Abstract
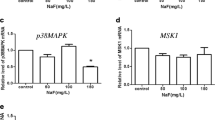
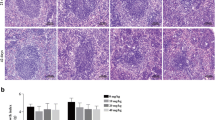
To investigate the mechanism of fluoride-induced splenic toxicity, 0, 25, 50, and 100 mg/L sodium fluoride (NaF) were administered in male mice via drinking water for 90 days. After NaF treatment, the histological structure of the spleen, the proportion of helper T 1 cell (Th1) and helper T 2 cell (Th2), and the relative expression levels of cytokines and T-bet and GATA3 were analyzed. The results showed that 50 and 100 mg/L NaF consumption can change the normal structure of mouse spleen and the proportion of Th1/Th2 cells. It also decreased the mRNA expression levels of IL-2, INF-γ, and TGF-β, but increased the levels of IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10. Importantly, fluoride increased the protein expression of GATA3 but decreased the expression of T-bet. Our findings indicate that superfluous fluoride intake damages the balance of Th1/Th2 cells by changing the levels of T-bet and GATA3 in the spleen, and further changes the expression of Th1/Th2 cell-related cytokines in the spleen microenvironment, eventually leading to spleen injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buzalaf MAR (2018) Review of fluoride intake and appropriateness of current guidelines. Adv Dent Res 29(2):157–166
Tayibi H, Choura M, Lopez FA, Alguacil FJ, Lopez-Delgado A (2009) Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J Environ Manag 90(8):2377–2386
Niu R, Xue X, Zhao Y, Sun Z, Yan X, Li X, Feng C, Wang J (2015) Effects of fluoride on microtubule ultrastructure and expression of Tubalpha1a and Tubbeta2a in mouse hippocampus. Chemosphere. 139:422–427
Sun Z, Nie Q, Zhang L, Niu R, Wang J, Wang S (2017) Fluoride reduced the immune privileged function of mouse Sertoli cells via the regulation of Fas/FasL system. Chemosphere. 168:318–325
Wang HW, Miao CY, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhu SQ, Zhou BH (2019) Fluoride-induced rectal barrier damage and microflora disorder in mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(7):7596–7607
Shi Z, Zhan Y, Zhao J, Wang J, Ma H (2016) Effects of fluoride on the expression of p38MAPK signaling pathway-related genes and proteins in spleen lymphocytes of mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 173(2):333–338
Ma Y, Zhang K, Ren F, Wang J (2017) Developmental fluoride exposure influenced rat’s splenic development and cell cycle via disruption of the ERK signal pathway. Chemosphere. 187:173–180
Kuang P, Guo H, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2019) Sodium fluoride impairs splenic innate immunity via inactivation of TLR2/MyD88 signaling pathway in mice. Chemosphere. 237:124437
Deng H, Kuang P, Cui H, Chen L, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Wang X, Zhao L (2016) Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis in cultured splenic lymphocytes from mice. Oncotarget. 7(42):67880–67900
Lv Y, Li Y, Liu N, Dong Y, Deng J (2019) Investigation into imbalance of Th1/Th2 cells in cirrhotic, hypersplenic rats. J Int Med Res:300060519889441. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519889441
Kidd P (2003) Th1/Th2 balance: the hypothesis, its limitations, and implications for health and disease. Altern Med Rev 8(3):223–246
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gu W, Sun B (2014) TH1/TH2 cell differentiation and molecular signals. Adv Exp Med Biol 841:15–44
Heo Y, Lee WT, Lawrence DA (1998) Differential effects of lead and cAMP on development and activities of Th1- and Th2-lymphocytes. Toxicol Sci 43(2):172–185
Wang H, Zhou B, Niu R, Wang J, Zhang J, Wang J (2017) Analysis of the roles of dietary protein and calcium in fluoride-induced changes in T-lymphocyte subsets in rat. Environ Toxicol 32(5):1587–1595
Yang L, Jin P, Wang X, Zhou Q, Lin X, Xi S (2018) Fluoride activates microglia, secretes inflammatory factors and influences synaptic neuron plasticity in the hippocampus of rats. Neurotoxicology. 69:108–120
Liu J, Wang HW, Zhao WP, Li XT, Lin L, Zhou BH (2019) Induction of pathological changes and impaired expression of cytokines in developing female rat spleen after chronic excess fluoride exposure. Toxicol Ind Health 35(1):43–52
Kreipe HH (2019) Neuroendocrine differentiation in breast cancer. Pathologe. 40(Suppl 3):325–330
Onodera A, Kokubo K, Nakayama T (2018) Epigenetic and transcriptional regulation in the induction, maintenance, heterogeneity, and recall-response of effector and memory Th2 cells. Front Immunol 9:2929
Hammam AA, Ezzat DA, Elwahab MH (2016) Differential expression of T-bet and GATA3 in Egyptian children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 32(4):460–467
Kardan M, Rafiei A, Ghaffari J, Valadan R, Morsaljahan Z, Haj-Ghorbani ST (2019) Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-γt in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with allergic asthma. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 47(4):378–385
Chen C, Su X, Hu Z (2019) Immune promotive effect of bioactive peptides may be mediated by regulating the expression of SOCS1/miR-155. Exp Ther Med 18(3):1850–1862
Pramanik S, Saha D (2017) The genetic influence in fluorosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 56:157–162
Li GS, Jing L, Xu H (2005) Progress of study on endemic fluorosis. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 34(10):632–634
Perumal E, Paul V, Govindarajan V, Panneerselvam L (2013) A brief review on experimental fluorosis. Toxicol Lett 223(2):236–251
Dubnika A, Manoukian MAC, Mohammadi MR, Parekh MB, Gurjarpadhye AA, Inayathullah M, Dubniks V, Lakey JRT, Rajadas J (2018) Cytokines as therapeutic agents and targets in heart disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 43:54–68
Wu TT, Li WM, Yao YM (2016) Interactions between autophagy and inhibitory cytokines. Int J Biol Sci 12(7):884–897
Rutz S, Ouyang W (2016) Regulation of interleukin-10 expression. Adv Exp Med Biol 941:89–116
Singh R, Alape D, de Lima A, Ascanio J, Majid A, Gangadharan SP (2019) Regulatory T cells in respiratory health and diseases. Pulm Med 2019:1907807
Xiao K, Zou WH, Yang Z, Rehman ZU, Ansari AR, Yuan HR, Zhou Y, Cui L, Peng KM, Song H (2015) The role of visfatin on the regulation of inflammation and apoptosis in the spleen of LPS-treated rats. Cell Tissue Res 359(2):605–618
Fang D, Zhu J (2017) Dynamic balance between master transcription factors determines the fates and functions of CD4 T cell and innate lymphoid cell subsets. J Exp Med 214(7):1861–1876
Stadhouders R, Lubberts E, Hendriks RW (2018) A cellular and molecular view of T helper 17 cell plasticity in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 87:1–15
Sopel N, Graser A, Mousset S, Finotto S (2016) The transcription factor BATF modulates cytokine-mediated responses in T cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 30:39–45
Van Gool F, Nguyen MLT, Mumbach MR, Satpathy AT, Rosenthal WL, Giacometti S, Le DT, Liu W, Brusko TM, Anderson MS, Rudensky AY, Marson A, Chang HY, Bluestone JA (2019) A mutation in the transcription factor Foxp3 drives T helper 2 effector function in regulatory T cells. Immunity 50(2):362–377.e6
Maehara T, Moriyama M, Kawano S, Hayashida JN, Furukawa S, Ohta M, Tanaka A, Yamauchi M, Ohyama Y, Kiyoshima T, Nakamura S (2015) Cytokine profiles contribute to understanding the pathogenic difference between good syndrome and oral lichen planus: two case reports and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(14):e704
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31672623) and Veterinary Environmental Lab (Shanxi Key Lab).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Du, X., Zhao, Y. et al. Fluoride Can Damage the Spleen of Mice by Perturbing Th1/Th2 Cell Balance. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 1493–1500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02264-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02264-y