Abstract
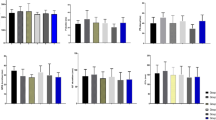
The toxic metalloid arsenic is known to cause liver and kidney injury in many humans and animals. The goal of this paper was to exemplify the antagonism of ginger against arsenic (As)-induced hepato-renal toxicity. In addition, the pathways Nrf2/Keap1 and NF/κB were studied to reveal the molecular mechanism of the stress. One hundred twenty 7-day-old White Pekin ducks were randomly allocated into five groups, having 24 birds in each. Each group contained three replicates having 8 birds in each replicate and maintained for 90 days. The groups were as follows: T-1 [control-basal diet with normal water], T-2 [T1 + As at 28 ppm/L of water], T-3 [T2 + ginger powder at 100 mg/kg feed], T-4 [T2 + ginger powder at 300 mg/kg feed], and T-5 [T2 + ginger powder at 1 g/kg feed]. It was observed that there was a significant increase in oxidative parameters whereas a significant decrease in antioxidant parameters in hepato-renal tissues in T-2. The exposure to As not only decreased the mRNA expression of antioxidant parameters like Nrf2, SOD-1, CAT, GPX, and HO-1and anti-inflammatory markers like IL-4 and IL-10 but also increased the m-RNA expression of NF-κB, Keap-1 and pro-inflammatory markers like IL-2, Il-6, IL-18, IL-1β, and TNF-α. There was also an accumulation of As in hepatic and renal tissue, confirmed by residual analysis of these tissues. By correlating the above parameters, As at 28 ppm showed significant toxic effects, and ginger powder at 1 g/kg feed effectively counteracted the toxic effects of As in ducks.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings are all included in the article.
References
Chen QY, Costa M (2021) Arsenic: a global environmental challenge. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 61(1):47–63. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030220-013418
NRC (National Research Council- US) Subcommittee to update the 1999 arsenic in drinking water report (2001) Arsenic in drinking water: 2001 update. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US)
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2004) Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer. ARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, vol 84
Pal A, Nayak B, Das B, Hossain MA, Ahamed S, Chakraborti D (2007) Additional danger of arsenic exposure through inhalation from burning of cow dung cakes laced with arsenic as a fuel in arsenic affected villages in Ganga-Meghna-Brahmaputra plain. J Environ Monit 9(10):1067–1070. https://doi.org/10.1039/b709339j
Bera AK, Rana T, Bhattacharya D, Das S, Pan D, Das SK (2011) Sodium arsenite-induced alteration in hepatocyte function of rat with special emphasis on superoxide dismutase expression pathway and its prevention by mushroom lectin. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109(4):240–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00718.x
Nevens F, Fevery J, Van Steenbergen W, Sciot R, Desmet V, De Groote J (1990) Arsenic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension- a report of eight cases. J Hepatol 11(1):80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-8278(90)90276-w
Guha Mazumder DN (2008) Chronic arsenic toxicity & human health. Indian J Med Res 128(4):436–444
WHO (1993) Guideline for drinking water quality, Recommendation .Vol. 1, 2nd ed. World Health Organisation, Geneva
Rahman AM, Hasegawa H, MahfuzurRahman M, MazidMiah MA, Tasmin A (2008) Arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.): human exposure through food chain. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69(2):317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.01.005
Kadirvel R, Sundaram K, Mani S, Samuel S, Elango N, Panneerselvam C (2007) Supplementation of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol prevents arsenic-induced protein oxidation and DNA damage induced by arsenic in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 26(12):939–946. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327107087909
Cai F, Ren J, Tao S, Wang X (2016) Uptake, translocation and transformation of antimony in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Environ Pollut 209:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.033
Rana T, Bera AK, Mondal DK, Das S, Bhattacharya D, Samanta S, Pan D, Das SK (2014) Arsenic residue in the products and by-products of chicken and ducks: a possible concern of avian health and environmental hazard to the population in West Bengal, India. India Toxicol Ind Health 30(6):576–580. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233712462467
Cavalera S, Di Nardo F, Spano G, Anfossi L, Manesiotis P, Baggiani C (2020) Stoichiometric molecular imprinting using polymerisable urea and squaramide receptors for the solid phase extraction of organo-arsenic compound roxarsone. Anal Methods 12(47):5729–5736. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ay01635g
Kuo CC, Moon KA, Wang SL, Silbergeld E, Navas-Acien A (2017) The association of arsenic metabolism with cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. Environ Health Perspect 125(8):087001. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP577
WHO (2003) Environmental health criteria-224. arsenic and arsenic compounds, 2nd Edition. World Health Organization, Geneva
Santra A, Maiti A, Chowdhury A, Mazumder DN (2000) Oxidative stress in liver of mice exposed to arsenic-contaminated water. Indian J Gastroenterol 19(3):112–115
Nandi D, Patra RC, Swarup D (2006) Oxidative stress indices and plasma biochemical parameters during oral exposure to arsenic in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 44(9):1579–1584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.04.013
Zhong G, Hu T, Tang L, Li T, Wu S, Duan X, Pan J, Zhang H, Tang Z, Feng X, Hu L (2022) Arsenic causes mitochondrial biogenesis obstacles by inhibiting the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway and also induces apoptosis and dysregulated mitophagy in the duck liver. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 230:113117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113117
Gul Kazi T, Qadir Shah A, Imran Afridi H, Ali Shah N, Balal Arain M (2013) Hazardous impact of organic arsenical compounds in chicken feed on different tissues of broiler chicken and manure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 87:120–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.10.012
Waalkes MP, Ward JM, Diwan BA (2004) Induction of tumors of the liver, lung, ovary and adrenal in adult mice after brief maternal gestational exposure to inorganic arsenic: promotional effects of postnatal phorbol ester exposure on hepatic and pulmonary, but not dermal cancers. Carcinogenesis 25(1):133–141. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgg181
Mazumder DN (2005) Effect of chronic intake of arsenic-contaminated water on liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206(2):169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.08.025
Zheng L, Kuo CC, Fadrowski J, Agnew J, Weaver VM, Navas-Acien A (2014) Arsenic and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Curr Environ Health Rep 1(3):192–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-014-0024-x
Palma-Lara I, Martínez-Castillo M, Quintana-Pérez JC, Arellano-Mendoza MG, Tamay-Cach F, Valenzuela-Limón OL, García-Montalvo EA, Hernández-Zavala A (2020) Arsenic exposure: a public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 110:104539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2019.104539
Renu K, Saravanan A, Elangovan A, Ramesh S, Annamalai S, Namachivayam A, Abel P, Madhyastha H, Madhyastha R, Maruyama M, Balachandar V, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A (2020) An appraisal on molecular and biochemical signalling cascades during arsenic-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci 1(260):118438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118438
Taggart MA, Figuerola J, Green AJ, Mateo R, Deacon C, Osborn D, Meharg AA (2006) After the Aznalcóllar mine spill: arsenic, zinc, selenium, lead and copper levels in the livers and bones of five waterfowl species. Environ Res 100(3):349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2005.07.009
Flora SJ (2011) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radic Biol Med 51(2):257–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.008
Kwak MK, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Sutter TR, Kensler TW (2001) Role of transcription factor Nrf2 in the induction of hepatic phase 2 and antioxidative enzymes in vivo by the cancer chemoprotective agent, 3H–1, 2-dimethiole-3-thione. Mol Med 7(2):135–1345
Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2004) Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med 10(11):549–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.003
Sinha D, Biswas J, Bishayee A (2013) Nrf2-mediated redox signaling in arsenic carcinogenesis: a review. Arch Toxicol 87(2):383–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0920-5
Souza ACF, Bastos DSS, Santos FC, Sertorio MN, Ervilha LOG, Gonçalves RV, de Oliveira LL, Machado-Neves M (2018) Arsenic aggravates oxidative stress causing hepatic alterations and inflammation in diabetic rats. Life Sci 209:472–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.08.054
Hu Y, Yu C, Yao M, Wang L, Liang B, Zhang B, Huang X, Zhang A (2018) The PKCδ-Nrf2-ARE signalling pathway may be involved in oxidative stress in arsenic-induced liver damage in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 62:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.05.012
Kwon DJ, Bae YS, Ju SM, Youn GS, Choi SY, Park J (2014) Salicortin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses via blockade of NF-κB and JNK activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. BMB Rep 47(6):318–323. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2014.47.6.200
Vilela MC, Campos RD, Mansur DS, Rodrigues DH, Lacerda-Queiroz N, Lima GK, Rachid MA, Kroon EG, Campos MA, Teixeira AL (2011) Role of IL-4 in an experimental model of encephalitis induced by intracranial inoculation of herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1). Arq Neuropsiquiatr 69(2A):237–241. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-282x2011000200019
Ahn J, Grün I, Fernando L (2002) Antioxidant properties of natural plant extracts containing polyphenolic compounds in cooked ground beef. J Food Sci 67:1364–1369. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb10290.x
Rima T and Narasu ML (2017) Evaluation of cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of Zerumbone on colon adenocarcinoma colo205 cells and human lymphocytes. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 9(11):92–96. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijpps.2017v9i11.21120
Kadnur SV, Goyal RK (2005) Beneficial effects of Zingiber officinale Roscoe on fructose induced hyperlipidemia and hyperinsulinemia in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 43(12):1161–1164
Gupta SK, Sharma A (2014) Medicinal properties of Zingiber officinale Roscoe-a review. J Pharma Biolog Sci 9(5):124–129. https://doi.org/10.9790/3008-0955124129
Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO, Nemmar A (2008) Some phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): a review of recent research. Food Chem Toxicol 46(2):409–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.09.085
Chrubasik S, Pittler MH, Roufogalis BD (2005) Zingiberis rhizoma: a comprehensive review on the ginger effect and efficacy profiles. Phytomedicine 12(9):684–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2004.07.009
Ahmed RS, Seth V, Banerjee BD (2000) Influence of dietary ginger (Zingiber officinales Rosc) on antioxidant defense system in rat: comparison with ascorbic acid. Indian J Exp Biol 38(6):604–606
Haleagrahara N, Jackie T, Chakravarthi S, Rao M, Kulur A (2010) Protective effect of Etlingera elatior (torch ginger) extract on lead acetate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. J Toxicol Sci 35(5):663–671. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.35.663
Andarwulan N, Kurniasih D, Apriady RA, Rahmat H, Roto AV, Bolling BW (2012) Polyphenols, carotenoids, and ascorbicacid in underutilized medicinal vegetables. J Funct Foods 4(1):339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2012.01.003
Kruawan K, Kangsadalampai K (2006) Antioxidant activity, phenolic compound contents and antimutagenic activity of some water extract of herbs. Thai J Pharm Sci 30:28–35
Panda SK, Kumar D, Jena GR, Sethy K, Mishra SK, Swain BK, Naik PK, Beura CK, Elmorsy MAM (2021) Efficacy of ginger on male reproductive traits and oxidative stress indices in White Pekin ducks intoxicated with arsenic. ANFT 21(3):559–569. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-181X.2021.00046.9
Das D, Pamia J, kumar D, Panda SK, Jenna G (2021) Histopathological grading of induced cardiotoxicity due to arsenic and its alleviation by Allium sativum in ducks. IJAR. B-4696. https://doi.org/10.18805/ijar.b-4696
BIS (2007) Bureau of Indian Standards, Poultry Feeds Specification (5th Revision), Manak Bhavan, 9 Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg, New Deli-110002
Cai SJ, Wu CX, Gong LM, Song T, Wu H, Zhang LY (2012) Effects of nano-selenium on performance, meat quality, immunefunction, oxidation resistance, and tissue selenium content inbroilers. Poult Sci 91(10):2532–2539. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2012-02160
Ehtisham S, Rahman SU, Siddique M, Qureshi AS (2011) Involvement of Mycoplasma synoviae in respiratory distress cases of broilers. Pak Vet J 31(2):117–119
Rehman SU (1984) Lead-induced regional lipid peroxidation in brain. Toxicol Lett 21(3):333–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4274(84)90093-6
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(68)90092-4
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Madesh M, Balasubramanian KA (1993) Microtiter plate assay for superoxide dismutase using MTT reduction by superoxide. Indian J Biochem Biophys 35(3):184–188
Grisham MB, Specian RD, Zimmerman TE (1994) Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on the pathophysiology observed in a model of chronic granulomatous colitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271(2):1114–1121
Patriarca P, Dri P, Snidero M (1997) Interference of myeloperoxidase with the estimation of superoxide dismutase activity. J Lab Clin Med 90(2):289–294
Wang HD, Pagano PJ, Du Y, Cayatte AJ, Quinn MT, Brecher P, Cohen RA (1998) Superoxide anion from the adventitia of the rat thoracic aorta inactivates nitric oxide. Circ Res 82(7):810–818. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.82.7.810
Sastry KV, Moudgal RP, Mohan J, Tyagi JS, Rao GS (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper-cadmium alloy. Anal Biochem 306(1):79–82. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2002.5676
Hershey JW, Oostdyk TS, Keliher PN (1988) Determination of arsenic and selenium in environmental and agricultural samples by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrophotometry. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 71(6):1090–1093
Dos Passos AS, Neri TS, Maciel MV, da Silva Rom~ao IL, Lemos VA (2012) Determination of arsenic in chicken feed by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration with polyurethane foam. Food Addit Contam. Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 29(11):1689–1695. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2012.706833
Kalavathi S, Anand KA, Gopala RA, Srilatha Ch, Rajasekhar RA (2011) Sodium arsenite toxicity in broiler chicks and its amelioration: haemato-biochemical and pathological studies. Indian J Vet Pathol 35(2):171–176
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2007) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 6th edition. Churchill Livingstone, London, UK pp 125–138
Sikandar A, Cheema AH, Younus M, Aslam A, Zaman MA, Rehman T (2012) Histopathological and serological studies on paratuberculosis in cattle and buffaloes. Pak Vet J 32(4):547–551
Khan A, Sharaf R, Khan MZ, Saleemi MK, Mahmood F (2013) Arsenic toxicity in broiler chicks and its alleviation with ascorbic acid: a toxico-patho-biochemical study. Int J Agric Biol 15(6):1105–1111
Das AK, Dewanjee S, Sahu R, Dua TK, Gangopadhyay M, Sinha MK (2010) Protective effect of Corchorus olitorius leaves against arsenic-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 29(1):64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2009.10.002
Yousef MI, El-Demerdash FM, Radwan FM (2008) Sodium arsenite induced biochemical perturbations in rats: ameliorating effect of curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol 46(11):3506–3511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.08.031
Adil M, Kandhare AD, Visnagri A, Bodhankar SL (2015) Naringin ameliorates sodium arsenite-induced renal and hepatic toxicity in rats: decisive role of KIM-1, Caspase-3, TGF-β, and TNF-α. Ren Fail 37(8):1396–1407. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2015.1074462
Bashir S, Sharma Y, Irshad M, Gupta SD, Dogra TD (2006) Arsenic-induced cell death in liver and brain of experimental rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 98(1):38–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_170.x
Sharma A, Sharma MK, Kumar M (2007) Protective effect of mentha piperita against arsenic-induced toxicity in liver of Swiss Albino mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100(4):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.00030.x
Khaki AA, Khaki A (2010) Antioxidant effect of ginger to prevents lead-induced liver tissue apoptosis in rat. J Med Plant Res 4(14):1492–1495
Abdel-Hameid N (2009) A protective effect of calcium carbonate against arsenic toxicity of the Nile Cat fish, Clarias gariepinus. Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci 9(2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.4194/trjfas.2009.0211
Tahirul M, Rahaman T, Islam MS, Ferdous KA, Hassan MA (2020) Effect of different doses of dietary arsenic on biochemical, gross and histo morphological changes in different organs of commercial broiler. SAJBR 3(1):1–17
Saleh N, Allam T, El-latif AA, Ghazy E (2019) The effects of different levels of thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and ginger (Zingiber officinale) essential oils on performance, hematological, biochemical and immunological parameters in broilers. Global Veterinaria 12(6):736–744. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.gv.2014.12.06.83189
Herve T, Raphaël KJ, Ferdinand N, Victor Herman N, Willy Marvel NM, Cyril D’Alex T, Laurine Vitrice FT (2019) Effects of ginger ( Zingiber officinale, Roscoe) essential oil on growth and laying performances, serum metabolites, and egg yolk antioxidant and cholesterol status in laying Japanese Quail. J Vet Med 2019:7857504. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7857504
Dalal B, Gangopadhyay P, Mukherjee A, Roychowdhury A (2007) Identification of indicators of arsenic induced nephrotoxicity in humans. Internet J Toxicol 5:2. https://doi.org/10.5580/e28
Saxena PN, Anand S, Saxena N, Bajaj P (2009) Effect of arsenic trioxide on renal functions and its modulation by Curcuma aromatica leaf extract in Albino rat. J Environ Biol 30(4):527–531
Muthumani M, Prabu SM (2014) Silibinin potentially attenuates arsenic-induced oxidative stress mediated cardiotoxicity and dyslipidemia in rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 14(1):83–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-013-9227-x
Akbarian A, Golian A, Sheikh Ahmadi A, Moravej H (2011) Effects of ginger root ( Zingiber officinale ) on egg yolk cholesterol, antioxidant status and performance of laying hens. J Appl Anim Res 39(1):19–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2011.558612
Barchowsky A, Klei LR, Dudek EJ, Swartz HM, James PE (1999) Stimulation of reactive oxygen, but not reactive nitrogen species, in vascular endothelial cells exposed to low levels of arsenite. Free Radic Biol Med 27(11–12):1405–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00186-0
Lynn S, Lai HT, Gurr JR, Jan KY (1997) Arsenite retards DNA break rejoining by inhibiting DNA ligation. Mutagenesis 12(5):353–358. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/12.5.353
Shi H, Shi X, Liu KJ (2004) Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 255(1–2):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000007262.26044.e8
Wang L, Xu Z (2006) Effects of arsenic (AsIII) on lipid peroxidation, glutathione content and antioxidant enzymes in growing pigs. Asian-Australas J Anim 19(5):727–733. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2006.727
Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J, Marshall PA, Freeman BA (1990) Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(4):1620–1624. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620
Lee SE, Song HJ, Park SY, Nam Y, Min CH, Lee DY, Jeong JY, Ha HS, Kim H-J, Whang WK, Jeong JH, Kim IK, Kim HR, Min YS, Sohn UD (2013) Effect of ECQ on iodoacetamide-induced chronic gastritis in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 17(5):469–467. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.5.469
Brunati AM, Pagano MA, Bindoli A, Rigobello MP (2010) Thiol redox systems and protein kinases in hepatic stellate cell regulatory processes. Free Radic Res 44(4):363–378. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715760903555836
Banerjee M, Banerjee N, Ghosh P, Das JK, Basu S, Sarkar AK, States JC, Giri AK (2010) Evaluation of the serum catalase and myeloperoxidase activities in chronic arsenic-exposed individuals and concomitant cytogenetic damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 249(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2010.08.013
Masella R, Di Benedetto R, Varı` R, Filesi C, Giovannini C, (2005) Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J Nutr Biochem 16(10):577–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.013
Imlay JA, Linn S (1988) DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science 240(4857):1302–1309. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3287616
Saraswathi KY, Muthal A, Kandhare A, Rojatkar S, Bodhankar S (2014) Study of methanolic extract of Artemisia pallens wall on endurance of laboratory animals. Pharmacologia 5(8):298–309. https://doi.org/10.5567/pharmacologia.2014.298.309
Gupta R, Flora SJ (2006) Protective effects of fruit extracts of Hippophae rhamnoides L. against arsenic toxicity in Swiss Albino mice. Hum Exp Toxicol 25(6):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1191/0960327106ht636oa
Das S, Santra A, Lahiri S, Guha Mazumder DN (2005) Implications of oxidative stress and hepatic cytokine (TNF-α and IL-6) response in the pathogenesis of hepatic collagenesis in chronic arsenic toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.08.010
Isuzugawa K, Inoue M, Ogihara Y (2001) Catalase contents in cells determine sensitivity to the apoptosis inducer gallic acid. Biol Pharm Bull 24(9):1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.24.1022
Gülçin İ (2009) Antioxidant activity of l-adrenaline: a structure–activity insight. Chem Biol Interact 179(2–3):71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2008.09.023
Buyukokuroglu M, Gulcin I (2009) In vitro antioxidant and antiradical properties of Hippophae rhamnoides L. Pharmacogn Mag 5(19):189–195
Sohaib M, Butt MS, Shabbir MA, Shahid M (2015) Lipid stability, antioxidant potential and fatty acid composition of broilers breast meat as influenced by quercetin in combination with α-tocopherol enriched diets. Lipids Health Dis 14(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-015-0058-6
Gjorgieva D, Panovska TK, Ruskovska T, BaIeva K, Stafilov T (2013) Influence of heavy metal stress on antioxidant status and DNA damage in Urtica dioica. BioMed Res Int 2013:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/276417
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR, Sadeghi M (2021) Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front Pharmacol 12:643972. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Duan T, Hu T, Wu C, Yeh YT, Lu J, Zhang Q, Li X, Jian W, Luo P (2020) PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is involved in NaAsO2-induced apoptosis of human hepatic cells through activation of ERK signaling. Toxicol Vitr 66:104857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2020.104857
Renu K, Chakraborty R, Myakala H, Koti R, Famurewa AC, Madhyastha H, Vellingiri B, George A, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A (2021) Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (lead, chromium, arsenic, mercury, nickel and cadmium) – induced hepatotoxicity – a review. Chemosphere 271:129735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129735
Sinha D, Biswas J, Bishayee A (2013) Nrf-2 mediated redox signaling in As carcinogenesis: a review. Arch Toxicol 87(2):383–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0920-5
Janasik B, Reszka E, Stanislawska M, Jablonska E, Kuras R, Wieczorek E, Malachowska B, Fendler W, Wasowicz W (2018) Effect of arsenic exposure on Nrf2-Keap1 pathway and epigenetic modification. Biol Trace Elem Res 185(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1219-4
Massrieh W, Derjuga A, Blank V (2006) Induction of endogenous Nrf2/Small Maf heterodimers by arsenic-mediated stress in placental choriocarcinoma cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(1–2):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.8.53
Zhao G, Yu R, Deng J, Zhao Q, Li Y, Joo M, van Breemen RB, Christman JW, Xiao L (2013) Pivotal role of reactive oxygen species in differential regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced prostaglandins production in macrophages. Mol Pharmacol 83(1):167–178. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.112.080762
Martin-Chouly C, Morzadec C, Bonvalet M, Galibert MD, Fardel O, Vernhet L (2011) Inorganic arsenic alters expression of immune and stress response genes in activated primary human T lymphocytes. Mol Immunol 48(6–7):956–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2011.01.005
Zhang K, Zhao P, Guo G, Guo Y, Tian L, Sun X, Li S, He Y, Sun Y, Chai H, Zhang W, Xing M (2016) Arsenic trioxide attenuates Nf-κb and cytokine mRNA levels in the livers of cocks. Biol Trace Elem Res 170(2):432–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0455-8
Saedisomeolia A, Makhdoomi Arzati M, Abdolahi M, Sedighiyan M, Rangel A, Muench G, Zarezadeh M, Jafarieh A, Mohammadzadeh Honarvar N (2019) Mechanisms of action of ginger in nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathways in diabetes. J Herb Med 16:100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2018.10.004
Sandberg M, Patil J, D’Angelo B, Weber SG, Mallard C (2014) NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology 79:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.004
Saha S, Buttari B, Panieri E, Profumo E, Saso L (2020) An overview of Nrf2 signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules 25(22):5474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225474
Kobayashi EH, Suzuki T, Funayama R, Nagashima T, Hayashi M, Sekine H, Tanaka N, Moriguchi T, Motohashi H, Nakayama K, Yamamoto M (2016) Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat Commun 7(1):11624. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11624
Kim SO, Chun KS, Kundu JK, Surh YJ (2004) Inhibitory effects of [6]-gingerol on PMA-induced COX-2 expression and activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in mouse skin. BioFactors 21(1–4):27–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.552210107
Aktan F, Henness S, Tran VH, Duke CC, Roufogalis BD, Ammit AJ (2006) Gingerol metabolite and a synthetic analogue Capsarol™ inhibit macrophage NF-κB-mediated iNOS gene expression and enzyme activity. Planta Med 72(08):727–734. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-931588
Fathi R, Akbari A, Nasiri K, Chardahcherik M (2021) Ginger (Zingiber officinale roscoe) extract could upregulate the renal expression of NRF2 and TNFα and prevents ethanol-induced toxicity in rat kidney. Avicenna J Phytomed 11(2):134–145
Pan M-H, Hsieh M-C, Hsu P-C, Ho S-Y, Lai C-S, Wu H, Sang S, Ho C-T (2008) 6-Shogaol suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced up-expression of iNOS and COX-2 in murine macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res 52(12):1467–1477. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200700515
Dutta AK (2007) Experimental studies on the pathology of induced sodium arsenite toxicity in mice with special reference to estimation of intramuscular tD50. Indian J Vet Pathol 31(1):83. https://indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijvp&volume=31&issue=1&article=abs006
Javaria M, Khan A, Khan M, Saleemi M, Mahmood F (2013) Arsenic induced clinico-hemato-pathological alterations in broilers and its attenuation by vitamin E and selenium. Pak J Agric Sci 50(1):131–138
Islam MS, Awal MA, Mostofa M, Begum F, Myenuddin M (2013) Detection of arsenic in chickens and ducks. Int J Sci Res Manag 1(1):56–62
Cullen NM, Wolf LR, Clair DS (1995) Pediatric arsenic ingestion. Am J Emerg Med 13(4):432–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-6757(95)90133-7
Roy S, Bhattacharya S (2006) Arsenic-induced histopathology and synthesis of stress proteins in liver and kidney of Channa punctatus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65(2):218–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.07.005
Acknowledgements
The authors all wish to acknowledge the Central Avian Research Institute (Bhubaneswar, India) for providing the experimental animal site and ensuring the progress of the scientific experiment smoothly and acknowledge the College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, Odisha University of Agriculture and Technology (Bhubaneswar, India) for experimental material assistance.
Funding
CARI funded this experiment with project number P-1/2017/1-IAV/L34/6200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Geeta Rani Jena, Dhirendra Kumar, Surya Kant Mishra, Bijaya Kumar Swain, Prafulla Kumar Naik, and Chandra Kant Beura designed the experiment; Ramesh Chandra Patra and Susen Kumar Panda provided helpful suggestions; statistical analysis of all data, original draft wrote, and modified were completed by Kamdev Sethy, and Santosh Kumar Panda conducted the animal feeding and the sample analysis; Bhagyalaxmi Panda participated in the sample collection.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, S.K., Kumar, D., Jena, G.R. et al. Hepatorenal Toxicity of Inorganic Arsenic in White Pekin Ducks and Its Amelioration by Using Ginger. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 2471–2490 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03317-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03317-0