Abstract
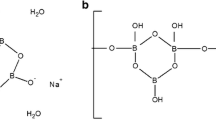
The present study characterizes the effects of the boric acid binding on calf thymus DNA (ct-DNA) by spectroscopic and calorimetric methods. UV–Vis absorbance spectroscopy, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy were employed to characterize binding properties. Changes in the secondary structure of ct-DNA were determined by CD spectroscopy. Sizes and morphologies of boric acid–DNA complexes were determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The kinetics of boric acid binding to calf thymus DNA (ct-DNA) was investigated by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). ITC results revealed that boric acid exhibits a moderate affinity to ct-DNA with a binding constant (K a) of 9.54 × 104 M−1. FT-IR results revealed that boric acid binds to the deoxyribose sugar of DNA without disrupting the B-conformation at tested concentrations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grimes RN (2004) Boron clusters come of age. J of Chem Educ 81:657–672
Barth RF, Coderre JA, Vicente MG, Blue TE (2005) Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: current status and future prospects. Clin Cancer Res 11:3987–4002
Tabassum S, Sharma GC, Arjmand F (2010) DNA interaction studies of new nano metal based anticancer agent: validation by spectroscopic methods. Nanotechnology 21:1–9
Kabalka GW (1998) Recent developments in boron neutron capture therapy. Expert Opin Ther Pat 8:445–551
Chen W, Mehta SC, Lu DR (1997) Selective boron drug delivery to brain tumors for boron neutron capture therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rew 26:231–247
Low LY, Hernández H, Robinson CV, O'Brien R, Grossmann JG, Ladbury JE et al (2002) Metal-dependent folding and stability of nuclear hormone receptor DNA-binding domains. J Mol Biol 319:87–106
Shelly K, Feaks DA, Hawthorne MF, Schmidt PG, Kritsch TA, Bauer WF (1992) Model studies directed toward the boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: boron delivery to murine tumors with liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:9039–9043
Lu DR, Mehta SC, Chen W (1997) Selective boron drug delivery to brain tumors for boron neutron capture therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 26:231–247
Barranco WT, Eckhert CD (2004) Boric acid inhibits human prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett 216:21–29
Barranco WT, Eckhert CD (2006) Cellular changes in boric acid-treated DU-145 prostate cancer cells. British J of Cancer 94:884–890
Meacham SL, Elwell KE, Ziegler S, Carper SW (2007) Advances in plant and animal boron nutrition. Springer, Netherlands
Scorei R, Ciubar R, Ciofrangeanu CM, Mitran V, Cimpean A, Iordachescu D (2008) Comparative effects of boric acid and calcium fructoborate on breast cancer cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 122:197–205
Weser U (1967) Chemistry and structure of some borate polyol compounds of biochemical interest. Struct Bond 2:160–180
Gabel D, Foster S, Fairchild RG (1987) The Monte Carlo simulation of the biological effect of the 10B(n, alpha)7Li reaction in cells and tissue and its implication for boron neutron capture therapy. Radiat Res 111:14–25
Rodríguez-Pulido A, Aicart E, Llorca O, Junquera E (2008) Compaction process of calf thymus DNA by mixed cationic-zwitterionic liposomes: a physicochemical study. J Phys Chem B 112:2187–2197
Ramakrishnan S, Suresh E, Riyasdeen A, Akbarsha MA, Palaniandavar M (2011) DNA binding, prominent DNA cleavage and efficient anticancer activities of tris(diimine)iron(II) complexes. Dalton Trans 40:3524–3536
Milyutin AV, Amirova LR, Kolla VE, Nazmetdinov FY, Drovosekova LP, Andreichikov YS (1998) Synthesis and study of antiinflammatory and analgesic activity of β-aroylpyruvoyl hydrazides of 2-methy(phenyl)-4-quinolinecarboxylic acids. Pharm Chem J 32:422–424
Moreira BG, You Y, Behlke MA, Owczarzy R. (2005) Effects of fluorescent dyes, quenchers, and dangling ends on DNA duplex stability. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 327:473-84.
Barreleiro PCA, Lindman B (2003) The kinetics of DNA–cationic vesicle complex formation. J Phys Chem B 107:6208–6213
Esposito D, Vecchio PD, Barone G (1997) Interactions with natural polyamines and thermal stability of DNA. A DSC study and a theoretical reconsideration. J Am Chem Soc 119:2606–2613
Jelesarov I, Bosshard HR (1999) Isothermal titration calorimetry and differential scanning calorimetry as complementary tools to investigate the energetics of biomolecular recognition. J Mol Recognit 12:3–18
Theophanides T (1981) Fourier transform infrared spectra of calf thymus DNA and its reactions with the anticancer drug cisplatin. Appl Spectrosc 35:461–465
Yang D, Wang AH-J (1996) Structural studies of interactions between anticancer platinum compounds and DNA. Prog Biophy Mol Biol 66:81–111
Arjmand F, Parveen S, Afzal M, Toupet L, Ben HT (2012) Molecular drug design, synthesis and crystal structure determination of CuII-SnIV heterobimetallic core: DNA binding and cleavage studies. Eur J Med Chem 49:141–150
Chitrapriya N, Jang YJ, Kim SK, Lee H (2011) Non-intercalative binding mode of bridged binuclear chiral Ru(II) complexes to native duplex DNA. J Inorg Biochem 105:1569–1575
Jangir DK, Charak S, Mehrotra R, Kundu S (2011) FTIR and circular dichroism spectroscopic study of interaction of 5-fluorouracil with DNA. J Photochem Photobiol B 105:143–148
Panja S, Jana B, Aich P, Basu T (2008) In vitro interaction between calf thymus DNA and Escherichia coli LPS in the presence of divalent cation Ca2+. Biopolymers 89:606–613
Kypr J, Vorlícková M (2002) Circular dichroism spectroscopy reveals invariant conformation of guanine runs in DNA. Biopolymers 67:275–277
Zaludová R, Zákovská A, Kasparková J, Balcarová Z, Kleinwächter V, Vrána O et al (1997) DNA interactions of bifunctional dinuclear platinum(II) antitumor agents. Eur J Biochem 246:508–517
Morales KA, Lasagna M, Gribenko AV, Yoon Y, Reinhart GD, Lee JC et al (2011) Pb2+ as modulator of protein-membrane interactions. J Am Chem Soc 133:10599–10611
Divsalar A, Damavandi SE, Saboury AA, Seyedarabi A, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2012) Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigations of β-lactoglobulin upon interaction with copper ion. J Dairy Res 79:209–215
Liu G, Xu H, Zhang L, Zheng Y (2011) Fe binding properties of two soybean (Glycine max L.) LEA4 proteins associated with antioxidant activity. Plant Cell Physiol 52:994–1002
Murai MJ, Sassonia RC, Zamboni AH, Conte FF, Martins-de-Souza D, Aparicio R et al (2008) Characterization of the C-terminal half of human juvenile myoclonic epilepsy protein EFHC1: dimer formation blocks Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding to its functional EF-hand. Arch Biochem Biophys 477:131–138
José TJ, Conlan LH, Dupureur CM (1999) Quantitative evaluation of metal ion binding to PvuII restriction endonuclease. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:814–823
Sacco C, Skowronsky RA, Gade S, Kenney JM, Spuches AM (2012) Calorimetric investigation of copper(II) binding to Aβ peptides: thermodynamics of coordination plasticity. J Biol Inorg Chem 17:531–541
Prislan I, Khutsishvili I, Marky LA (2011) Interaction of minor groove ligands with G-quadruplexes: thermodynamic contributions of the number of quartets, T-U substitutions, and conformation. Biochimie 93:1341–1350
Bhattacharjee AJ, Ahluwalia K, Taylor S, Jin O, Nicoludis JM, Buscaglia R et al (2011) Induction of G-quadruplex DNA structure by Zn(II) 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphyrin. Biochimie 93:1297–1309
Shukla S, Sastry M (2009) Probing differential Ag + -nucleobase interactions with isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC): towards patterned DNA metallization. Nanoscale 1:122–127
Wu J, Du F, Zhang P, Khan IA, Chen J, Liang Y (2005) Thermodynamics of the interaction of aluminum ions with DNA: implications for the biological function of aluminum. J Inorg Biochem 99:1145–1154
Zhang Y, Wilcox DE (2002) Thermodynamic and spectroscopic study of Cu(II) and Ni(II) binding to bovine serum albumin. J Biol Inorg Chem 7:327–337
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Turkish National Boron Research Institute (BOREN, Ankara, Turkey), for the financial support through Research Grant No. 2012.ç0356 and to A. D. Özkan and Z. Erdoğan for their help in conducting the experiments described. We also thank Middle East Technical University Central Laboratory for their expert help in the acquisition of transmission electron microscopy images. A.Ö. is supported by TUBITAK BIDEB (2211) PhD fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdemir, A., Gursaclı, R.T. & Tekinay, T. Non-intercalative, Deoxyribose Binding of Boric Acid to Calf Thymus DNA. Biol Trace Elem Res 158, 268–274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9924-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9924-8