Abstract
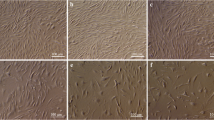
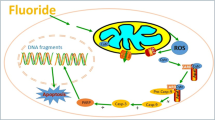
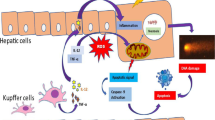
The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the toxicity of fluoride to tumor cells was investigated by culturing Hepa1-6 cells in medium containing gradient concentrations of fluoride (0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mmol/L). The viability of Hepa1-6 cells was detected via MTT assay. Interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-1β levels in the supernatant were determined via an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the protein expression levels of these enzymes in Hepa1-6 cells were evaluated by immunofluorescence staining. Results showed that the viability of Hepa1-6 cells remarkably decreases after fluoride exposure, especially at concentration of 3, 4, and 5 mmol/L fluoride. Levels of IL-2, TNF-α, and IL-1β in the supernatant markedly decreased when cells were exposed to fluoride at concentrations of 1 mmol/L or higher. However, levels of TNF-α and IL-1β substantially increased and IL-2 showed no remarkable change when the fluoride concentration was 0.5 mmol/L. The content of IL-6 remarkably increased with increasing fluoride concentrations up to 2 mmol/L, and then markedly decreased at 3, 4, and 5 mmol/L fluoride; the decreasing trend of IL-6 content under high fluoride exposure is consistent with the decrease in Hepa1-6 cell viability observed at the same concentration. The protein expression levels of IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β were in accordance with their contents in the supernatant. In summary, our study demonstrated that fluoride inhibits Hepa1-6 cell growth and results in disorders in the expression and secretion pro-inflammatory cytokines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun ZL, Xue XC, Zhang YL, Niu RY, Wang JD (2017) Effect of sodium fluoride on the sperm mitochondrial DNA in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 492(3):295–299
Niu RY, Wang JM, Sun ZL, Xue XC, Yan XY, Wang JM, Zhang JH, Wang JD (2015) Transcriptional regulatory dynamics of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis in male mice exposed to fluoride. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(2):557–562
Singh R, Khatri P, Srivastava N, Jain S, Brahmachari V, Mukhopadhyay A, Mazumder S (2017) Fluoride exposure abates pro-inflammatory response and induces in vivo apoptosis rendering zebrafish (Danio rerio) susceptible to bacterial infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 63:314–321
Niu RY, Han HJ, Zhang YL, Wang JM, Zhang JH, Yin W, Yin XF, Sun ZL, Wang JD (2016) Changes in liver antioxidant status of offspring mice induced by maternal fluoride exposure during gestation and lactation. Biol Trace Elem Res 172(1):172–178
Kuang P, Deng HD, Cui HM, Chen L, Fang J, Zuo ZC, Deng JL, Wang X, Zhao L (2017) Sodium fluoride (NaF) causes toxic effects on splenic development in mice. Oncotarget 8(3):4703–4717
Tian YH, Huo MJ, Li GS, Li YY, Wang JD (2016) Regulation of LPS-induced mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines via alteration of NF-κB activity in mouse peritoneal macrophages exposed to fluoride. Chemosphere 161:89–95
Kuang P, Deng HD, Cui HM, Chen L, Guo HR, Fang J, Zuo ZC, Deng JL, Wang X, Zhao L (2016) Suppressive effects of sodium fluoride on cultured splenic lymphocyte proliferation in mice. Oncotarget 7(38):61905–61915
Sun ZL, Nie QL, Zhang LJ, Niu RY, Wang JD, Wang SL (2017) Fluoride reduced the immune privileged function of mouse Sertoli cells via the regulation of Fas/FasL system. Chemosphere 168:318–325
Parkin J, Cohen B (2001) An overview of the immune system. Lancet 357(9270):1777–1789
Davidi S, Fremder E, Kan T, Raviv Z, Timaner M, Karin N, Hershkovitz D, Arohneim A, Shaked Y (2017) The antiangiogenic role of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-31. Oncotarget 8(10):16430–16444
Nasef NA, Mehta S, Ferguson LR (2017) Susceptibility to chronic inflammation: an update. Arch Toxicol 91(3):1131–1141
Mendoza-Rodríguez M, Romero HA, Fuentes-Panana EM, Ayala-Sumuano JT, Meza I (2017) IL-1β induces up-regulation of BIRC3, a gene involved in chemoresistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 390:39–44
Shen J, Liu YL, Ren XC, Gao K, Li YL, Li SZ, Yao JH, Yang XJ (2016) Changes in DNA methylation and chromatin structure of pro-inflammatory cytokines stimulated by LPS in broiler peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Poultry Sci 95(7):1636–1645
Wijekoon S, Bwalya EC, Fang J, Kim S, Hosoya K, Okumura M (2017) Chronological differential effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines on RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of canine bone marrow-derived macrophages. J Vet Med Sci 79(12):2030–2035
Demaria S, Pikarsky E, Karin M et al (2010) Cancer and inflammation: promise for biological therapy. J Immunother 33(4):335
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A, Bhatt AN (2016) Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumor Biol 37(9):11553–11572
Reichert TE, Watkins S, Stanson J, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (1998) Endogenous IL-2 in cancer cells: a marker of cellular proliferation. J Histochem Cytochem 46(5):603–611
Antony GK, Dudek AZ (2010) Interleukin 2 in cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem 17(29):3297–3302
Sun KH, Sun GH, Wu YC, Ko BJ, Hsu HT, Wu ST (2016) TNF-α augments CXCR 2 and CXCR 3 to promote progression of renal cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 20(11):2020–2028
Li XN, Zuo YZ, Qin L, Liu W, Li YH, Li JL (2018) Atrazine-xenobiotic nuclear receptor interactions induce cardiac inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in quail (Coturnix coturnix coturnix). Chemosphere 206:549–559
Ochoa CD, Wu RF, Terada LS (2018) ROS signaling and ER stress in cardiovascular disease. Mol Aspects Med 63:18–29
Wang HW, Liu J, Zhao WP, Zhang ZH, Li SQ, Li SH, Zhu SQ, Zhou BH (2019) Effect of fluoride on small intestine morphology and serum cytokine contents in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 189(2):511–518
Wang HW, Zhou BH, Cao JW, Zhao J, Zhao WP, Tan PP (2017) Pro-inflammatory cytokines are involved in fluoride-induced cytotoxic potential in HeLa cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 175(1):98–102
Sharma D, Singh A, Verma K, Paliwal S, Sharma S, Dwivedi J (2017) Fluoride: a review of pre-clinical and clinical studies. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 56:297–313
Zhou BH, Tan PP, Jia LS, Zhao WP, Wang JC, Wang HW (2018) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway involvement in fluoride-induced apoptosis in C2C12 cells. Chemosphere 199:297–302
Boshtam M, Asgary S, Kouhpayeh S, Shariati L, Khanahmad H (2017) Aptamers against pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines: a review. Inflammation 40(1):340–349
Luo Q, Cui HM, Deng HD, Kuang P, Liu H, Lu YJ, Fang J, Zuo ZC, Deng JL, Li YL, Wang X, Zhao L (2017) Sodium fluoride induces renal inflammatory responses by activating NF-κB signaling pathway and reducing anti-inflammatory cytokine expression in mice. Oncotarget 8(46):80192–80207
Gaffen SL, Liu KD (2004) Overview of interleukin-2 function, production and clinical applications. Cytokine 28(3):109–123
Li Y, Strick-Marchand H, Lim AI, Ren JZ, Masse-Ranson G, Li D, Jouvion G, Rogge L, Lucas S, Li B, Di Santo JP (2017) Regulatory T cells control toxicity in a humanized model of IL-2 therapy. Nat Commun 8(1):1762
Zhao XN, Wang YG, Yan P, Cheng GD, Wang C, Geng N, Wang XP, Liu JZ (2017) Effects of polysaccharides from Platycodon grandiflorum on immunity-enhancing activity in vitro. Molecules 22(11):1918
Singh R, Hussain MA, Kumar J, Kumar M, Kumari U, Mazumder S (2017) Chronic fluoride exposure exacerbates headkidney pathology and causes immune commotion in Clarias gariepinus. Aquat Toxicol 192:30–39
Naugler WE, Karin M (2008) The wolf in sheep’s clothing: the role of interleukin-6 in immunity, inflammation and cancer. Trends Mol Med 14(3):109–119
Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, Maeda S, Kim K, Elsharkawy AM, Karin M (2007) Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science 317(5834):121–124
Zhao J, Lawless MW (2013) Stop feeding cancer: pro-inflammatory role of visceral adiposity in liver cancer. Cytokine 64(3):626–637
Park EJ, Lee JH, Yu GY, He G, Ali SR, Holzer RG, Österreicher CH, Takahashi H, Karin M (2010) Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell 140(2):197–208
Apte RN, Voronov E (2017) Immunotherapeutic approaches of IL-1 neutralization in the tumor microenvironment. J Leukoc Biol 102(2):293–306
Bonomi M, Patsias A, Posner M, Sikora A (2014) The role of inflammation in head and neck cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 816:107–127
Acknowledgments
This work is sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31201963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhou, Bh., Tan, Pp. et al. Key Role of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in the Toxic Effect of Fluoride on Hepa1-6 Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 197, 115–122 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01967-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01967-1