Abstract
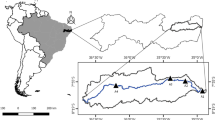
This study had a purpose to evaluate the seasonal biodistribution of some trace elements (cadmium, Cd; Lead, Pb; chrome, Cr; and mercury, Hg) in different tissues (muscle, gills, liver, stomach, and intestine) of striped mullet Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) and the hematological and biochemical responses of this species to aquatic pollution by trace metals. For this purpose, 80 M. cephalus (20 for each season) were captured in three different stations of Faro Lake, Messina, Sicily. Biometric indices (weight, fork length, and total length) of each fish were registered. The physico-chemical parameters of the water of the study area were also measured, and the content of trace elements in water and sediment was determined. The hematological (white blood cell, WBC; red blood cell, RBC; hemoglobin concentration, Hb; hematocrit, Hct; mean corpuscular volume, MCV; mean corpuscular hemoglobin, MCH; mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, MCHC; thrombocytes count, TC), biochemical parameters (aspartate aminotransferase, AST; alanine aminotransferase, ALT; alkaline phosphatase, ALP; lactate dehydrogenase, LDH), and the seasonal concentration of the trace elements in the different tissues of M. cephalus were assessed. Our results showed a different biodistribution of the trace elements in M. cephalus and significant variations of the blood parameters in the different seasons. This research provides a valid contribute to environmental biomonitoring techniques useful in aquatic pollution control and water management. It also contributes to broadening the studies on the improvement of the health and sustainability of aquatic environments.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Masri M, Aba S, Khalil AH, Al-Hares Z (2002) Sedimentation rates and pollution history of a dried lake: Al-Oteibeh Lake. Sci Total Environ 293:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(02)00013-x
Karbassi R, Bayati I, Moattar F (2006) Origin and chemical partioning of heavy metals in riverbed sediments. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325905
Mansour SA, Sidky MM (2002) Ecotoxicological studies 3. Heavy metals contaminating water and fish from Fayoum, Governorate, Egypt. Food Chem 78:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00197-2
Gochfeld M (2003) Cases of mercury exposure, bioavailability, and adsorption. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0147-6513(03)00060-5
Yang H, Rose NL (2003) Distribution of Hg in the lake sediments across the UK. Sci Total Environ 304:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00584-3
Vander Oost R, Beyer J, Verneykebm NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment. A review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1382-6689(02)00126-6
Adams S, Shepard KL, Greeley MS Jr, Jimenez BD, Ryon MG, Shugart LR, McCarthy JF (1989) The use of bioindicators for assess the effects of pollutant stress on fish. Mar Environ Res 28:459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-1136(89)90284-5
Southworth GR, Peterson MJ, Adams SM, Baylock BG (1994) Estimation of appropriate background concentrations for assessing mercury contamination in fish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 53:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192035
Lamas S, Fernández JA, Aboal JR, Carballeira A (2007) Testing the use of juvenile Salmo trutta L. as biomonitors of heavy metal pollution in freshwater. Chemosphere 67:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.040
Rashed MN (2001) Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from Nasser Lake. Environ Int 27:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00050-2
Authman MMN (2008) Oreochromus niloticus as a biomonitor of heavy metal pollution with emphasis on potential risk and relation to some biological aspects. Glob Vet 2:104–109
Capillo G, Panarello G, Savoca S, Sanfilippo M, Albano M, Li Volsi R, Consolo G, Spanò N (2018) Intertidal ponds of Messina’s beachrock faunal assemblage, evaluation of ecosystem dynamics and communities’ interactions. Atti Accad Pelorit Pericol, Cl Sci Fis Mat Nat 96:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1478/AAPP.96S3A4
Capillo G, Savoca S, Costa R, Sanfilippo M, Rizzo C, Lo Giudice A, Albergamo A, Rando R, Bartolomeo G, Spanò N, Faggio C (2018) New insights into the culture method and antibacterial potential of Gracilaria gracilis. Mar Drugs 16:492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120492
Spinelli A, Capillo G, Faggio C, Vitale D, Spanò N (2018) Returning of Hippocampus hippocampus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Syngnathidae) in the Faro Lake-oriented Natural Reserve of Capo Peloro, Italy. Nat Prod Res 34:595–598. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1490909
Fazio F, Filiciotto F, Marafioti S, DiStefano V, Assenza A, Placenti F, Buscaino G, Piccione G, Mazzola S (2012) Automatic analysis to assess haematological parameters in farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758). Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 45:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236244.2012.677559
Fazio F, Faggio C, Marafioti S, Torre A, Sanfilippo M, Piccione G (2012b) Comparative study of haematological profile on Gobius niger in two different habitat sites, Faro Lake and Tyrrhenian Sea. Cah Biol Mar 53:213–219
Filiciotto F, Fazio F, Marafioti S, Buscaino G, Maccarrone V, Faggio C (2012) Assessment of hematological parameter range values using an automatic method in European sea bass (Dicentrarcus labrax L.). Nat Rerum 1:29–36
Fazio F, Marafioti S, Torre A, Sanfilippo M, Panzera M, Faggio C (2013) Haematological and serum protein profiles of Mugil cephalus, effect of two different habitats. Ichthyol Res 60:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-012-0303-1
Fazio F, Saoca C, Sanfilippo M, Capillo G, Spanò N, Piccione G (2019) Response of vanadium bioaccumulation in tissues of Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus 1758). Sci Total Environ 689:774–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.476
Fazio F, Saoca C, Ferrantelli V, Cammilleri G, Capillo G, Piccione G (2019) Relationship between arsenic accumulation in tissues and haematological parameters in mullet caught in faro lake: a preliminary study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8821–8827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04343-7
Fazio F, Saoca C, Acar Ü, Tezel R, Çelik M, Yilmaz S, Kesbiç OS, Yalgin F, Yigit M (2020) A comparative evaluation of hematological and biochemical parameters between italian Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus 1758) and turkish Chelon auratus (Risso 1810) mullet. Turk J Zool 44:22–30. https://doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1907-37
Fazio F, D’Iglio C, Capillo G, Saoca C, Peycheva K, Piccione G, Makedonski L (2020) Environmental investigations and tissue bioaccumulation of heavy metals in grey mullet from the Black sea (Bulgaria) and the Ionian sea (Italy). Animals 10:1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10101739
Fazio F, Piccione G, Tribulato K, Ferrantelli V, Giangrosso G, Arfuso F, Faggio C (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two Italian lakes. J Aquat Anim Health 26:278–284. https://doi.org/10.1080/08997659.2014.938872
Gao L, Gao B, Xu D, Peng W, Lu J (2019) Multiple assessments of trace metals in sediments and their response to the water level fluctuation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 648:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.112
Okbah MA, El-Gammal MI, Ibrahim MS, Waheshi YA (2020) Geochemical speciation of trace metals in sediments of the northern Nile Delta Lake by sequential extraction technique. Chem Ecol 36:236–255. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2020.1718118
Marzouk M (1994) Fish and environmental pollution. J Vet Med 42:51–52
Khalil M, Faragallah H (2008) The distribution of some leachable and total heavy metals in core sediments of Manzala lagoon,Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 34:1–11
Hemens J, Connell AD (1975) Richards Bay: Southern Bay conservation area. CSIR / NIWR Progress Report No. 29 CSIR, Durban, South Africa
Ansari T, Marr I, Tariq N (2004) Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective- A mini review. J Appl Sci 4:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2004.1.20
Karadede H, Oymak SA, Ünlü E (2004) Heavy metals in mullet, Liza abu, and Catfish, Silurus triostegus, from the Ataturk Dam Lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Environ Int 30:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00169-7
Ali M, Abdel-Satar A (2005) Studies of some heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and fish diets in some fish farms in EL-Fayoum province. Egypt J Aquat Res 31:261–273
Ramalingam V, Vimaladevi V, Narmadaraji R, Prabakaran P (2000) Effect of lead on haematological and biochemical changes in freshwater fish Cirrhina mrigala. Pollut Res 19:81–84
Mastan S, Priya GI, Babu E (2008) Haematological profile of Clarias batrachus (Linn.) exposed to sub-lethal doses of lead nitrate. Int J Hematol 6. https://doi.org/10.5580/1c2d
Mahmoud UM, Ebied A-B M, Mohamed SM (2013) Effect of lead on some haematological and biochemical characteristics of Clarias gariepinus dietary supplemented with lycopene and vitamin E. Egypt Acad J Biol Sci 5:67–89. https://doi.org/10.21608/EAJBSC.2013.16112
Bujjamma P, Padmavathi P (2018) Effect of cadmium on haematological changes in a freshwater catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis. Int J Zool Stud 3:132–141
Islam SMM, Rohani MdF, Zabed SA, Islam MdT, Jannat R, Akter Y, Shahjahan Md (2020) Acute effects of chromium on hemato-biochemical parameters and morphology of erythrocytes in striped carfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Toxicol Rep 7:664–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.04.016
Authman MMN, Zaki MS, Khallaf EA, Abbas HH (2015) Use of fish as bioindicator of the effects of heavy metals pollution. J Aquac Res Dev 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000328
Nanda P, Bikkini A (2016) Haematological changes in fish Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) under vanadium stress. Biolife 4:695–696
Zaki MS, Sharaf NE, Osfor MH (2010) Effect of vanadium toxicity in Clarias lazera. Am J Sci 6:291–296
Pedlar RM, Ptashynski MD, Wautier KG, Evans R, Baron CL, Klaverkamp JF (2002) The accumulation, distribution and toxicological effects of dietary arsenic exposure in lake white (Coregonus clupeaformis) and lake trout (Salvelinus namay-cush). Comp Biochem Physiol C 131:73–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1532-0456(01)00281-2
Chokkalingam K, Annamalai M, Satyanarayanan SK, Mathan R (2010) Toxicological effects of arsenate exposure on hematological, biochemical and liver transaminases activity in an Indian major carp, Catla catla. Food Chem Toxicol 28:2848–2854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.017
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Director of the Food Department of Experimental Zooprophylactic Institute of Sicily Dr. Vincenzo Ferrantelli and the health researcher Dr. Gaetano Cammilleri for the support to the analytical chemistry part of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Concetta Saoca, Francesca Arfuso, and Claudia Giannetto. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Concetta Saoca and Francesco Fazio, and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saoca, C., Arfuso, F., Giannetto, C. et al. Seasonal Biodistribution of Some Trace Elements (Cd, Pb, Cr, Hg) and “Blood Biomarkers” Response in Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758). Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 1987–1995 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03272-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03272-w