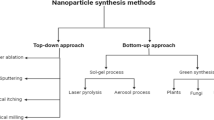
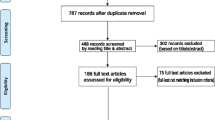
Abstract
Biological features of silver nanoparticles in rising the insulin level of diabetic animal models were considered in recent years, which resulted in decreasing hyperglycemia condition. We reviewed the published literature to investigate the possible role of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) throughout the treatment of diabetes mellitus in animal studies. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we performed a search throughout the English literature of electronic databases, including Scopus, PubMed, and ISI Web of Science, up to the date of May 22, 2020. Primary outcomes and data regarding fast blood sugar (FBS), lipid profile, and liver enzyme were collected from the available articles, while the studies that did not provide sufficient information on the effects of silver nanoparticles through the course of diabetes mellitus were excluded. Our search yielded 1283 results that included five animal studies in the meta-analysis. The comparison between the plasma insulin level of the diabetic group treated by Ag-NPs with the diabetic control group displayed no significant differences with the P values = 0.299. In addition, significant differences were revealed by comparing the FBS level of the diabetic group treated by Ag-NPs with the diabetic control group (P value < 0.001). According to the present meta-analysis, the application of Ag-NPs in animal models resulted in displaying the anti-diabetic effects, which can be applied in future treatments. Furthermore, a correlation was noticed between these nanoparticles and the reduction of serum FBS among diabetic cases.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27(5):1047–1053
Sharma R, Juyal D, Negi A (2018) Epidemiology of diabetes mellitus and its recent awareness with the use of advance medication. The Pharma Innovation Journal 7(6):87–88
Virgen-Ortiz A, Limon-Miranda S, Soto-Covarrubias M, Apolinar-Iribe A, Rodriguez-Leon E, Iniguez-Palomares R (2015) Biocompatible silver nanoparticles synthesized using Rumex hymenosepalus extract decreases fasting glucose levels in diabetic rats. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 10(3):927–933
Patel D, Kumar R, Prasad S, Sairam K, Hemalatha S (2011) Antidiabetic and in vitro antioxidant potential of Hybanthus enneaspermus (Linn) F. Muell in streptozotocin–induced diabetic rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 1(4):316–322
Modi P (2007) Diabetes beyond insulin: review of new drugs for treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr Drug Discov Technol 4(1):39–47
El Amrani F, Rhallab A, Alaoui T, El Badaoui K, Chakir S (2009) Hypoglycaemic effect of Thymelaea hirsuta in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Med Plant Res 3(9):625–629
Baynes JW, Thorpe SR (1999) Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 48(1):1–9
San Tang K (2019) The current and future perspectives of zinc oxide nanoparticles in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Life Sci 239:117011
Martínez-Esquivias F, Guzmán-Flores JM, Pérez-Larios A, Rico JL, Becerra-Ruiz JS (2021) A review of the effects of gold, silver, selenium, and zinc nanoparticles on diabetes mellitus in murine models. Mini Rev Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557521666210203154024
Sengottaiyan A, Aravinthan A, Sudhakar C, Selvam K, Srinivasan P, Govarthanan M, Manoharan K, Selvankumar T (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Solanum nigrum-mediated silver nanoparticles and its protective effect on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry 6(1):41–48
Satyavani K, Gurudeeban S, Ramanathan T, Balasubramanian T (2011) Biomedical potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized from calli cells of Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad. J Nanobiotechnology 9(1):43
Ansari MA, Khan HM, Khan AA, Alzohairy MA, Waseem M, Ahmad MK, Mahdi AA (2016) Biochemical, histopathological, and transmission electron microscopic ultrastructural changes in mice after exposure to silver nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol 31(8):945–956. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22104
Oberdörster G, Ferin J, Finkelstein G, Wade P, Corson N (1990) Increased pulmonary toxicity of ultrafine particles? II Lung lavage studies. J Aerosol Sci 21(3):384–387
Liu Y-C, Lin L-H (2004) New pathway for the synthesis of ultrafine silver nanoparticles from bulk silver substrates in aqueous solutions by sonoelectrochemical methods. Electrochem Commun 6(11):1163–1168
Bae CH, Nam SH, Park SM (2002) Formation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation of a silver target in NaCl solution. Appl Surf Sci 197:628–634
Basavaraja S, Balaji S, Lagashetty A, Rajasab A, Venkataraman A (2008) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium semitectum. Mater Res Bull 43(5):1164–1170
Jha AK, Prasad K (2010) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cycas leaf. International Journal of Green Nanotechnology: Physics and Chemistry 1(2):P110–P117
Alkaladi A, Abdelazim AM, Afifi M (2014) Antidiabetic activity of zinc oxide and silver nanoparticles on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Mol Sci 15(2):2015–2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15022015
Malapermal V, Botha I, Krishna SBN, Mbatha JN (2017) Enhancing antidiabetic and antimicrobial performance of Ocimum basilicum, and Ocimum sanctum (L.) using silver nanoparticles. Saudi J Biol Sci 24(6):1294–1305
Furchner JE, Richmond CR, Drake GA (1968) Comparative metabolism of radionuclides in mammals-IV. Retention of silver-110m in the mouse, rat, monkey, and dog. Health Phys 15(6):505–514. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-196812000-00005
Nefzger M, Kreuter J, Voges R, Liehl E, Czok R (1984) Distribution and elimination of polymethyl methacrylate nanoparticles after peroral administration to rats. J Pharm Sci 73(9):1309–1311. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600730934
Gaillet S, Rouanet JM (2015) Silver nanoparticles: their potential toxic effects after oral exposure and underlying mechanisms–a review. Food Chem Toxicol 77:58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.12.019
Loeschner K, Hadrup N, Qvortrup K, Larsen A, Gao X, Vogel U, Mortensen A, Lam HR, Larsen EH (2011) Distribution of silver in rats following 28 days of repeated oral exposure to silver nanoparticles or silver acetate. Part Fibre Toxicol 8:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-8-18
van der Zande M, Vandebriel RJ, Van Doren E, Kramer E, Herrera Rivera Z, Serrano-Rojero CS, Gremmer ER, Mast J, Peters RJB, Hollman PCH, Hendriksen PJM, Marvin HJP, Peijnenburg AACM, Bouwmeester H (2012) Distribution, elimination, and toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in rats after 28-day oral exposure. ACS Nano 6(8):7427–7442. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn302649p
Hyun JS, Lee BS, Ryu HY, Sung JH, Chung KH, Yu IJ (2008) Effects of repeated silver nanoparticles exposure on the histological structure and mucins of nasal respiratory mucosa in rats. Toxicol Lett 182(1–3):24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.08.003
Kim YS, Kim JS, Cho HS, Rha DS, Kim JM, Park JD, Choi BS, Lim R, Chang HK, Chung YH, Kwon IH, Jeong J, Han BS, Yu IJ (2008) Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhalation Toxicol 20(6):575–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/08958370701874663
Macleod MR, O’Collins T, Howells DW, Donnan GA (2004) Pooling of animal experimental data reveals influence of study design and publication bias. Stroke 35(5):1203–1208
Nouri Z, Hajialyani M, Izadi Z, Bahramsoltani R, Farzaei MH, Abdollahi M (2020) Nanophytomedicines for the prevention of metabolic syndrome: a pharmacological and biopharmaceutical review. Frontiers Bioeng Biotechnol 8:425. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00425
Masood N, Ahmed R, Tariq M, Ahmed Z, Masoud MS, Ali I, Asghar R, Andleeb A, Hasan A (2019) Silver nanoparticle impregnated chitosan-PEG hydrogel enhances wound healing in diabetes induced rabbits. Int J Pharm 559:23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.01.019
Monteiro DR, Gorup LF, Takamiya AS, Ruvollo-Filho AC, de Camargo ER, Barbosa DB (2009) The growing importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion: antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int J Antimicrob Agents 34(2):103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.01.017
Coma V (2013) Polysaccharide-based biomaterials with antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Polímeros 23(3):287–297
Mostafavian Z, Ghareh S, Torabian F, Yazdi MS, Khazaei MR (2018) Corrigendum to “Data on insulin therapy refusal among type II diabetes mellitus patients in Mashhad, Iran” [Data in Brief 18 (2018) 2047–2050]. Data Brief 19:2487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.07.024
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, Edwards R, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Bull S, Cannon CP, Capuano G, Chu PL, de Zeeuw D, Greene T, Levin A, Pollock C, Wheeler DC, Yavin Y, Zhang H, Zinman B, Meininger G, Brenner BM, Mahaffey KW (2019) Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 380(24):2295–2306. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1811744
Attanayake AP, Jayatilaka KA, Pathirana C, Mudduwa LK (2013) Study of antihyperglycaemic activity of medicinal plant extracts in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Anc Sci Life 32(4):193–198. https://doi.org/10.4103/0257-7941.131970
Sung JH, Ji JH, Park JD, Yoon JU, Kim DS, Jeon KS, Song MY, Jeong J, Han BS, Han JH, Chung YH, Chang HK, Lee JH, Cho MH, Kelman BJ, Yu IJ (2009) Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 108(2):452–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn246
Choi JE, Kim S, Ahn JH, Youn P, Kang JS, Park K, Yi J, Ryu DY (2010) Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by silver nanoparticles in the liver of adult zebrafish. Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 100(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.12.012
Xue Y, Zhang S, Huang Y, Zhang T, Liu X, Hu Y, Zhang Z, Tang M (2012) Acute toxic effects and gender-related biokinetics of silver nanoparticles following an intravenous injection in mice. J Appl Toxicol: JAT 32(11):890–899. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2742
Prabhu S, Vinodhini S, Elanchezhiyan C, Rajeswari D (2018) Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Pouteria sapota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes 10(1):28–42
Fröde TS, Medeiros YS (2008) Animal models to test drugs with potential antidiabetic activity. J Ethnopharmacol 115(2):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.038
Umrani RD, Paknikar KM (2014) Zinc oxide nanoparticles show antidiabetic activity in streptozotocin- induced type 1 and 2 diabetic rats. Nanomedicine 9(1):89–104. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.12.205
Chausmer AB (1998) Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 17(2):109–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.1998.10718735
Ramaiah SK (2007) A toxicologist guide to the diagnostic interpretation of hepatic biochemical parameters. Food Chem Toxicol 45(9):1551–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.06.007
Johnston DE (1999) Special considerations in interpreting liver function tests. Am Fam Physician 59(8):2223–2230
Pandey MM, Rastogi S, Rawat AK (2013) Indian traditional ayurvedic system of medicine and nutritional supplementation. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine :eCAM 2013:376327. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/376327
Ji JH, Bae G-N, Yun SH, Jung JH, Noh HS, Kim SS (2007) Evaluation of a silver nanoparticle generator using a small ceramic heater for inactivation of S. epidermidis bioaerosols. Aerosol Sci Technol 41(8):786–793
Braydich-Stolle L, Hussain S, Schlager JJ, Hofmann MC (2005) In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci 88(2):412–419. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfi256
Tang J, Xiong L, Wang S, Wang J, Liu L, Li J, Yuan F, Xi T (2009) Distribution, translocation and accumulation of silver nanoparticles in rats. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9(8):4924–4932. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.1269
Borm PJ, Kreyling W (2004) Toxicological hazards of inhaled nanoparticles–potential implications for drug delivery. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 4(5):521–531. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2004.081
Chrastina A, Schnitzer JE (2010) Iodine-125 radiolabeling of silver nanoparticles for in vivo SPECT imaging. Int J Nanomed 5:653–659. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s11677
Furchner J, Richmond C, Drake G (1968) Comparative metabolism of radionuclides in mammals-IV. Retention of silver-110m in the mouse, rat, monkey, and dog. Health Phy 15(6):505–514
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the research council of the Mashhad University of Medical Sciences for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Farnaz Torabian: Writing original draft, review, and editing. Arash Akhavan Rezayat: Writing original draft, review, and editing. Mohammad Ghasemi Nour: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, review, and editing, funding, and resources acquisition. Atefeh Ghorbanzadeh: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, review, and editing, funding, and resources acquisition. Sara Najafi: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, review, and editing, funding, and resources acquisition. Amirhossein Sahebkar: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, review, and editing, funding, and resources acquisition. Zahra Sabouri: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, review, and editing, funding, and resources acquisition. Majid Darroudi: Supervision, project administration, review and editing, funding, and resources acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
For this type of study, ethical approval is not required.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torabian, F., Akhavan Rezayat, A., Ghasemi Nour, M. et al. Administration of Silver Nanoparticles in Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on Animal Studies. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 1699–1709 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02776-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02776-1