Abstract
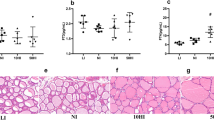
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of prolonged iodine overdose on type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase (D2) ubiquitination-related enzymes. Male Wistar rats were fed different doses of iodine and were then euthanized at the 4, 8, 12, or 24 weeks (4w, 8w, 12w, or 24w) after iodine administration. Urinary iodine concentration (UIC), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), total thyroxine (TT4), and total triiodothyronine (TT3) were determined. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Western blot were used to measure mRNA and protein expression levels of pituitary D2 as well as two D2-specific ubiquitin ligases [WD repeat and SOCS box-containing protein 1 (WSB-1), membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 6 (MARCH6 or TEB4)] and two D2-specific deubiquitinating enzymes [ubiquitin-specific peptidase 20 (USP20) and ubiquitin-specific peptidase 33 (USP33)]. The mRNA and protein expression levels of USP19, a TEB4-specific deubiquitinating enzyme, were also measured. Prolonged high iodine intake significantly increased TSH expression. At 12w, TSH was 1.57-, 1.44-, and 2.11-fold of NI group in 6HI, 10HI, and 50HI groups, respectively. At 24w, TSH had increased to 2.11-fold in the 50HI group. The pituitary D2 protein level decreased at 12w and 24w; though the mRNA level did not change. Prolonged iodine intake increased mRNA and protein expression levels of pituitary WSB-1 and TEB4. High iodine intake had no discernible effects on USP20. Temporary increases in USP33 and USP19 mRNA levels were observed. The enzymes related to D2 ubiquitination change with prolonged high iodine intake. Increased D2 ubiquitination suppresses the activity of D2, causing a decrease in negative feedback of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun X, Shan Z, Teng W (2014) Effects of increased iodine intake on thyroid disorders. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul, Korea) 29(3):240–247. doi:10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.240
Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, Hannon WH, Gunter EW, Spencer CA, Braverman LE (2002) Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(2):489–499. doi:10.1210/jcem.87.2.8182
Guan H, Shan Z, Teng X, Li Y, Teng D, Jin Y, Yu X, Fan C, Chong W, Yang F, Dai H, Yu Y, Li J, Chen Y, Zhao D, Shi X, Hu F, Mao J, Gu X, Yang R, Chen W, Tong Y, Wang W, Gao T, Li C, Teng W (2008) Influence of iodine on the reference interval of TSH and the optimal interval of TSH: results of a follow-up study in areas with different iodine intakes. Clin Endocrinol 69(1):136–141. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03150.x
Rosene ML, Wittmann G, Arrojo e Drigo R, Singru PS, Lechan RM, Bianco AC (2010) Inhibition of the type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase underlies the elevated plasma TSH associated with amiodarone treatment. Endocrinology 151(12):5961–5970. doi:10.1210/en.2010-0553
Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR (2002) Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr Rev 23(1):38–89
Zavacki AM, Arrojo EDR, Freitas BC, Chung M, Harney JW, Egri P, Wittmann G, Fekete C, Gereben B, Bianco AC (2009) The E3 ubiquitin ligase TEB4 mediates degradation of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase. Mol Cell Biol 29(19):5339–5347. doi:10.1128/mcb.01498-08
Fekete C, Freitas BC, Zeold A, Wittmann G, Kadar A, Liposits Z, Christoffolete MA, Singru P, Lechan RM, Bianco AC, Gereben B (2007) Expression patterns of WSB-1 and USP-33 underlie cell-specific posttranslational control of type 2 deiodinase in the rat brain. Endocrinology 148(10):4865–4874. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0448
Curcio-Morelli C, Zavacki AM, Christofollete M, Gereben B, de Freitas BC, Harney JW, Li Z, Wu G, Bianco AC (2003) Deubiquitination of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase by von Hippel-Lindau protein-interacting deubiquitinating enzymes regulates thyroid hormone activation. J Clin Invest 112(2):189–196. doi:10.1172/jci18348
Nakamura N, Harada K, Kato M, Hirose S (2014) Ubiquitin-specific protease 19 regulates the stability of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH6. Exp Cell Res 328(1):207–216. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.07.025
Li N, Jiang Y, Shan Z, Teng W (2012) Prolonged high iodine intake is associated with inhibition of type 2 deiodinase activity in pituitary and elevation of serum thyrotropin levels. Br J Nutr 107(5):674–682. doi:10.1017/S0007114511003552
Teng W, Shan Z, Teng X, Guan H, Li Y, Teng D, Jin Y, Yu X, Fan C, Chong W, Yang F, Dai H, Yu Y, Li J, Chen Y, Zhao D, Shi X, Hu F, Mao J, Gu X, Yang R, Tong Y, Wang W, Gao T, Li C (2006) Effect of iodine intake on thyroid diseases in China. N Engl J Med 354(26):2783–2793. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa054022
Sun X, Zhang X, Jiang Y, Bao S, Shan Z, Teng W (2015) Expression of iodotyrosine deiodinase in thyroid and other organs in iodine-deficient and iodine-excess rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0328-1
Markou K, Georgopoulos N, Kyriazopoulou V, Vagenakis AG (2001) Iodine-induced hypothyroidism. Thyroid: Off J Am Thyroid Assoc 11(5):501–510. doi:10.1089/105072501300176462
Boukis MA, Koutras DA, Souvatzoglou A, Evangelopoulou A, Vrontakis M, Moulopoulos SD (1983) Thyroid hormone and immunological studies in endemic goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57(4):859–862. doi:10.1210/jcem-57-4-859
Rose NR, Rasooly L, Saboori AM, Burek CL (1999) Linking iodine with autoimmune thyroiditis. Environ Health Perspect 107(Suppl 5):749–752
Rohner F, Zimmermann M, Jooste P, Pandav C, Caldwell K, Raghavan R, Raiten DJ (2014) Biomarkers of nutrition for development—iodine review. J Nutr 144(8):1322S–1342S. doi:10.3945/jn.113.181974
Baqui MM, Gereben B, Harney JW, Larsen PR, Bianco AC (2000) Distinct subcellular localization of transiently expressed types 1 and 2 iodothyronine deiodinases as determined by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. Endocrinology 141(11):4309–4312. doi:10.1210/endo.141.11.7872
Schneider MJ, Fiering SN, Thai B, Wu SY, St Germain E, Parlow AF, St Germain DL, Galton VA (2006) Targeted disruption of the type 1 selenodeiodinase gene (Dio1) results in marked changes in thyroid hormone economy in mice. Endocrinology 147(1):580–589. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0739
Schneider MJ, Fiering SN, Pallud SE, Parlow AF, St Germain DL, Galton VA (2001) Targeted disruption of the type 2 selenodeiodinase gene (DIO2) results in a phenotype of pituitary resistance to T4. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, Md) 15(12):2137–2148. doi:10.1210/mend.15.12.0740
Suzuki H, Kadena N, Takeuchi K, Nakagawa S (1979) Effects of three-day oral cholecystography on serum iodothyronines and TSH concentrations: comparison of the effects among some cholecystographic agents and the effects of iopanoic acid on the pituitary-thyroid axis. Acta Endocrinol 92(3):477–488
Steinsapir J, Harney J, Larsen PR (1998) Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in rat pituitary tumor cells is inactivated in proteasomes. J Clin Invest 102(11):1895–1899. doi:10.1172/jci4672
Sagar GD, Gereben B, Callebaut I, Mornon JP, Zeold A, da Silva WS, Luongo C, Dentice M, Tente SM, Freitas BC, Harney JW, Zavacki AM, Bianco AC (2007) Ubiquitination-induced conformational change within the deiodinase dimer is a switch regulating enzyme activity. Mol Cell Biol 27(13):4774–4783. doi:10.1128/mcb.00283-07
Dentice M, Bandyopadhyay A, Gereben B, Callebaut I, Christoffolete MA, Kim BW, Nissim S, Mornon JP, Zavacki AM, Zeold A, Capelo LP, Curcio-Morelli C, Ribeiro R, Harney JW, Tabin CJ, Bianco AC (2005) The Hedgehog-inducible ubiquitin ligase subunit WSB-1 modulates thyroid hormone activation and PTHrP secretion in the developing growth plate. Nat Cell Biol 7(7):698–705. doi:10.1038/ncb1272
Arrojo EDR, Egri P, Jo S, Gereben B, Bianco AC (2013) The type II deiodinase is retrotranslocated to the cytoplasm and proteasomes via p97/Atx3 complex. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, Md) 27(12):2105–2115. doi:10.1210/me.2013-1281
Man N, Guan HX, Shan ZY, Li YS, Fan CL, Guo XJ, Chen W, Tong YJ, Chong W, Mao JY, Teng WP (2006) Long-term effects of high iodine intake: inhibition of thyroid iodine uptake and organification in Wistar rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86(48):3420–3424
Fonseca TL, Correa-Medina M, Campos MP, Wittmann G, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Arrojo e Drigo R, Mora-Garzon M, Ueta CB, Caicedo A, Fekete C, Gereben B, Lechan RM, Bianco AC (2013) Coordination of hypothalamic and pituitary T3 production regulates TSH expression. J Clin Invest 123(4):1492–1500. doi:10.1172/jci61231
Zhang M, Zou X, Lin X, Bian J, Meng H, Liu D (2015) Effect of excessive potassium iodide on rat aorta endothelial cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 166(2):201–209. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0264-0
Stoddard FR 2nd, Brooks AD, Eskin BA, Johannes GJ (2008) Iodine alters gene expression in the MCF7 breast cancer cell line: evidence for an anti-estrogen effect of iodine. Int J Med Sci 5(4):189–196
Arroyo-Helguera O, Anguiano B, Delgado G, Aceves C (2006) Uptake and antiproliferative effect of molecular iodine in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Endocr Relat Cancer 13(4):1147–1158. doi:10.1677/erc.1.01250
Berthouze M, Venkataramanan V, Li Y, Shenoy SK (2009) The deubiquitinases USP33 and USP20 coordinate beta2 adrenergic receptor recycling and resensitization. EMBO J 28(12):1684–1696. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.128
Li Z, Na X, Wang D, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (2002) Ubiquitination of a novel deubiquitinating enzyme requires direct binding to von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem 277(7):4656–4662. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108269200
Li Z, Wang D, Na X, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (2002) Identification of a deubiquitinating enzyme subfamily as substrates of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294(3):700–709. doi:10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00534-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81370893), Research Foundation, Department of Science and Technology, Liaoning Province Government, China (Grant no. 2011225023), the Research Foundation of Innovative Team in Advanced Educational Institute of Liaoning Province (Grant LT 2012015), Important Platform of Science and Technology for Universities in Liaoning Province (16010), and Guanghua Science and Technology Foundation of China (Grant 2007–02).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Xiaowen Zhang and Yaqiu Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Jiang, Y., Han, W. et al. Effect of Prolonged Iodine Overdose on Type 2 Iodothyronine Deiodinase Ubiquitination-Related Enzymes in the Rat Pituitary. Biol Trace Elem Res 174, 377–386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0723-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0723-2