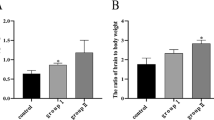
Abstract
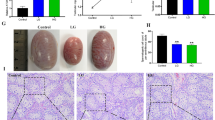
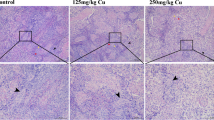
Copper (Cu) is listed as one of the main heavy metal pollutants, which poses potential health risks to humans. Excessive intake of Cu has shown toxic effects on the organs of many animals, and the liver is one of the most important organs to metabolize it. In this study, pigs, the mammal with similar metabolic characteristics to humans, were selected to assess the effects of long-term exposure to Cu on mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, which are of great significance for studying the toxicity of Cu to humans. Pigs were fed a diet with different contents of Cu (10, 125, and 250 mg/kg) for 80 days. Samples of blood and liver tissue were collected on days 40 and 80. Experimental results demonstrated that the accumulation of Cu in the liver was increased in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. Meanwhile, the curve of pig’s body weight showed that a 125 mg/kg Cu diet promoted the growth of pigs during the first 40 days and then inhibited it from 40 to 80 days, while the 250 mg/kg Cu diet inhibited the growth of pigs during 80 days of feeding. Additionally, the genes and protein expression levels of Caspase-3, p53, Bax, Bak1, Bid, Bad, CytC, and Drp1 in the treatment group were higher than that in the control group, while Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Opa1, Mfn1, and Mfn2 were decreased. In conclusion, these results indicated that long-term excessive intake of Cu could inhibit the growth of pigs and induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by breaking the mitochondrial dynamic balance.
Graphical abstract

Synopsis: Long-term exposure to high doses of Cu could lead to mitochondrial dysfunction by breaking the mitochondrial dynamic balance, which ultimately induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in the liver of pigs. This might be closely related to the growth inhibition and liver damage in pigs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JH, Kang YJ (2016) The toxic effects on the stress and immune responses in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii exposed to hexavalent chromium. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 43:128–133
Mondal C, Ganguly M, Pal J, Roy A, Jana J, Pal T (2014) Morphology controlled synthesis of SnS 2 nanomaterial for promoting photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr (VI) under visible light. Langmuir 30:4157–4164
US-EPA, 2014. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Effluent guidelines: toxic and priority pollutants under the Clean Water Act (Priority Pollutants, 40 CFR Part 423, Appendix A)
WHO, 2020. The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification, 2019 Edition. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2020. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Vetlényi E, Rácz G (2020) The physiological function of copper, the etiological role of copper excess and deficiency. Orv Hetil 161:1488–1496
Hosseini MJ, Shaki F, Ghazi-Khansari M, Pourahmad J (2014) Toxicity of copper on isolated liver mitochondria: impairment at complexes I, II, and IV leads to increased ROS production. Cell Biochem Biophys 70:367–381
Li S, Zhao H, Wang Y, Shao Y, Li J, Liu J et al (2017) The inflammatory responses in Cu-mediated elemental imbalance is associated with mitochondrial fission and intrinsic apoptosis in Gallus gallus heart. Chemosphere 189:489–497
Puchkova LV, Skvortsov AN, Rusconi P, Ilyechova EY, Broggini M (2016) In vivo effect of copper status on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biometals 29:841–849
Lei C, Liao J, Li Q, Shi J, Zhang H, Guo J et al (2021) Copper induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis via ampk-mtor pathway in hypothalamus of pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 220:112395
Liao J, Yang F, Bai Y, Yu W, Qiao N, Han Q et al (2021) Metabolomics analysis reveals the effects of copper on mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in kidney of broiler chicken (Gallus gallus). J Inorg Biochem 224:111581
Liao J, Yang F, Chen H, Yu W, Han Q, Li Y et al (2019) Effects of copper on oxidative stress and autophagy in hypothalamus of broilers. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 185:109710
Li Q, Liao J, Lei C, Shi J, Zhang H, Han Q et al (2021) Metabolomics analysis reveals the effect of copper on autophagy in myocardia of pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 213:112040
Wang X, Cao H, Fang Y, Bai H, Chen J, Xing C et al (2022) Activation of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria coupling drives copper-induced autophagy in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 235:113438
Liao J, Li Q, Hu Z, Yu W, Zhang K, Ma F, Han Q, Zhang H, Guo J, Hu L, Pan J, Li Y, Tang Z (2022) Mitochondrial miR-1285 regulates copper-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy by impairing IDH2 in pig jejunal epithelial cells. J Hazard Mater 422:126899
Wen Y, Li R, Piao X, Lin G, He P (2021) Different copper sources and levels affect growth performance, copper content, carcass characteristics, intestinal microorganism and metabolism of finishing pigs. Sciencedirect 8(1):321–330
Nowak KL, Edelstein CL (2020) Apoptosis and autophagy in polycystic kidney disease (PKD). Cell Signal 68:109518
Obeng E (2020) Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals - a review. Braz J Biol 81(4):1133–1143
Bock FJ, Tait S (2019) Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(2):85–100
Abate M, Festa A, Falco M, Lombardi A, Luce A, Grimaldi A et al (2020) Mitochondria as playmakers of apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. Semin Cell Dev Biol 98:139–153
Sheridan C, Martin SJ (2010) Mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics and apoptosis. Mitochondrion 10:640–648
Dietz JV, Bohovych I, Viana MP, Khalimonchuk O (2019) Proteolytic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Mitochondrion 49:289–304
Khan S, Raj D, Jaiswal K, Lahiri A (2020) Modulation of host mitochondrial dynamics during bacterial infection. Mitochondrion 53:140–149
Cui G, Li Y, Ding K, Hao S, Wang J, Zhang Z (2017) Attribution of Bax and mitochondrial permeability transition pore on cantharidin-induced apoptosis of Sf9 cells. Pestic Biochem Phys 142:91–101
Liu H, Guo H, Jian Z, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z et al (2020) Copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:1359164
Wang T, Wen X, Hu Y, Zhang X, Wang D, Yin S (2019) Copper nanoparticles induced oxidation stress, cell apoptosis and immune response in the liver of juvenile Takifugu fasciatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:648–655
Wang K (2015) Autophagy and apoptosis in liver injury. Cell Cycle 14(11):1631–1642
Adeyemi JA, Machado ART, Ogunjimi AT, Alberici LC, Antunes LMG, Barbosa F (2020) Cytotoxicity, mutagenicity, oxidative stress and mitochondrial impairment in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells exposed to copper oxide, copper-iron oxide and carbon nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109982
Lunney JK (2007) Advances in swine biomedical model genomics. Int J Biol Sci 3:179–184
Ojano-Dirain CP, Iqbal M, Cawthon D, Swonger S, Wing T, Cooper M, Bottje W (2004) Determination of mitochondrial function and site-specific defects in electron transport in duodenal mitochondria in broilers with low and high feed efficiency. Poultry Science 83(8):1394–1403. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/83.8.1394
Bost M, Houdart S, Oberli M, Kalonji E, Huneau JF, Margaritis I (2016) Dietary copper and human health: current evidence and unresolved issues. J Trace Elem Med Biol 35:107–115
Chen J, Jiang Y, Shi H, Peng Y, Fan X, Li C (2020) The molecular mechanisms of copper metabolism and its roles in human diseases. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol 472:1415–1429
Kim M, Cho JH, Seong PN, Jung H, Jeong JY, Kim S et al (2021) Fecal microbiome shifts by different forms of copper supplementations in growing pigs. J Anim Sci Technol 63(6):1386–1396
Ding H, Zhang Q, Xu H, Yu X, Feng J (2021) Selection of copper and zinc dosages in pig diets based on the mutual benefit of animal growth and environmental protection. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 216:112177
Valenzuela C, Romaña DLD, Schmiede C, Morales MS, Olivares M, Pizarro F (2011) Total iron, heme iron, zinc, and copper content in rabbit meat and viscera. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1489–1496
Lada E, Anna M, Patrik M, Zbynek T, Miroslav J, Hynek M et al (2020) Porcine liver anatomy applied to biomedicine. J Surg Res 250:70–79
Pabst R (2020) The pig as a model for immunology research. Cell Tissue Res 380(2):287–304
Camacho P, Fan H, Liu Z, He JQ (2016) Large mammalian animal models of heart disease. J Cardiovas Dev Dis 3(4):30
Schelstraete W, Devreese M, Croubels S (2020) Comparative toxicokinetics of Fusarium mycotoxins in pigs and humans. Food Chem Toxicol 137:111140
Balogun SO, da Silva Jr IF, Colodel EM, de Oliveira RG, Ascêncio SD, Martins DT (2014) Toxicological evaluation of hydroethanolic extract of Helicteres sacarolha A. St.- Hil. et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 157:285–291
Leong YH, Isa A, Mohamed Mahmood M, Moey C, Utar Z, Soon YI, Majid M (2018) Acute and repeated dose 28-day oral toxicity of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 95:280–288
Wang S, Wang N, Pan D, Zhang H, Sun G et al (2021) Effects of copper supplementation on blood lipid level: a systematic review and a meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:2851–2857
Zhou J, Liu C, Francis M, Sun Y, Ryu MS, Grider A et al (2020) The causal effects of blood iron and copper on lipid metabolism diseases: evidence from phenome-wide Mendelian randomization study. Nutrients 12:3174
Wu X, Cui H, Gao X, Yang F (2015) Effects of dietary copper on elemental balance, plasma minerals and serum biochemical parameters of growing-furring male mink (Mustela vison). Anim Nutr 1:36–40
Araya M, Núñez H, Pavez L, Arredondo M, Méndez M, Cisternas F et al (2012) Administration of high doses of copper to capuchin monkeys does not cause liver damage but induces transcriptional activation of hepatic proliferative responses. J Nutr 142:233–237
Araya M, Kelleher SL, Arredondo MA, Sierralta W, Vial MT, Uauy R et al (2005) Effects of chronic copper exposure during early life in rhesus monkeys. Am J Clin Nutr 81:1065–1071
Qinna NA, Ghanim BY (2019) Chemical induction of hepatic apoptosis in rodents. J Appl Toxicol 39(2):178–190
Yang F, Pei R, Zhang Z, Liao J, Yu W, Qiao N et al (2019) Copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in chicken hepatocytes. Toxicol in Vitro 54:310–316
Zhang H, Chang Z, Mehmood K, Abbas RZ, Nabi F, Rehman MU et al (2018) Nano copper induces apoptosis in PK-15 cells via a mitochondria-mediated pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 181:62–70
Fricker M, Tolkovsky AM, Borutaite V, Coleman M, Brown GC (2018) Neuronal cell death. Physiol Rev 98(2):813–880
Wang C, Nie G, Yang F, Chen J, Zhuang Y, Dai X et al (2020) Molybdenum and cadmium co-induce oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. J Hazard Mater 383:121157
Dhanraj P, Venter C, Bester MJ, Oberholzer HM (2020) Induction of hepatic portal fibrosis, mitochondria damage, and extracellular vesicle formation in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to copper, manganese, and mercury, alone and in combination. Ultrastruct Pathol 44(2):182–192
Fei D, Zhao H, Wang Y, Liu J, Mu M, Guo M et al (2019) The disturbance of autophagy and apoptosis in the gizzard caused by copper and/or arsenic are related to mitochondrial kinetics. Chemosphere 231:1–9
Chen H, Chomyn A, Chan DC (2005) Disruption of fusion results in mitochondrial heterogeneity and dysfunction. J Biol Chem 280(28):26185–26192
Zhao Y, Cui JG, Zhang H, Li XN, Li MZ, Talukder M et al (2021) Role of mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum coupling in lycopene preventing DEHP-induced hepatotoxicity. Food Funct 12(21):10741–10749
Adebayo M, Singh S, Singh AP, Dasgupta S (2021) Mitochondrial fusion and fission: the fine-tune balance for cellular homeostasis. FASEB J 35(6):e21620
Wang GW, Lvj C, Shi ZR, Zeng RT, Dong XY, Zhang WD et al (2014) Abieslactone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinomas through the mitochondrial pathway and the generation of reactive oxygen species. PLoS ONE 9:e115151
Prenek L, Boldizsár F, Kugyelka R, Ugor E, Berta G, Németh P et al (2017) The regulation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by glucocorticoid receptor in collaboration with Bcl-2 family proteins in developing T cells. Apoptosis 22:239–253
Kureel J, John AA, Raghuvanshi A, Awasthi P, Goel A, Singh D (2016) Identification of GRP78 as a molecular target of medicarpin in osteoblast cells by proteomics. Mol Cell Biochem 418:71–80
Delre D, Amgalan D, Linkermann A, Liu Q, Kitsis RN (2019) Fundamental mechanisms of regulated cell death and implications for heart disease. Physiol Rev 99(4):1765–1817
Ma ZJ, Lu L, Yang JJ, Wang XX, Su G, Wang ZL et al (2018) Lariciresinol induces apoptosis in hepg2 cells via mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 821:1–10
Ranjan A, Iwakuma T (2016) Non-canonical cell death induced by p53. Int J Mol Sci 17:2068
Frión-Herrera Y, Díaz-García A, Ruiz-Fuentes J, Rodríguez-Sánchez H, Sforcin JM (2015) Brazilian green propolis induced apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through mitochondrial-mediated pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol 67(10):1448–1456
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32072930 and 31572585) and the National Key R & D Program of China (No. 2016YFD0501205 and 2017YFD0502200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhaoxin Tang: conceptualization; methodology; supervision; project administration; funding acquisition. Zhuoying Hu: conceptualization; methodology; formal analysis; investigation; visualization; writing — original draft. Jianzhao Liao: data curation; formal analysis; investigation; writing — review and editing. Kai Zhang: data curation; formal analysis; software; methodology. Kunxuan Huang: investigation; writing — review and editing. Quanwei Li: supervision. Chaiqin Lei: writing — review and editing. Qingyue Han: investigation. Hui Zhang: visualization. Jianying Guo: methodology. Lianmei Hu: writing — review and editing; resources. Jiaqiang Pan: methodology. Ying Li: resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhuoying Hu and Jianzhao Liao share the first authorship
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Liao, J., Zhang, K. et al. Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Copper on Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Pig Liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 1726–1739 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03303-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03303-6