Abstract
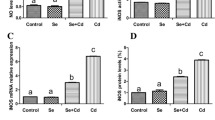
Cd-induced apoptosis and the protective effects of Se against Cd-induced injury have been reported in previous studies. However, little is known regarding the effects of Cd-induced apoptosis in hepatic cells and the antagonistic effects of Se on Cd in poultry. In the present study, 128 healthy 31-week-old laying hens were randomly divided into four groups, which were fed basic diets, with the addition of Se (Na2SeO3, 2 mg/kg), Cd (CdCl2, 150 mg/kg), or Se + Cd (150 mg/kg of CdCl2 and 2 mg/kg of Na2SeO3) for 90 days. Ultrastructural changes, nitric oxide (NO) concentrations, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activities, results of the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay of apoptosis, and the expression of iNOS and apoptosis-related genes in livers were determined. It was observed that Cd treatment significantly increased the concentrations of NO and iNOS activity in chicken livers. The production of excessive NO initiated the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Exposure to Cd increased the mRNA and the protein expression levels of iNOS, caspase-3, Bax, p53, and Cyt-c. Furthermore, the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 increased, while the expression of Bcl-2 decreased. Treatment with Se significantly alleviated Cd-induced apoptosis in chicken livers, as evidenced by a reduction in the production of NO, iNOS activity, the number of apoptotic cells, and mRNA and protein expression levels of iNOS, caspase-3, Bax, and Cyt-c. It indicated that Cd induced NO-mediated apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and Se exerted antagonizing effects. The present study provides new insights as to how Se affects Cd-induced toxicity in the chicken liver.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nordberg GF (2009) Historical perspectives on cadmium toxicology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:192–200
Berzina N, Markovs J, Isajevs S, Apsite M, Smirnova G (2007) Cadmium-induced enteropathy in domestic cocks: a biochemical and histological study after subchronic exposure. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 101:29–34
Jurczuk M, Brzoska MM, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J, Galazyn-Sidorczuk M, Kulikowska-Karpinska E (2004) Antioxidant enzymes activity and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of rats exposed to cadmium and ethanol. Food Chem Toxicol 42:429–438
Dudley RE, Svoboda DJ, Klaassen CD (1984) Time course of cadmium-induced ultrastructural changes in rat liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 76:150–160
Subhan F, Khan A, Wahid F, Shehzad A, Jan AU (2011) Determination of optimal toxic concentration and accumulation of cadmium in broiler chicks. Toxicol Res 27:143–147
Lucia M, Andre JM, Gonzalez P, Baudrimont M, Bernadet MD, Gontier K, Maury-Brachet R, Guy G, Davail S (2010) Effects of dietary cadmium contamination on bird Anas Platyrhynchos--comparison with species Cairina moschata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:2010–2016
Go YM, Sutliff RL, Chandler JD, Khalidur R, Kang BY, Anania FA, Orr M, Hao L, Fowler BA, Jones DP (2015) Low-dose cadmium causes metabolic and genetic dysregulation associated with fatty liver disease in mice. Toxicol Sci 147:524–534
Tzirogiannis KN, Panoutsopoulos GI, Demonakou MD, Hereti RI, Alexandropoulou KN, Basayannis AC, Mykoniatis MG (2003) Time-course of cadmium-induced acute hepatotoxicity in the rat liver: the role of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 77:694–701
Liu S, Xu FP, Yang ZJ, Li M, Min YH, Li S (2014) Cadmium-induced injury and the ameliorative effects of selenium on chicken splenic lymphocytes: mechanisms of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biol Trace Elem Res 160:340–351
Li JL, Jiang CY, Li S, Xu SW (2013) Cadmium induced hepatotoxicity in chickens (Gallus Domesticus) and ameliorative effect by selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 96:103–109
Chen L, Zhou J, Gao W, Jiang YZ (2003) Action of NO and TNF-alpha release of rats with cadmium loading in malfunctiion of multiple system organ. Sheng Li Xue Bao 55:535–540
Chae IH, Park KW, Kim HS, Oh BH (2004) Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis is mediated by Bax/Bcl-2 gene expression, transition of cytochrome c, and activation of caspase-3 in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Clin Chim Acta 341:83–91
Melkova Z, Lee SB, Rodriguez D, Esteban M (1997) Bcl-2 prevents nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage. FEBS Lett 403:273–278
Messmer UK, Brune B (1996) Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis: p53-dependent and p53-independent signalling pathways. Biochem J 319(Pt 1):299–305
Borutaite V, Budriunaite A, Morkuniene R, Brown GC (2001) Release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and activation of cytosolic caspases induced by myocardial ischaemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1537:101–109
Degterev A, Boyce M, Yuan J (2003) A decade of caspases. Oncogene 22:8543–8567
Zhang Z, Bi M, Liu Q, Yang J, Xu S (2016) Meta-analysis of the correlation between selenium and incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 7:77110–77116
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Zhang JL, Li S, Huang JQ, Ren FZ, Xu SW, Wang XL, Lei XG (2013) Gene expression of endoplasmic reticulum resident selenoproteins correlates with apoptosis in various muscles of se-deficient chicks. J Nutr 143:613–619
El-Boshy ME, Risha EF, Abdelhamid FM, Mubarak MS, Hadda TB (2015) Protective effects of selenium against cadmium induced hematological disturbances, immunosuppressive, oxidative stress and hepatorenal damage in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:104–110
Jihen EH, Imed M, Fatima H, Abdelhamid K (2009) Protective effects of selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) on cadmium (Cd) toxicity in the liver of the rat: effects on the oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1559–1564
Jihen EH, Imed M, Fatima H, Abdelhamid K (2008) Protective effects of selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) on cadmium (Cd) toxicity in the liver and kidney of the rat: histology and Cd accumulation. Food Chem Toxicol 46:3522–3527
Newairy AA, El-Sharaky AS, Badreldeen MM, Eweda SM, Sheweita SA (2007) The hepatoprotective effects of selenium against cadmium toxicity in rats. Toxicology 242:23–30
Zhang R, Wang L, Zhao J, Wang C, Bao J, Li J (2016) Effects of selenium and cadmium on ion profiles in the brains of chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 174:218–225
Liu LL, Zhang JL, Zhang ZW, Yao HD, Sun G, Xu SW (2014) Protective roles of selenium on nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis of immune organs induced by cadmium in chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:199–209
Al-Waeli A, Zoidis E, Pappas AC, Demiris N, Zervas G, Fegeros K (2013) The role of organic selenium in cadmium toxicity: effects on broiler performance and health status. Animal 7:386–393
Marettova E, Maretta M, Legath J, Kosutzka E (2012) The retention of cadmium and selenium influence in fowl and chickens of F1 generation. Biol Trace Elem Res 147:130–134
Yun CH, Yang JS, Kang SS, Yang Y, Cho JH, Son CG, Han SH (2007) NF-kappaB signaling pathway, not IFN-beta/STAT1, is responsible for the selenium suppression of LPS-induced nitric oxide production. Int Immunopharmacol 7:1192–1198
Ayaz M, Turan B (2006) Selenium prevents diabetes-induced alterations in [Zn2+]i and metallothionein level of rat heart via restoration of cell redox cycle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H1071–H1080
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Li S, Wang XL, Lei XG, Xu SW (2013) Selenoprotein W serves as an antioxidant in chicken myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3112–3120
Liu C, Fu J, Liu C, Li S (2015) The role of nitric oxide and autophagy in liver injuries induced by selenium deficiency in chickens. RSC Adv 5:50549–50556
Habeebu SS, Liu J, Klaassen CD (1998) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 149:203–209
Rani A, Kumar A, Lal A, Pant M (2014) Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: a review. Int J Environ Health Res 24:378–399
Gu X, Chen R, Hu G, Zhuang Y, Luo J, Zhang C, Guo X, Huang A, Cao H (2015) Cell apoptosis of caprine spleen induced by toxicity of cadmium with different levels of molybdenum. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:49–56
Soyupek S, Oksay T, Sutcu R, Armagan A, Gokalp O, Perk H, Delibas N (2012) The effect of cadmium toxicity on renal nitric oxide synthase isoenzymes. Toxicol Ind Health 28:624–628
Fouad AA, Jresat I (2011) Protective effect of telmisartan against cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Life Sci 89:29–35
Zheng JL, Yuan SS, Wu CW, Lv ZM (2016) Acute exposure to waterborne cadmium induced oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in the brain, ovary and liver of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 180:36–44
Yang S, Zhang Z, He J, Li J, Zhang J, Xing H, Xu S (2012) Ovarian toxicity induced by dietary cadmium in hen. Biol Trace Elem Res 148:53–60
He H, Feng YS, Zang LH, Liu WW, Ding LQ, Chen LX, Kang N, Hayashi T, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Qiu F, Ikejima T (2014) Nitric oxide induces apoptosis and autophagy; autophagy down-regulates NO synthesis in physalin A-treated A375-S2 human melanoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 71:128–135
Desagher S, Martinou JC (2000) Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 10:369–377
Boyd CS, Cadenas E (2002) Nitric oxide and cell signaling pathways in mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Biol Chem 383:411–423
Messmer UK, Reed UK, Brune B (1996) Bcl-2 protects macrophages from nitric oxide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 271:20192–20197
Oh SH, Lim SC (2006) A rapid and transient ROS generation by cadmium triggers apoptosis via caspase-dependent pathway in HepG2 cells and this is inhibited through N-acetylcysteine-mediated catalase upregulation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 212:212–223
Wang Y, Wu Y, Luo K, Liu Y, Zhou M, Yan S, Shi H, Cai Y (2013) The protective effects of selenium on cadmium-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via mitochondria pathway in mice kidney. Food Chem Toxicol 58:61–67
Jin Y, Zhang S, Tao R, Huang J, He X, Qu L, Fu Z (2016) Oral exposure of mice to cadmium (II), chromium (VI) and their mixture induce oxidative- and endoplasmic reticulum-stress mediated apoptosis in the livers. Environ Toxicol 31:693–705
Yiran Z, Chenyang J, Jiajing W, Yan Y, Jianhong G, Jianchun B, Xuezhong L, Zongping L (2013) Oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways involved in cadmium-induced BRL 3A cell apoptosis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:516051
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O, Chittenden T, Pancoska P, Moll UM (2003) p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell 11:577–590
Zwolak I, Zaporowska H (2012) Selenium interactions and toxicity: a review. Selenium interactions and toxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol 28:31–46
Liu L, Yang B, Cheng Y, Lin H (2015) Ameliorative effects of selenium on cadmium-induced oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chicken kidney. Biol Trace Elem Res 167:308–319
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31501992, 31672466), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M591505), and the Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Fund (Grant No. LBH-Z14223). All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures used in the present study were approved by the institutional animal care and use committee of Northeast Agricultural University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Yi, R., Bi, Y. et al. The Effect of Selenium on the Cd-Induced Apoptosis via NO-Mediated Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway in Chicken Liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 178, 310–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0925-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0925-7