Abstract
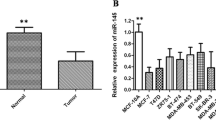
Nickel is an important kind of metal and a necessary trace element in people’s production and livelihood; it is also a well-confirmed human carcinogen. In the past few years, researchers did a large number of studies about the molecular mechanisms of nickel carcinogenesis, and they focused on activation of proto-oncogenes and inactivation of anti-oncogenes caused by gene point mutation, gene deletion, gene amplification, DNA methylation, chromosome condensation, and so on that were induced by nickel. However, the researches on tumorigenic molecular mechanisms regulated by microRNAs (miRNAs) are rare. In this study, we established nickel-induced tumor by injecting Ni3S2 compounds to Wistar Rattus. By establishing a cDNA library of miRNA from rat muscle tumor tissue induced by Ni3S2, we found that the expression of miR-222 was significantly upregulated in tumor tissue compared with the normal tissue. As we expected, the expression levels of target genes of miR-222, CDKN1B and CDKN1C, were downregulated in the nickel-induced tumor. The same alteration of miR-222 and its target genes was also found in malignant 16HBE cells induced with Ni3S2 compounds. We conclude that miR-222 may promote cell proliferation infinitely during nickel-induced tumorigenesis in part by regulating the expression of its target genes CDKN1B and CDKN1C. Our study elucidated a novel molecular mechanism of nickel-induced tumorigenesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Q, Suen TC, Sun H, Arita A, Costa M (2009) Nickel compounds induce apoptosis in human bronchial epithelial Beas-2B cells by activation of c-Myc through ERK pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 235:191–198
Doll R, Morgan LG, Speizer FE (1970) Cancers of the lung and nasal sinuses in nickel workers. Br J Cancer 24:623–632
Sutherland JE, Peng W, Zhang QW, Costa M (2001) The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A reduces nickel-induced gene silencing in yeast and mammalian cells. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 479:225–233
Costa M, Davidson TL, Chen HB, Ke QD, Zhang P, Yan Y et al (2005) Nickel carcinogenesis: epigenetics and hypoxia signaling. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 592:79–88
Bartel DP (2007) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function (reprinted from Cell, vol 116, pg 281–297, 2004). Cell 131:11–29
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Veronese A, Sabbioni S et al (2008) MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 27:5651–5661
Ohmori T, Okada K, Terada M, Tabei R (1999) Low susceptibility of specific inbred colonies of rats to nickel tumorigenesis in soft tissue. Cancer Lett 136:53–58
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115:787–798
Wang WC, Shi CY, Zhang JS, Gu WT, Li TJ, Gen MM, Chu WY, Huang RL, Liu YL, Hou YQ, Li P, Yin YL (2009) Molecular cloning, distribution and ontogenetic expression of the oligopeptide transporter PepT1 mRNA in Tibetan suckling piglets. Amino Acids 37:593–601
Lee Y-W, Broday L, Costa M (1998) Effects of nickel on DNA methyltransferase activity and genomic DNA methylation levels. Mutat Res 3:213–218
Golebiowski F, Kasprzak KS (2005) Inhibition of core histones acetylation by carcinogenic nickel(II). Mol Cell Biochem 279:133–139
Yan Y, Kluz T, Zhang P, Chen H-b, Costa M (2003) Analysis of specific lysine histone H3 and H4 acetylation and methylation status in clones of cells with a gene silenced by nickel exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 3:272–277
Huang X, Zhuang Z, KF R, C B K, M C (1994) The role of nickel and nickel-mediated reactive oxygen species in the mechanism of nickel carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect 120:281–284
Zhou D, Salnikow K, Costa M (1998) Cap43, a novel gene specifically induced by Ni2+ compounds. Cancer Res 58(10):2182–2189
Calin GA et al (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:7004–7009
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y, Takahashi T (2005) A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65:9628–9632
Bottoni A, Piccin D, Tagliati F, Luchin A, Zatelli MC, degli Uberti EC (2005) MiR-15a and miR-16-1 down-regulation in pituitary adenomas. J Cell Physiol 204:280–285
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15524–15529
Tang J-T, Wang J-L, Wan D, Hong J, Zhao S-L, Wang Y-C, Xiong H, Chen H-M, Fang J-Y (2011) MicroRNA 345, a methylation-sensitive microRNA is involved in cell proliferation and invasion in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 8:1207–1215
Weber B, Stresemann C, Brueckner B, Lyko F (2007) Methylation of human microRNA genes in normal and neoplastic cells. Cell Cycle 6:1001–1005
Shen HM, Zhang QF (1994) Risk assessment of nickel carcinogenicity and occupational lung cancer. Environ Health Perspect 102(Suppl 1):275–282
Grimsrud TK, Berge SR, Haldorsen T, Andersen A (2002) Exposure to different forms of nickel and risk of lung cancer. Am J Epidemiol 156(12):1123–1132
Gao W, Shen H, Liu L, Jian X, Jing X, Shu Y (2011) MiR-21 overexpression in human primary squamous cell lung carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. Cancer Res Clin Oncol 4:557–566
Gang Y, Guodong F, Cui S, Zhao S, Bernaudo S, Bai Y, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Yang BB, Peng C (2011) MicroRNA 376c enhances ovarian cancer cell survival by targeting activin receptor-like kinase7: implications for chemoresistance. Cell Science 124:359–368
Hwang J-H, Voortman J, Giovannetti E, Steinberg SM, Leon LG et al (2010) Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 5(5):e10630
Carlos le S, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrie M, Mesman E, Mangiola A, Anile C, Maira G, Mercatelli N, Ciafrè SA, Farace MG, Agami R (2007) Regulation of the p27Kip1 tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J 26:3699–3708
Sun K, Wang W, Zeng J-j, Cheng-tang W, Lei S-t, Li G-x (2011) MicroRNA-221 inhibits CDKN1C/p57 expression in human colorectal carcinoma. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 32:375–384
Lee MH, Reynisdottir I, Massague J (1995) Cloning of p57KIP2, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev 9:639–649
Matsuoka S, Edwards MC, Bai C, Parker S, Zhang P, Baldini A et al (1995) p57KIP2, a structurally distinct member of the p21CIP1 Cdk inhibitor family, is a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Genes Dev 9:650–662
Susaki E, Nakayama KI (2009) Functional similarities and uniqueness of p27 and p57: insight from a knock-in mouse model. Cell Cycle 8:2497–2501
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrier M, Mesman E, Mangiola A et al (2007) Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J 26:3699–3708
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Lijuan Zhang for kindly providing 16HBE cell line to our laboratory. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31271120, 31171012, and 81041069), National Key Basic Research Program of China (2011CB965102), and International Cooperation Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2011DFA30480 and 2011DFB30010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jing Zhang, Yang Zhou, and Lin Ma contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhou, Y., Ma, L. et al. The Alteration of MiR-222 and Its Target Genes in Nickel-Induced Tumor. Biol Trace Elem Res 152, 267–274 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9619-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9619-6