallothionein in metal mediated-apoptosis: biochemical and cytochemical aspects. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 146(4):443–459
Jarosz M, Olbert M, Wyszogrodzka G, Młyniec K, Librowski T (2017) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling. Inflammopharmacology 25(1):11–24
Mleczek M, Budka A, Gąsecka M, Budzyńska S, Drzewiecka K, Magdziak Z, Rutkowski P, Goliński P, Niedzielski P (2023) Copper, lead and zinc interactions during phytoextraction using Acer platanoides L.-a pot trial. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30(10):27191–27207
Anjum MR, Madhu P, Reddy KP, Reddy PS (2016) The protective effects of zinc in lead-induced testicular and epididymal toxicity in Wistar rats. Toxicol Ind Health 33(3):265–276
Wang X, Zhang X, Sun K, Wang S, Gong D (2022) Polystyrene microplastics induce apoptosis and necroptosis in swine testis cells via ROS/MAPK/HIF1α pathway. Environ Toxicol 37(10):2483–2492
Chen H, Chen J, Shi X, Li L, Xu S (2022) Naringenin protects swine testis cells from bisphenol A-induced apoptosis via Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biofactors 48(1):190–203
Sun K, Wang X, Zhang X, Shi X, Gong D (2022) The antagonistic effect of melatonin on TBBPA-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in swine testis cells. Environ Toxicol 37(9):2281–2290
Xu S, Xiaojing L, Xinyue S, Wei C, Honggui L, Shiwen X (2021) Pig lung fibrosis is active in the subacute CdCl(2) exposure model and exerts cumulative toxicity through the M1/M2 imbalance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 225:112757
Maciorowski Z, Chattopadhyay PK, Jain P (2017) Basic multicolor flow cytometry. Curr Protoc Immunol 117:5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haoyu Zhang was in charge of conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, and writing the main manuscript text.
Kexin Sun was in charge of resources, visualization, and also writing part of the manuscript text.
Meichen Gao was in charge of validation and investigation.
Shiwen Xu was in charge of review and editing the manuscript text.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Sun, K., Gao, M. et al. Zinc Inhibits Lead-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis of ST Cells Through ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT Axis. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 980–989 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03721-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03721-0