Abstract
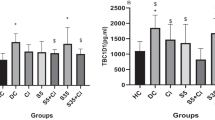
In this study, we report the effect of zinc supplementation on the distribution of elements in kidney tissue of diabetic rats subjected to acute swimming exercise. Diabetes was induced by two subcutaneous injections of 40 mg/kg of streptozotocin within a 24-h period. Zinc was given intraperitoneally at a dose of 6 mg/kg per day for a period of 4 weeks. The rats (n = 80) were equally divided into eight study groups: controls, zinc-supplemented, swimming, diabetic, zinc-supplemented diabetic, zinc-supplemented swimming, diabetic swimming, and zinc-supplemented diabetic swimming. The levels of lead, cobalt, molybdenum, chromium, boron, magnesium, iron, copper, calcium, zinc, and selenium were determined in the kidney tissue samples by ICP-AES. Higher molybdenum, calcium, zinc, and selenium values were found in both swimming and nonswimming diabetic rats. Significantly higher iron values were found in swimming, diabetic, diabetic swimming, and zinc-supplemented diabetic swimming rats (p < 0.001). Diabetic, zinc-supplemented diabetic, diabetic swimming, and zinc-supplemented diabetic swimming rats had the highest copper values. These results show that zinc supplementation normalized the higher levels of molybdenum, calcium, selenium, and iron levels seen in diabetic rats, indicating that zinc may have a regulatory effect on element metabolism in kidney tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P (1997) The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections by 2010. Diabetic Med 14(Suppl 5):5–85
Jensen T, Stender S, Deckert T (1988) Abnormalities in plasmas concentrations of lipoproteins and fibrinogen in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with increased urinary albumin excretion. Diabetologia 31(3):142–145
Islam MS, du Loots T (2007) Diabetes, metallothionein, and zinc interactions: a review. Biofactors 29(4):203–212
Ross R (1986) The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: an update. N Engl J Med 314(8):488–500
Scott DA (1934) Crystalline insulin. Biochem J 28(4):1592–1602
Brandao-Neto J, Silva CAB, Rezende AA, Almeida MG, Sales VSP, Marchini JS (2003) Zinc pharmacokinetics in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients after oral zinc tolerance test. Nutr Res 23(2):141–150
Chausmer AB (1998) Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 17(2):109–115
McNair P, Kiilerich S, Christiansen C, Christensen MS, Madsbad S, Transbol I (1981) Hyperzincuria in insulin treated diabetes mellitus—its relation to glucose homeostasis and insulin administration. Clin Chim Acta 112(3):343–348
Levine AS, McClain CJ, Handwerger BS, Brown DM, Morley JE (1983) Tissue zinc status of genetically diabetic and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Am J Clin Nutr 37(3):382–386
Lau AL, Failla ML (1984) Urinary excretion of zinc, copper and iron in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. J Nutr 114(1):224–233
Jansen J, Karges W, Rink L (2009) Zinc and diabetes—clinical links and molecular mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 20(6):399–417
Paffenbarger RS, Kampert JB, Lee IM, Hyde RT, Leung RW, Wing AL (1994) Changes in physical activity and other lifeway patterns influencing longevity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26(7):857–865
Kim JD, Yu BP, McCarter RJM, Lee SY, Herlihy JT (1996) Exercise and diet modulate cardiac lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defenses. Free Radic Biol Med 20(1):83–88
Fushimi H, Inoue T, Yamada Y, Horie H, Kameyama M, Minami T, Okazaki Y (1993) Zinc deficiency exaggerares diabetic osteoporosis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 20(3):191–196
Cordova A (1994) Zinc content in selected tissues in streptozotocin-diabetic rats after maximal exercise. Biol Trace Elem Res 42(3):209–216
Singh A, Failla ML, Deuster PA (1994) Exercise-induced changes in immune function: effects of zinc supplementation. J Appl Physiol 76(6):2298–2303
Gleeson M, Nieman DC, Pedersen BK (2004) Exercise, nutrition and immune function. J Sports Sci (London) 22(1):115–125
Havel PJ, Uriu-Hare JY, Liu T, Stanhope KL, Stern JS, Keen CL, Ahrén B (1998) Marked and rapid decreases of circulating leptin in streptozotocin diabetic rats: reversal by insulin. Am J Physiol 274(5 Pt 2):1482–491
Cemek M, Emin Büyükokuroğlu M, Yürümez Y, Yavuz Y, Aslan A, Büyükben A, Aymelek F (2010) Tissue trace and major element levels in organophosphate insecticide fenthion (Lebaycid) toxicity in rats: prophylactic and therapeutic effect of exogenous melatonin. Toxicol Environ Saf 73(2):206–212
Kaptanoğlu B, Turgut G, Genç O, Enli Y, Karabulut I, Zencir M, Turgut S (2003) Effects of acute exercise on the levels of iron, magnesium, and uric acid in liver and spleen tissues. Biol Trace Elem Res 91(2):173–178
Liu YQ, Duan XL, Chang YZ, Wang HT, Qian ZM (2006) Molecular analysis of increased iron status in moderately exercised rats. Mol Cell Biochem 282(1–2):117–123
Dogukan A, Sahin N, Tuzcu M, Juturu V, Orhan C, Onderci M, Komorowski J, Sahin K (2009) The effects of chromium histidinate on mineral status of serum and tissue in fat-fed and streptozotocin-treated type II diabetic rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 131(2):124–132
Reuter H, Grönke S, Adam C, Ribati M, Brabender J, Zobel C, Frank KF, Wippermann J, Schwinger RH, Brixius K, Müller-Ehmsen J (2008) Sarcoplasmic Ca2+ release is prolonged in nonfailing myocardium of diabetic patients. Mol Cell Biochem 308(1–2):141–149
Saltman PD, Strause LG (1993) The role of trace minerals in osteoporosis. J Am Coll Nutr 12(4):384–389
Baltaci AK, Sunar F, Mogulkoc R, Oztekin E (2004) Effect of zinc deficiency and supplementation on lipid peroxidation of renal tissue in ovariectomized rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 101:231–239
Simon SF, Taylor CG (2001) Dietary zinc supplementation attenuates hyperglycemia in db/db mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226(1):43–51
Jansen J, Karges W, Rink L (2009) Zinc and diabetes—clinical links and molecular mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 20(6):399–417
Gupta R, Garg VK, Mathur DK, Goyal RK (1998) Oral zinc therapy in diabetic neuropathy. J Assoc Physicians India 46(11):939–942
Duzguner V, Kaya S (2007) Effect of zinc on the lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant defense systems of the alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. Free Radic Biol Med 42:1481–86
Wu Y, Sun Z, Che S, Chang H (2004) Effects of zinc and selenium on the disorders of blood glucose and lipid metabolism and its molecular mechanism in diabetic rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 33(1):70–73
Holben DH, Smith AM (1999) The diverse role of selenium within selenoproteins: a review. J Am Diet Assoc 99(7):836–843
Bicer M, Akil M, Sivrikaya A, Kara E, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2011) Effect of zinc supplementation on the distribution of various elements in the serum of diabetic rats subjected to an acute swimming exercise. J Physiol Biochem 67(4):511–517
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivrikaya, A., Bicer, M., Akil, M. et al. Effects of Zinc Supplementation on the Element Distribution in Kidney Tissue of Diabetic Rats Subjected to Acute Swimming. Biol Trace Elem Res 147, 195–199 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9284-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9284-6