Abstract
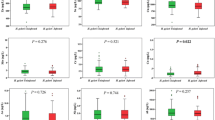
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is known as the most common cause of worldwide common chronic gastritis. Pathogenic mechanisms caused by H. pylori in diseases are still not fully understood. In addition, it has been reported that H. pylori can alter gene expressions in infected tissues and affect transcription factor activation. It is reported that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), which is a cytoplasmic transcription factor, functions in the immune system and plays a role in immune cells in barrier organs such as the gastrointestinal system, skin, and lungs. H. pylori infection affects the absorption of micronutrients such as trace elements, minerals, and vitamins by disrupting gastric secretion and acidification functions. Zinc (Zn) trace element is thought to be able to modulate the induction of AhR-responsive genes in endothelial cells. Although it is emphasized that trace elements are related with gastritis, relationship between Zn and AhR is not fully known, especially in chronic gastritis accompanied by H. pylori infection. In this study, serum levels of AhR, Zn, and AhR antagonist vitamin B12 were determined in chronic gastritis with H. pylori infection. Fifty volunteers diagnosed with H. pylori positive and negative chronic gastritis were included in this study. Collected from individuals participating were 5 ml of venous blood samples, and their serums were separated. AhR serum level of the study group was determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method. Zn concentrations in serum samples were measured using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. When AhR and Zn serum levels were compared in H. pylori positive and negative chronic gastritis patients, it was found that AhR serum level of H. pylori positive chronic gastritis patients increased but it was not statistically significant (p = 0.595). However it was determined Zn and B12 serum levels were statistically significantly decreased (p < 0.001). This study has a crucial importance since to be the first one investigating relationship between serum AhR, Zn, and vitamin B12 levels in the pathogenesis of H. pylori gastritis in adults. Examination of AhR, Zn and B12 levels in H. pylori positive gastritis patients contributes to elucidating molecular mechanism of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fock KM, Graham DY, Malfertheiner P (2013) Helicobacter pylori research: historical insights and future directions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:495
Varbanova M, Frauenschläger K, Malfertheiner P (2014) Chronic gastritis–an update. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 28:1031–1042
Kudo T, Lu H, Wu J, Ohno T, Wu MJ, Genta RM, Graham DY, Yamaoka Y (2007) Pattern of transcription factor activation in Helicobacter pylori–infected Mongolian gerbils. Gastroenterology 132:1024–1038
Chiou CC, Chan CC, Sheu DL, Chen KT, Li YS, Chan EC (2001) Helicobacter pylori infection induced alteration of gene expression in human gastric cells. Gut 48:598–604
Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Quintana FJ (2018) Regulation of the immune response by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Immunity 48:19–33
Rothhammer V, Quintana FJ (2019) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: an environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 19:184–197
Dantsuka A, Ichii O, Hanberg A, Elewa YHA, Otsuka-Kanazawa S, Nakamura T, Kon Y (2019) Histopathological features of the proper gastric glands in FVB/N-background mice carrying constitutively-active aryl-hydrocarbon receptor. BMC Gastroenterol 19:102
Park W, Jun DW, Kim JT, Jeong JH, Park H, Chang Y, Park KS, Lee HK, Pak YK (2013) Novel cell-based assay reveals associations of circulating serum AhR-ligands with metabolic syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biofactors 39:494–504
Esser C, Rannug A (2015) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology and toxicology. Pharmacol Rev 67:259–279
Zhu R, Gao C, Wang L, Zhang G, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Shen L, Wang S (2018) Involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor in Helicobacter pylori-related gastric pathogenesis. J Cancer 9:2757
Akçam M (2010) Helicobacter pylori and micronutrients. Indian Pediatr 47:119–126
Cavalcoli F, Zilli A, Conte D, Massironi S (2017) Micronutrient deficiencies in patients with chronic atrophic autoimmune gastritis: a review. World J Gastroenterol 23:563
Cousins RJ, Blanchard RK, Moore JB, Cui L, Green CL, Liuzzi JP, Cao J, Bobo JA (2003) Regulation of zinc metabolism and genomic outcomes. J Nutr 133:1521S–1526S
Öztürk N, Kurt N, Özgeriş FB, Baygutalp NK, Tosun MS, Bakan N, Bakan E (2015) Serum zinc, copper, magnesium and selenium levels in children with helicobacter pylori infection. Eur J Med 47:126
Klug A, Schwabe JWR (1995) Zinc fingers. FASEB J 9:597–604
Gammoh NZ, Rink L (2017) Zinc in infection and inflammation. Nutrients 9:624
Marjanović K, Dovhanj J, Kljaić K, Šakić K, Kondža G, Tadžić R, Včev A (2010) Role of zinc in chronic gastritis. Coll Antropol 34:599–603
Molodovets O, Pozur N, Glushko L, Fedorov S, Gavrysh T, Chaplynska N (2013) The features of trace elements metabolism in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. Pharm Innov 2:49
Dovhanj J, Kljaic K, Dodig-Curkovic K, Curkovic M, Volarevic M, Marjanovic K (2009) Helicobacter pylori, zinc and iron in oxidative stress-induced injury of gastric mucosa. Mini-Rev Med Chem 9:26–30
Shen H, Arzuaga X, Toborek M, Hennig B (2008) Zinc nutritional status modulates expression of AhR-responsive P450 enzymes in vascular endothelial cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 25:197–201
Dovhanj J, Kljaic K, Vcev A, Ilakovac V (2010) Helicobacter pylori and trace elements. Clin Lab 56:137–142
Ikuta T, Kawajiri K (2006) Zinc finger transcription factor Slug is a novel target gene of aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Cell Res 312:3585–3594
O’Leary F, Samman S (2010) Vitamin B12 in health and disease. Nutrients 2:299–316
Mahmood L (2014) The metabolic processes of folic acid and vitamin B12 deficiency. J Health Res Rev 1:5
Raut SC, Chandel RS (2014) Comparison of vitamin B12 levels in gastritis with and without H. pylori. Walawalkar Int Med J 1:28–32
Civan HA (2020) Vitamin B12 status in children with Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Med J Bakirkoy 16:120–124
Kim DJ, Venkataraman A, Jain PC, Wiesler EP, DeBlasio M, Klein J, Tu SS, Lee S, Medzhitov R, Iwasaki A (2020) Vitamin B12 and folic acid alleviate symptoms of nutritional deficiency by antagonizing aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117:15837–15845
Santos MLC, de Brito BB, da Silva FAF, Sampaio MM, Marques HS, e Silva NO, de Magalhães Queiroz DM, de Melo FF (2020) Helicobacter pylori infection: beyond gastric manifestations. World J Gastroenterol 26:4076
Reiterer G, Toborek M, Hennig B (2006) Zinc and cell signaling during inflammation: implications in atherosclerosis. Curr Nutr Food Sci 2:23–28
Yakoob J, Abbas Z, Jafri W, Usman MW, Awan S (2014) Zinc chloride inhibits Helicobacter pylori growth and reduces expression of interleukinβ by gastric epithelial cells. Br J Biomed Sci 71:43–45
Christudoss P, Selvakumar R, Fleming JJ, Mathew G (2010) Zinc levels in paired normal and malignant human stomach and colon tissue. Biomed Res 21:4
Zhang W-H, Wu X-J, Niu J-X, Yan H, Wang X-Z, Yin X-D, Pang Y (2012) Serum zinc status and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric disease patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13:5043–5046
Sempértegui F, Diaz M, Mejia R, Rodríguez-Mora OG, Rentería E, Guarderas C, Estrella B, Recalde R, Hamer DH, Reeves PG (2007) Low concentrations of zinc in gastric mucosa are associated with increased severity of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Helicobacter 12:43–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed the study. SE collected samples; DDE and NPO measured trace element; AS and GK measured AhR level; AS, DDE, and GK drafted manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soyocak, A., Ergun, D.D., Koc, G. et al. Investigation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, Zinc, and Vitamin B12 Levels in Chronic Gastritis with Helicobacter pylori Infection. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 2431–2437 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02667-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02667-5