Abstract
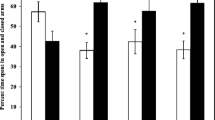
The objective of this study was to evaluate the toxicity of individual and mixtures of di(n-butyl) phthalates (DBP) and their active metabolite monobutyl phthalate (MBP) and arsenic (As) on spatial cognition associated with hippocampal apoptosis in mice. Mice were exposed, individually or in combination, to DBP (50 mg/kg body weight, intragastrically), MBP (50 mg/kg body weight, intragastrically), and As (10 mg/L, per os) for 8 weeks. The Morris water maze test showed that mice exposed to DBP/MBP combined with As exhibited longer escape latencies and the lower average number of crossing the platform. The As content in the hippocampus after As exposure increased as compared to those without As exposure. In mice exposed to DBP/MBP combined with As, pathological alterations and oxidative damage to the hippocampus were found. Expression of apoptosis-related protein: Bax and caspase-3 were significantly increased in the hippocampus, while there was no significant change in expression of Bcl-2. The results suggested that DBP and MBP combined with As can induce spatial cognitive deficits through altering the expression of apoptosis-related protein and As played a critical role in cognition impairments. And the joint exposure has antagonistic effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy CO, Liu YP, Longfellow D, Aposhian HV, Beck B, Fowler B, Goyer R, Menzer R, Rossman T, Thompson C (1999) As: health effects, mechanisms of actions, and research issues. Environ Health Perspect 107:593–597
Rodriguez VM, Jimenez-Capdeville ME, Giordano M (2003) The effects of arsenic exposure on the nervous system. Toxicol Lett 145:1–18
Duker AA, Carranza EJM, Hale M (2005) Arsenic geochemistry and health. Environ Int 31:631–641
Tsai SY, Chou HY, The HW, Chen CM, Chen CJ (2003) The effects of chronic arsenic exposure from drinking water on the neurobehavioral development in adolescence. Neurotoxicology 24:747–753
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Factor-Litvak P, van Geen A, Slavkovich V, Lolacono NJ, Cheng Z, Hussain I (2004) Water arsenic exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 112:1329–1333
Wright RO, Amarasiriwardena C, Woolf AD, Jim R, Bellinger DC (2006) Neuropsychological correlates of hair arsenic, manganese, and cadmium levels in school-age children residing near a hazardous waste site. NeuroToxicology 27:210–216
Hamadani JD, Tofail F, Nermell B, Gardner R, Shiraji S, Bottai M, Arifeen SE, Huda SN, Vahter M (2011) Critical windows of exposure for arsenic-associated impairment of cognitive function in pre-school girls and boys: a population-based cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 40:1593–1604
Jin Y, Xi S, Li X, Lu C, Li G, Xu Y, Qu C, Niu Y, Sun G (2006) Arsenic speciation transported through the placenta from mother mice to their newborn pups. Environ Res 101:349–355
Xi S, Sun W, Wang F, Jin Y, Sun G (2009) Transplacental and early life exposure to inorganic arsenic affected development and behavior in offspring rats. Arch Toxicol 83:549–556
Mikula P, Svobodova Z, Smutna M (2005) Phthalates: toxicology and food safety—a review. Czech J Food Sci 23:217–223
Koch HM, Drexler H, Angerer J (2003) An estimation of the daily intake of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) and other phthalates in the general population. Int J Hyg Environ Health 206:77–83
O’Connor JC, Frame SR, Ladics GS (2002) Evaluation of a 15-day screening assay using intact male rats for identifying antiandrogens. Toxicol Sci 69:92–108
Shultz VD, Phillips S, Sar M, Foster PMD, Gaido KW (2001) Altered gene profiles in fetal rat testes after in utero exposure to di(n-butyl) phthalate. Toxicol Sci 64:233–242
Li X, Jiang L, Cheng L, Chen H (2014) Dibutyl phthalate-induced neurotoxicity in the brain of immature and mature rat offspring. Brain and Development 36:653–660
Shen O, Du G, Sun H, Wu W, Jiang Y, Song L, Wang X (2009) Comparison of in vitro hormone activities of selected phthalates using reporter gene assays. Toxicol Lett 191:9–14
Weiss B (2011) Endocrine disruptors as a threat to neurological function. J Neurol Sci 305:11–21
Tanaka A, Matsumoto A, Yamaha T (1978) Biochemical studies on phthalic esters. III. Metabolism of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) in animals. Toxicology 9:109–123
Hallmark N, Walker M, McKinnell C, Mahood IK, Scott H, Bayne R, Coutts S, Anderson RA, Greig I, Morris K, Sharpe RM (2007) Effects of monobutyl and di(n-butyl) phthalate in vitro on steroidogenesis and Leydig cell aggregation in fetal testis explants from the rat: comparison with effects in vivo in the fetal rat and neonatal marmoset and in vitro in the human. Environ Health Perspect 115:390–396
Suk WA, Olden K, Yang RSH (2002) Chemical mixtures research: significance and future perspectives. Environ Health Perspect 110:891–892
Chen XM, An H, Ao L, Sun L, Liu WB, Zhou ZY, Wang YX, Cao J (2011) The combined toxicity of dibutyl phthalate and benzo(a)pyrene on the reproductive system of male Sprague Dawley rats in vivo. J Hazard Mater 186:835–841
Prasanth GK, Divya LM, Sadasivan C (2009) Effects of mono and di(n-butyl) phthalate on superoxide dismutase. Toxicology 262:38–42
Xu H, Shao X, Zhang Z, Zou Y, Chen Y, Han S, Wang S, Wu X, Yang L, Chen Z (2013) Effects of Di-n-butyl phthalate and diethyl phthalate on acetylcholinesterase activity and neurotoxicity related gene expression in embryonic zebrafish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:635–639
Chen X, Zhou QH, Leng L, Chen X, Sun ZR, Tang NJ (2013) Effects of di(n-butyl) and monobutyl phthalate on steroidogenesis pathways in the murine Leydig tumor cell line MLTC-1. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:332–338
Roth KA (2001) Caspases, apoptosis, and Alzheimer disease: causation, correlation, and confusion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:829–838
Andersen JK (2001) Does neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease involve programmed cell death? Bioessays 23:640–646
Lu K, Abo RP, Schlieper KA, Graffam ME, Levine S, Wishnok JS, Swenberg JA, Tannenbaum SR, Fox JG (2014) Arsenic exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in mice: an integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ Health Perspect 122:284–291
Mylchreest E, Wallace DG, Cattley RC, Foster PMD (2000) Dose-dependent alterations in androgen-regulated male reproductive development in rats exposed to di(n-butyl) phthalate during late gestation. Toxicol Sci 55:143–151
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Habibi E, Ghanemi K, Fallah-Mehrjardi M, Dadolahi-Sohrab A (2013) A novel digestion method based on a choline chloride-oxalic acid deep eutectic solvent for determining Cu, Fe, and Zn in fish samples. Anal Chim Acta 762:61–67
D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 36:60–90
Lever C, Wills T, Cacucci F, Burgess N, O’Keefe J (2002) Long-term plasticity in hippocampal place-cell representation of environmental geometry. Nature 416:90–94
Tracy AL, Jarrard LE, Davidson TL (2001) The hippocampus and motivation revisited: appetite and activity. Behav Brain Res 127:13–23
Leib SL, Heimgartner C, Bifrare YD, Loeffler JM, Tauber MG (2003) Dexamethasone aggravates hippocampal apoptosis and learning deficiency in pneumococcal meningitis in infant rats. Pediatr Res 54:353–357
Magliozzi R, Howell OW, Reeves C, Roncaroli F, Nicholas R, Serafini B, Aloisi F, Reynolds R (2010) A gradient of neuronal loss and meningeal inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 68:477–493
Nakazawa K, Quirk MC, Chitwood RA, Watanabe M, Yeckel MF, Sun LD, Kato A, Carr CA, Johnston D, Wilson MA, Tonegawa S (2002) Requirement for hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors in associative memory recall. Science 297:211–218
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Chen M, Watkins SC, Marion DW, Chen J, Hamilton RL, Loeffert JE, Graham SH (1999) Increases in Bcl-2 and cleavage of caspase-1 and caspase-3 in human brain after head injury. FASEB J 13:813–821
Li ZG, Zhang WX, Grunberger G, Sima AAF (2002) Hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in type 1 diabetes. Brain Res 946:221–231
Swanton E, Savory P, Cosulich S, Clarke P, Woodman P (1999) Bcl-2 regulates a caspase-3/caspase-2 apoptotic cascade in cytosolic extracts. Oncogene 18:1781–1787
Lossi L, Cantile C, Tamagno I, Merighi A (2005) Apoptosis in the mammalian CNS: lessons from animal models. Vet J 170:52–66
Del Razo LM, Quintanilla-Vega B, Brambila-Colombres E, Calderon-Aranda ES, Manno M, Albores A (2001) Stress proteins induced by arsenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177:132–148
Luna AL, Acosta-Saavedra LC, Lopez-Carrillo L, Conde P, Vera E, De Vizcaya-Ruiz A, Bastida M, Cebrian ME, Calderon-Aranda ES (2010) Arsenic alters monocyte superoxide anion and nitric oxide production in environmentally exposed children. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245:244–251
Larochette N, Decaudin D, Jacotot E, Brenner C, Marzo I, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Xie Z, Reed J, Kroemer G (1999) Arsenite induces apoptosis via a direct effect on the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Exp Cell Res 249:413–421
Banerjee N, Banerjee M, Ganguly S, Bandyopadhyay S, Das JK, Bandyopadhay A, Chatterjee M, Giri AK (2008) Arsenic-induced mitochondrial instability leading to programmed cell death in the exposed individuals. Toxicology 246:101–111
Wang Y, Song L, Chen J, He J, Liu R, Zhu Z, Wang X (2004) Effects of di-butyl phthalate on sperm motility and oxidative stress in rats. Natl J Androl 10:253–256
Nagaraja T, Desiraju T (1994) Effects on operant learning and brain acetylcholine esterase activity in rats following chronic inorganic arsenic intake. Human Exp Toxicol 13:353–356
Sarvestani NN, Khodagholi F, Ansari N, Farimani MM (2013) Involvement of p-CREB and phase II detoxifying enzyme system in neuroprotection mediated by the flavonoid calycopterin isolated from Dracocephalum kotschyi. Phytomedicine 20:939–946
Lu TH, Tseng TJ, Su CC, Tang FC, Yen CC, Liu YY, Yang CY, Wu CC, Chen KL, Hung DZ, Chen YW (2014) Arsenic induces reactive oxygen species-caused neuronal cell apoptosis through JNK/ERK-mediated mitochondria-dependent and GRP 78/CHOP-regulated pathways. Toxicol Lett 224:130–140
Xu Z, Wang Z, Li JJ, Chen C, Zhang PC, Dong L, Chen JH, Chen Q, Zhang XT, Wang ZL (2013) Protective effects of selenium on oxidative damage and oxidative stress related gene expression in rat liver under chronic poisoning of arsenic. Food Chem Toxicol 58:1–7
Flora SJS, Bhadauria S, Pant SC, Dhaked RK (2005) Arsenic induced blood and brain oxidative stress and its response to some thiol chelators in rats. Life Sci 77:2324–2337
Lane RM, Kivipelto M, Greig NH (2004) Acetylcholinesterase and its inhibition in Alzheimer disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 27:141–149
Yousef MI, El-Demerdash FM, Radwan FME (2008) Sodium arsenite induced biochemical perturbations in rats: ameliorating effect of curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol 46:3506–3511
Kannan GM, Tripathi N, Dube SN, Gupta M, Flora SJS (2001) Toxic effects of arsenic (III) on some hematopoietic and central nervous system variables in rats and guinea pigs. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 39:675–682
Flora SJS, Bhatt K, Mehta A (2009) Arsenic moiety in gallium arsenide is responsible for neuronal apoptosis and behavioral alterations in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240:236–244
Butterweck V, Böckers T, Korte B, Wittkowski W, Winterhoff H (2002) Long-term effects of St. John’s wort and hypericin on monoamine levels in rat hypothalamus and hippocampus. Brain Res 930:21–29
Chen SM, Swilley S, Bell R, Rajanna S, Reddy SLN, Rajanna B (2000) Lead induced alterations in nitrite and nitrate levels in different regions of the rat brain. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 125:315–323
Rios R, Zarazúa S, Santoyo M, Sepúlveda-Saavedra J, Romero-Díaz V, Jiménez V, Pérez-Severiano F, Vidal-Cantú G, Delgado J, Jiménez-Capdeville M (2009) Decreased nitric oxide markers and morphological changes in the brain of arsenic-exposed rats. Toxicology 261:68–75
Barchowsky A, Dudek EJ, Treadwell MD, Wetterhahn KE (1996) Arsenic induces oxidant stress and NF-KB activation in cultured aortic endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 21:783–790
Chattopadhyay S, Bhaumik S, Nag Chaudhury A, Das Gupta S (2002) Arsenic induced changes in growth development and apoptosis in neonatal and adult brain cells in vivo and in tissue culture. Toxicol Lett 128:73–84
Antunes F, Nunes C, Laranjinha J, Cadenas E (2005) Redox interactions of nitric oxide with dopamine and its derivatives. Toxicology 208:207–212
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material of Water Treatment, Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Chinese Universities from the Ministry of Education (20113227110020).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guanghua Mao and Zhaoxiang Zhou co-first authors.
Guanghua Mao and Zhaoxiang Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, G., Zhou, Z., Chen, Y. et al. Neurological Toxicity of Individual and Mixtures of Low Dose Arsenic, Mono and Di (n-butyl) Phthalates on Sub-Chronic Exposure to Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 170, 183–193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0457-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0457-6