Abstract
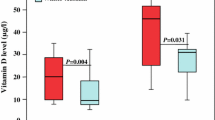
The aim of present study was to compare levels of serum zinc and haptoglobin between patients with chronic active hepatitis C and controls. Two groups including Azeri patients with chronic active hepatitis C (n = 274) and their healthy family members (n = 100) were studied. Serum zinc and haptoglobin were measured using colorimetric and nephelometric methods, respectively. Patients were 156 males (56.9 %) and 118 females (43.1 %) with the mean age of 40.15 ± 12.24 years. Controls were 56 males (56 %) and 44 females (44 %) with the mean age of 39.32 ± 4.40 (p = 0.87 for sex and 0.51 for age). Both the mean levels of serum zinc (72.04 ± 19.08 vs. 106.18 ± 25.52 μg/dL) and haptoglobin (0.72 ± 0.45 vs. 1.08 ± 0.34 g/L) were significantly lower in patients than in controls (p < 0.001 for both comparisons). Serum zinc concentration was significantly higher in males and did not correlate significantly with age, serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), or serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT). Serum haptoglobin did not differ significantly between males and females, and it correlated significantly with age (r = −0.20), serum SGPT (r = −0.22), and SGOT (r = −0.20). This study showed lower levels of serum zinc and haptoglobin in patients with chronic hepatitis C than in controls. Major confounding factors in previous studies were left out.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohammad MK, Zhou Z, Cave M, Barve A, McClain CJ (2012) Zinc and liver disease. Nutr Clin Pract: Off Publ Am Soc Parenter Enter Nutr 27(1):8–20. doi:10.1177/0884533611433534
Dardenne M (2002) Zinc and immune function. Eur J Clin Nutr 56(Suppl 3):S20–23. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601479
Stamoulis I, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2007) Zinc and the liver: an active interaction. Dig Dis Sci 52(7):1595–1612. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-9462-0
Grungreiff K, Reinhold D (2010) Zinc: A complementary factor in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C? (Review). Molecular Med Reports 3(3):371–375. doi:10.3892/mmr_00000267
Davis GL, Albright JE, Cook SF, Rosenberg DM (2003) Projecting future complications of chronic hepatitis C in the United States. Liver Transplan: Off Publ Am Assoc Study Liver Dis Int Liver Transplant Soc 9(4):331–338. doi:10.1053/jlts.2003.50073
Nazari MA, Malayeri SH, Pourhoseingholi MA, Mohebi SR, Zali MR (2010) Evaluation of zinc plasma level in Iranian cirrhotic patients due to hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Hepat Mon 10(1):62–64
Himoto T, Hosomi N, Nakai S, Deguchi A, Kinekawa F, Matsuki M, Yachida M, Masaki T, Kurokochi K, Watanabe S, Senda S, Kuriyama S (2007) Efficacy of zinc administration in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 42(9):1078–1087. doi:10.1080/00365520701272409
Himoto T, Yoneyama H, Deguch A, Kurokohchi K, Inukai M, Masugata H, Goda F, Senda S, Watanabe S, Kubota S, Kuriyama S, Masaki T (2010) Insulin resistance derived from zinc deficiency in non-diabetic patients with chronic hepatitis C. Exp Ther Med 1(4):707–711. doi:10.3892/etm_00000109
Cesur S, Cebeci SA, Kavas GO, Yilmaz N, Buyukkagnici DI (2005) Serum copper and zinc concentrations in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Infect 51(1):35–37. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2004.08.003
Grungreiff K, Hebell T, Gutensohn K, Reinhold A, Reinhold D (2009) Plasma concentrations of zinc, copper, interleukin-6 and interferon-gamma, and plasma dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity in chronic hepatitis C. Molecular Med Reports 2(1):63–68. doi:10.3892/mmr_00000062
Kim KI, Kim SR, Sasase N, Akimoto Y, Shikata M, Ohtani A, Hirooka T, Tanaka K (2008) Blood cell, liver function, and response changes by PEG-interferon-alpha2b plus ribavirin with polaprezinc therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Int 2(1):111–115. doi:10.1007/s12072-007-9029-y
Kolachi NF, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Kazi NG, Mughal MA, Khan S (2013) Effects of selenium and zinc status in biological samples of hepatitis C patient after herbal and pharmaceutical supplements. Biol Trace Elem Res 152(2):187–194. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9617-8
Hambidge KM, Krebs NF (2007) Zinc deficiency: a special challenge. J Nutr 137(4):1101–1105
Lopes PA, Santos MC, Vicente L, Rodrigues MO, Pavao ML, Neve J, Viegas-Crespo AM (2004) Trace element status (Se, Cu, Zn) in healthy Portuguese subjects of Lisbon population: a reference study. Biol Trace Elem Res 101(1):1–17. doi:10.1385/BTER:101:1:01
Moneib HA, Salem SA, Darwish MM (2010) Evaluation of zinc level in skin of patients with necrolytic acral erythema. Br J Dermatol 163(3):476–480. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09820.x
Maret W, Krezel A (2007) Cellular zinc and redox buffering capacity of metallothionein/thionein in health and disease. Mol Med 13(7–8):371–375. doi:10.2119/2007-00036.Maret
Lin CC, Huang JF, Tsai LY, Huang YL (2006) Selenium, iron, copper, and zinc levels and copper-to-zinc ratios in serum of patients at different stages of viral hepatic diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 109(1):15–24. doi:10.1385/BTER:109:1:015
Kalkan A, Bulut V, Avci S, Celik I, Bingol NK (2002) Trace elements in viral hepatitis. J Trace Elem Med Biol: Organ Soc Miner Trace Elem 16(4):227–230. doi:10.1016/S0946-672X(02)80049-9
Takagi H, Nagamine T, Abe T, Takayama H, Sato K, Otsuka T, Kakizaki S, Hashimoto Y, Matsumoto T, Kojima A, Takezawa J, Suzuki K, Sato S, Mori M (2001) Zinc supplementation enhances the response to interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat 8(5):367–371
Ebara M, Fukuda H, Hatano R, Yoshikawa M, Sugiura N, Saisho H, Kondo F, Yukawa M (2003) Metal contents in the liver of patients with chronic liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus. Reference to hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 65(4):323–330
Kormoczi GF, Saemann MD, Buchta C, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Mayr WR, Schwartz DW, Dunkler D, Spitzauer S, Panzer S (2006) Influence of clinical factors on the haemolysis marker haptoglobin. Eur J Clin Investig 36(3):202–209. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01617.x
Volchkova EV, Pak SG, Malov VA, Umbetova KT (2000) Changes in the levels of acute phase proteins in viral hepatitis. Ter Arkh 72(11):18–21
Asazawa H, Kamada Y, Takeda Y, Takamatsu S, Shinzaki S, Kim Y, Nezu R, Kuzushita N, Mita E, Kato M, Miyoshi E (2015) Serum fucosylated haptoglobin in chronic liver diseases as a potential biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma development. Clin Chem Lab Med 53(1):95–102. doi:10.1515/cclm-2014-0427
Zhu J, Lin Z, Wu J, Yin H, Dai J, Feng Z, Marrero J, Lubman DM (2014) Analysis of serum haptoglobin fucosylation in hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis of different etiologies. J Proteome Res 13(6):2986–2997. doi:10.1021/pr500128t
Abbasinazari M, Behnava B, Panahi Y, Hajhossein Talasaz A, Salimi S, Keshvari M, Mehrnoush L, Karim Elizee P, Gholami Fesharaki M, Asgharinia M, Alavian SM (2013) Plasma zinc level in hepatitis C patients with or without Beta thalassemia major; is there any difference? Hepat Mon 13(8):e11138. doi:10.5812/hepatmon.11138
Bacq Y, Schillio Y, Brechot JF, De Muret A, Dubois F, Metman EH (1993) Decrease of haptoglobin serum level in patients with chronic viral hepatitis C. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 17(5):364–369
Arain SA, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Talpur FN, Mughal MA, Shah F, Arain SS, Panhwar AH (2014) Estimation of copper and iron burden in biological samples of various stages of hepatitis C and liver cirrhosis patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(2):197–205. doi:10.1007/s12011-014-0058-9
Arain SA, Afridi HI, Kazi TG, Talpur FN, Shah F, Arain SS, Panhwar AH, Brahman KD (2013) Investigation of alteration in the levels of iron and copper in scalp hair samples of patients having different types of viral hepatitis. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9832-3
Arain SA, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Abbasi AR, Panhwar AH, Naeemullah SB, Arain MB (2014) Application of dual-cloud point extraction for the trace levels of copper in serum of different viral hepatitis patients by flame atomic absorption spectrometry: a multivariate study. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 133:651–656. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2014.05.077
Kawaguchi T, Nagao Y, Abe K, Imazeki F, Honda K, Yamasaki K, Miyanishi K, Taniguchi E, Kakuma T, Kato J, Seike M, Yokosuka O, Ohira H, Sata M (2015) Effects of branched-chain amino acids and zinc-enriched nutrients on prognosticators in HCV-infected patients: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Mol Med Rep 11(3):2159–2166. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2943
Abbasinazari M, Alavian SM, Behnava B, Asgharinia M, Salimi S, Keshvari M, Mehrnoush L, Karim P (2014) Effect of zinc supplementation on viral response in patients with chronic hepatitis C and Beta thalassemia major, a pilot study. J Clin Diagn Res 8(12):HC16–19. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2014/10403.5305
Iwata K, Enomoto H, Nishiguchi S, Aizawa N, Sakai Y, Iwata Y, Tanaka H, Ikeda N, Takashima T, Saito M, Imanishi H, Iijima H, Tsuda Y, Higuchi K (2014) Serum zinc value in patients with hepatitis virus-related chronic liver disease: association with the histological degree of liver fibrosis and with the severity of varices in compensated cirrhosis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 55(2):147–152. doi:10.3164/jcbn. 14-33
Mohamed AA, Abbassi MM, Hamed WA, EzzEl-Arab MA, Aref AM (2014) Can zinc levels predict response to pegylated-interferon and ribavirin therapy in hepatitis C genotype 4 infected Egyptian patients? Acta Gastroenterol Belg 77(2):217–223
Moriyama M, Matsumura H, Fukushima A, Ohkido K, Arakawa Y, Nirei K, Yamagami H, Kaneko M, Tanaka N, Arakawa Y (2006) Clinical significance of evaluation of serum zinc concentrations in C-viral chronic liver disease. Dig Dis Sci 51(11):1967–1977. doi:10.1007/s10620-005-9051-7
Overbeck S, Rink L, Haase H (2008) Modulating the immune response by oral zinc supplementation: a single approach for multiple diseases. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 56(1):15–30. doi:10.1007/s00005-008-0003-8
Matsuoka S, Matsumura H, Nakamura H, Oshiro S, Arakawa Y, Hayashi J, Sekine N, Nirei K, Yamagami H, Ogawa M, Nakajima N, Amaki S, Tanaka N, Moriyama M (2009) Zinc supplementation improves the outcome of chronic hepatitis C and liver cirrhosis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 45(3):292–303. doi:10.3164/jcbn. 08-246
Papanikolopoulos K, Alexopoulou A, Dona A, Hadziyanni E, Vasilieva L, Dourakis S (2014) Abnormalities in Cu and Zn levels in acute hepatitis of different etiologies. Hippokratia 18(2):144–149
Imai K, Beppu T, Yamao T, Okabe H, Hayashi H, Nitta H, Hashimoto D, Mima K, Nakagawa S, Sakamoto K, Chikamoto A, Ishiko T, Baba H (2014) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of preoperative serum zinc status in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after initial hepatectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3786-3
Murakami Y, Koyabu T, Kawashima A, Kakibuchi N, Kawakami T, Takaguchi K, Kita K, Okita M (2007) Zinc supplementation prevents the increase of transaminase in chronic hepatitis C patients during combination therapy with pegylated interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 53(3):213–218
Suzuki H, Takagi H, Sohara N, Kanda D, Kakizaki S, Sato K, Mori M, Gunma Liver Study G (2006) Triple therapy of interferon and ribavirin with zinc supplementation for patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomized controlled clinical trial. World J Gastroenterol: WJG 12(8):1265–1269
Poynard T, Imbert-Bismut F, Ratziu V, Chevret S, Jardel C, Moussalli J, Messous D, Degos F, group Gc (2002) Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients infected by hepatitis C virus: longitudinal validation in a randomized trial. J Viral Hepat 9(2):128–133
Fowkes FJ, Imrie H, Migot-Nabias F, Michon P, Justice A, Deloron P, Luty AJ, Day KP (2006) Association of haptoglobin levels with age, parasite density, and haptoglobin genotype in a malaria-endemic area of Gabon. AmJTrop Med Hyg 74(1):26–30
Rosenthal-Allieri MA, Tran A, Halfon P, Imbert-Bismut F, Munteanu M, Messous D, Peritore ML, Poynard T, Bernard A (2007) Optimal correlation between different instruments for Fibrotest-Actitest protein measurement in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 31(10):815–821
Acknowledgments
The authors report no conflict of interests or external source of financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abolfazl Pourhassan holds a degree in MD, Department of Infectious Disease, Sina Teaching Hospital, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences
Daniel Fadaei Fouladi holds a degree in MD, Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences
Simin Mirakhor Samani holds a degree in MD, Department of Pathology, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences
Sam Morshedi Asl holds a degree in MD, Neurosciences Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourhassan, A., Fouladi, D.F., Samani, S.M. et al. Serum Zinc and Haptoglobin in Noncirrhotic Azeri Patients with Chronic Active Hepatitis C: a Case–Control Study. Biol Trace Elem Res 167, 187–193 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0309-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0309-4