Abstract
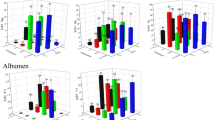
This paper focuses on negative effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on element content in male chicken calvaria and α-tocopherol (vitamin E) ability to reduce its toxic potential on bone mineralization in offspring. In the experiment carried out once, a solution containing only DMSO, TCDD, TCDD + α-tocopherol, and exclusively α-tocopherol was administrated. Subsequently, on the 5th day after hatching, the mineral composition of the chicken calvaria was evaluated. The results obtained suggest that the use of α-tocopherol contributes to the maintenance of the concentration of calcium, magnesium, and manganese in the chicken calvaria treated with TCDD in the embryonic period. In turn, vitamin E increases the level of zinc. It has been found that α-tocopherol in chicken embryos has a protective effect against disturbance of level of chosen trace elements in the bones of offspring caused by the TCDD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viluksela M, Bager Y, Tuomisto JT, Scheu G, Unkila M, Pohjanvirta R, Flodstrom S, Kosma V, Maki-Paakkanen J, Vartiainen T, Klimm C, Schramm KW, Warnard L, Tuomisto J (2006) Liver tumor-promoting activity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in TCDD-sensitive and TCDD-resistant rat strains. Cancer Res 60:1660–1667
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (1997) Polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 69:33–343
Calkosinski I, Gostomska-Pampuch K, Majda J, Leskow A, Janeczek M, Melnyk OP, Gamian A (2017) The influence of α-tocopherol on serum biochemical markers during experimentally induced pleuritis in rats exposed to dioxin. Inflammation 40:913–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0536-2
Dobrzyński M, Kaczmarek U, Kuropka P, Reichert P, Grzech-Leśniak K, Całkosiński I (2017) Tooth development disorders in infants of rat dams exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and protective role of tocopherol and acetylsalicylic acid. Pol J Vet Sci 20:769–778. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjvs-2017-0097
Hites RA (2011) Dioxins: an overview and history. Environ Sci Technol 45:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1013664
Fiedler H, Hutzinger O, Timms CW (1990) Dioxins: sources of environmental load and human exposure. Toxicol Environ Chem 29:157–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772249009357628
Calkosinski I, Rosinczuk-Tonderys J, Bronowicka-Szydełko A, Dzierzba K, Bazan J, Dobrzynski M, Majda J, Gamian A (2015) Effect of tocopherol on biochemical blood parameters in pleuritis-induced rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Ind Health 31:510–522. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713475497
Skinner MK, Manikkam M, Guerrero-Bosagna C (2010) Epigenetic transgenerational actions of environmental factors in disease etiology. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2009.12.007
Manikkam M, Tracey R, Guerrero-Bosagna C, Skinner MK (2012) Dioxin (TCDD) induces epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of adult onset disease and sperm epimutations. PLoS One 7:e46249. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046249
Sorg O, Zennegg M, Schmid P, Fedosyuk R, Valikhnovskyi R, Gaide O, Kniazevych V, Saurat J-H (2009) 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) poisoning in Victor Yushchenko: identification and measurement of TCDD metabolites. Lancet 374:1179–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60912-0
Sonne C, Leifsson PS, Dietz R, Born EW, Letcher RJ, Hyldstrup L, Riget FF, Kirkegaard M, Muir DCG (2006) Xenoendocrine pollutants may reduce size of sexual organs in East Greenland polar bears (Ursus maritimus). Environ Sci Technol 40:5668–5674. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES060836N
Zober A, Ott MG, Messerer P (1994) Morbidity follow up study of BASF employees exposed to 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) after a 1953 chemical reactor incident. Occup Environ Med 51:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1136/OEM.51.7.479
Centre ICE (2000) Dioxins in the environment: what are the health risks? Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale
Grochowalski A, Lassen C, Holtzer M, Sadowski M, Hudyma T (2007) Determination of PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and HCB emissions from the metallurgical sector in Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res - Int 14:326–332. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2006.05.303
Calkosinski I, Rosinczuk-Tonderys J, Bazan J, Dobrzyński M, Bronowicka-Szydełko A, Dzierzba K (2014) The influence of dioxin intoxication on the human system and possibilities of limiting its negative effects on the environment and living organisms. Ann Agric Environ Med 21:518–524. https://doi.org/10.5604/12321966.1120594
Bánáti D (2011) Consumer response to food scandals and scares. Trends Food Sci Technol 22:56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2010.12.007
Kloser E, Böhmdorfer S, Brecker L, Kählig H, Netscher T, Mereiter K, Rosenau T (2011) Synthesis of 5-(fluorophenyl)tocopherols as novel dioxin receptor antagonists. European J Org Chem 2011:2450–2457. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201100178
Gostomska-Pampuch K, Ostrowska A, Kuropka P, Dobrzyński M, Ziółkowski P, Kowalczyk A, Łukaszewicz E, Gamian A, Całkosiński I (2017) Protective effects of levamisole, acetylsalicylic acid, and α-tocopherol against dioxin toxicity measured as the expression of AhR and COX-2 in a chicken embryo model. Histochem Cell Biol 147:523–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1528-2
Ostrowska A, Gostomska-Pampuch K, Leśków A, Kuropka P, Gamian E, Ziółkowski P, Kowalczyk A, Łukaszewicz E, Gamian A, Całkosiński I (2017) Expression of advanced glycation end-products and NFκB in chick embryos exposed to dioxins and treated with acetylsalicylic acid and α-tocopherol. Poult Sci 96:1874–1883. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pew450
Chaffin CL, Hutz RJ (1997) Regulation of the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) by in-utero and lactational exposure to 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). J Reprod Dev 43:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.43.47
Gregoraszczuk EL, Zabielny E, Ochwat D (2001) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor AhR-linked inhibition of luteal cell progresterone secretion in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin treated cells. J Physiol Pharmacol 52:303–311
Neal RA, Beatty PW, Gasiewicz TA (1979) Studies of the mechanisms of toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Ann N Y Acad Sci 320:204–213
Sterling JB, Hanke CW Dioxin toxicity and chloracne in the Ukraine. J Drugs Dermatol 4:148–150
Chaffin CL, Heimler I, Rawlins RG, Wimpee BAB, Sommer C, Hutz RJ (1996) Estrogen receptor and aromatic hydrocarbon receptor in the primate ovary. Endocrine 5:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739065
Ivens IA, Löser E, Rinke M, Schmidt U, Neupert M (1992) Toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrabromodibenzo-p-dioxin in rats after single oral administration. Toxicology 73:53–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(92)90170-J
Vos JG, Moore JA, Zinkl JG (1973) Effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on the immune system of laboratory animals. Environ Health Perspect 5:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7305149
Singh S (2000) Inhibition of dioxin effects on bone formation in vitro by a newly described aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonist, resveratrol. J Endocrinol 167:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1670183
Całkosinski I, Rosińczuk-Tonderys J, Dobrzyński M, Pałka L, Bazan J (2013) Occurrence of disseminated intravascular coagulation in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced pneumonia in the rat. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, In, pp 283–292
Finnilä MAJ, Zioupos P, Herlin M, Miettinen HM, Simanainen U, Håkansson H, Tuukkanen J, Viluksela M, Jämsä T (2010) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure on bone material properties. J Biomech 43:1097–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.12.011
Watson ATD, Planchart A, Mattingly CJ, Winkler C, Reif DM, Kullman SW (2017) From the cover: embryonic exposure to TCDD impacts osteogenesis of the axial skeleton in Japanese medaka, Oryzias latipes. Toxicol Sci 155:485–496. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw229
Miettien H (2006) The effects of TCDD on the development of teeth and cortical bone in rats: implications for risk assessment. University of Eastern Finland
De Vries M, Kwakkel RP, Kijlstra A (2006) Dioxins in organic eggs: a review. NJAS - Wageningen J Life Sci 54:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1573-5214(06)80023-0
Cohen-Barnhouse AM, Zwiernik MJ, Link JE, Fitzgerald SD, Kennedy SW, Hervé JC, Giesy JP, Wiseman S, Yang Y, Jones PD, Wan Y, Collins B, Newsted JL, Kay D, Bursian SJ (2011) Sensitivity of Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica), common pheasant (Phasianus colchicus), and White Leghorn chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) embryos to in ovo exposure to TCDD, PeCDF, and TCDF. Toxicol Sci 119:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq289
Piskorska-Pliszczynska J, Mikolajczyk S, Warenik-Bany M, Maszewski S, Strucinski P (2014) Soil as a source of dioxin contamination in eggs from free-range hens on a Polish farm. Sci Total Environ 466–467:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.061
Ghimpeţeanu OM, Militaru M, Scippo ML (2014) Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls contamination in poultry liver related to food safety - a review. Food Control 38:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.09.054
Cheryl L, Summer John P, Giesy Steven CLSJPGSJBJARTJKPDJDAVRJ (1996) Effects induced by feeding organochlorine contaminated carp from Saginaw bay lake Huron to laying white leghorn hens ii embryotoxic and teratogenic effects. J Toxicol Environ Health 49:409–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/009841096160790
Alsharif NZ, Hassoun EA (2004) Thymic atrophy, production of reactive oxygen species and DNA damage in C57BL / 6J Mice. 131–138
Dobrzynski M, Pezowicz C, Tomanik M, Kuropka P, Dudek K, Fita K, Styczynska M, Wiglusz RJ (2018) Modulating effect of selected pharmaceuticals on bone in female rats exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo- p -dioxin (TCDD). RSC Adv 8:27537–27545. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03619E
Aybar Odstrcil A, Territoriale E, Missana L (2005) An experimental model in calvaria to evaluate bone therapies. Acta Odontol Latinoam 18:63–67
Gomes PS, Fernandes MH (2011) Rodent models in bone-related research: the relevance of calvarial defects in the assessment of bone regeneration strategies. Lab Anim 45:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1258/la.2010.010085
Jiang H, Wang Y, Deng Z, Jin J, Meng J, Chen S, Wang J, Qiu Y, Guo T, Zhao J (2018) Construction and evaluation of a murine calvarial osteolysis model by exposure to CoCrMo particles in aseptic loosening. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/56276
European standard commitee (2014) Food products - determination of trace elements - pressure mineralization. http://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-en-13805-2014-11e.html
Kuropka P, Dobrzynski M, Herman K, Parulska O, Kowalczyk-Zajac M, Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz A, Fita K, Kumala A, Całkosiński I (2015) Evaluation of the protective influence of various doses of α-tocopherol on the zinc and iron level in the bone tissue of rat offspring after exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-ρ-dioxin. Polish J Environ Stud 24:188–193
Tõnsuaadu K, Gruselle M, Kriisa F, Trikkel A, Gredin P, Villemin D (2018) Dependence of the interaction mechanisms between l-serine and O-phospho-l-serine with calcium hydroxyapatite and copper modified hydroxyapatite in relation with the acidity of aqueous medium. JBIC J Biol Inorg Chem 23:929–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-018-1594-0
Guo L, Zhao Y-Y, Zhao Y-Y, Sun Z-J, Liu H, Zhang S-L (2007) Toxic effects of TCDD on osteogenesis through altering IGFBP-6 gene expression in osteoblasts. Biol Pharm Bull 30:2018–2026
Yamada T, Hirata A, Sasabe E, Yoshimura T, Ohno S, Kitamura N, Yamamoto T (2014) TCDD disrupts posterior palatogenesis and causes cleft palate. J Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg 42:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2013.01.024
Gierthy JF, Silkworth JB, Tassinari M, Stein GS, Lian JB (1994) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin inhibits differentiation of normal diploid rat osteoblasts in vitro. J Cell Biochem 54:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.240540211
Janz DM, Bellward GD (1996) In ovo 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure in three avian species: 2. Effects on estrogen receptor and plasma sex steroid hormones during the perinatal period. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 139:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1006/TAAP.1996.0168
Carpi D, Korkalainen M, Airoldi L, Fanelli R, Hakansson H, Muhonen V, Tuukkanen J, Viluksela M, Pastorelli R (2009) Dioxin-sensitive proteins in differentiating osteoblasts: effects on bone formation in vitro. Toxicol Sci 108:330–343. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp021
Naruse M, Ishihara Y, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Koyama A, Hagiwara H (2002) 3-Methylcholanthrene, which binds to the arylhydrocarbon receptor, inhibits proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro and ossification in vivo. Endocrinology 143:3575–3581. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2002-220003
Thompson HM, Fernandes A, Rose M, White S, Blackburn A (2006) Possible chemical causes of skeletal deformities in grey heron nestlings (Ardea cinerea) in north Nottinghamshire, UK. Chemosphere 65:400–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.007
Fox GA, Lundberg R, Wejheden C, Lind L, Larsson S, Örberg J, Lind PM (2008) Health of herring gulls (Larus argentatus ) in relation to breeding location in the early 1990s. III. Effects on the bone tissue. J Toxicol Environ Heal Part A 71:1448–1456. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287390802328788
Dobrzyński M, Calkosiński I, Przywitowska I, Kobierska-Brzoza C-WA, Soltan E, Parulska O (2009) Effects of dioxins in environmental pollution on development of tooth disorders. Polish J Environ Stud 18:319–323
Katsumata S, Katsumata-Tsuboi R, Uehara M, Suzuki K (2009) Severe iron deficiency decreases both bone formation and bone resorption in rats. J Nutr 139:238–243. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.108.093757
Katsumata S, Tsuboi R, Uehara M, Suzuki K (2006) Dietary Iron deficiency decreases serum osteocalcin concentration and bone mineral density in rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:2547–2550. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60221
Leek JC, Keen CL, Vogler JB, Golub MS, Hurley LS, Hendrickx AG, Gershwin ME (1988) Long-term marginal zinc deprivation in rhesus monkeys. IV effects on skeletal growth and mineralization. Am J Clin Nutr 47:889–895. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/47.5.889
Yamaguchi M, Goto M, Uchiyama S, Nakagawa T (2008) Effect of zinc on gene expression in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells: enhancement of Runx2, OPG, and regucalcin mRNA expressions. Mol Cell Biochem 312:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9731-7
Yamaguchi M (2010) Role of nutritional zinc in the prevention of osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem 338:241–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0358-0
Lutz W, Burritt MF, Nixon DE, Kao PC, Kumar R (2000) Zinc increases the activity of vitamin D-dependent promoters in osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 271:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.2570
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. PhD Ireneusz Całkosiński (1951-2017) for inspiration and his helpful advice, help in organization and welfare of the animals.
Funding
This project is supported by Wroclaw Centre of Biotechnology and The Leading National Research Centre (KNOW) program, for years 2014–2018, and the National Science Centre over the course of the realization of the projects “Preparation and characterization of nanoapatites doped with rare earth ions and their biocomposites” (no. UMO-2012/05/E/ST5/03904) and “Preparation and characterization of biocomposites based on nanoapatites for theranostic” (no. UMO-2015/19/B/ST5/01330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All of the procedures involving animals were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. All of the procedures involving animals were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. Prior to the experiment, the manner of acquisition of biological material and the range of steps to be performed on animals had been approved of by the Local Ethics Council for Animal Experiments (Permission number: 52/2015).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobrzynski, M., Kuropka, P., Tarnowska, M. et al. The Protective Effect of α-Tocopherol on the Content of Selected Elements in the Calvaria for Exposed Hens to TCDD in the Early Embryonic Period. Biol Trace Elem Res 190, 517–525 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1580-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1580-y