Abstract
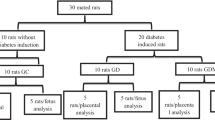
Oxidative stress is considered to be the main cause of diabetic complications. In the current study, we investigated the effect of selenium–vitamin E combination and melatonin on lipid peroxidation (LPO) and scavenging enzyme activity in the blood of streptozocin (STZ)-induced diabetic pregnant rats. Forty female Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups. The first and second groups were used as the non-pregnant control and pregnant control groups, respectively. The third group was the pregnant diabetic group. Vitamin E plus selenium and melatonin were administered to the diabetic pregnant rats consisting fourth and fifth groups, respectively. Diabetes was induced on day 0 of the study by STZ. Blood samples were taken from all animals on the 20th day of pregnancy. LPO level was higher in diabetic pregnant rats than in control, although superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase activities were lower in diabetic pregnant animals than in control. LPO levels were lower both in the two treatment groups than in the diabetic pregnant rats, whereas selenium–vitamin E combination and melatonin caused a significant increase in the activities of these antioxidant enzymes (p < 0.01). In conclusion, vitamin E plus selenium seems to be a more potent antioxidant compared to melatonin in diabetic pregnant rats. Melatonin did not significantly affect the elevated glucose concentration of diabetic pregnant treated with melatonin group. Vitamin E plus selenium may play a role in preventing diabetes-related diseases of pregnant subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- C:
-
Control
- DPM:
-
Diabetic pregnant treated with melatonin
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DPVESe:
-
Diabetic pregnant treated with VE plus Se
- GSH-Px:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MLT:
-
Melatonin
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- DP:
-
Pregnant diabetic untreated
- PC:
-
Pregnant control
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Se:
-
Selenium
- STZ:
-
Streptozocin
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- VE:
-
Vitamin E
References
Naziroglu M, Cay M (2001) Protective role of intraperitoneally administered vitamin E and selenium on the antioxidative defense mechanism in rats with diabetes induced streptozotocin. Biol Trace Elem Res 79:149–159
Vanheest JL, Rodgers CD (1997) Effects of exercise in diabetic rats before and during gestation on maternal and neo-natal outcomes. Am J Physiol 273(7):27–33
Damasceno DC, Volpato GT, Calderon İMP, Rudge MVC (2002) Oxidative stress and diabetes in pregnant rats. Anim Reprod Sci 72:235–244
Zhao Z, Reece EA (2005) Experimental mechanisms of diabetic embryopathy and strategies for developing therapeutic interventions. J Soc Gynecol Investig 12(8):549–557
Naziroglu M, Butterworth PJ (2005) Protective effects of moderate exercise with dietary vitamin C and E on blood antioxidative defense mechanism in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Can J Appl Physiol 30(2):172–185
Kutlu M, Naziroglu M, Simsek H, Yilmaz T, Sahap Kukner A (2005) Moderate exercise combined with dietary vitamins C and E counteracts oxidative stress in the kidney and lens of streptozotocin-induced diabetic-rat. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 75(1):71–80
Simsek M, Naziroglu M, Erdinc A (2005) Moderate exercise with a dietary vitamin C and e combination protects against streptozotocin-induced oxidative damage to the kidney and lens in pregnant rats. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 113(1):53–59
Oktem F, Ozguner F, Yilmaz HR, Uz E, Dundar B (2006) Melatonin reduces urinary excretion of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, albumin and renal oxidative markers in diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33(1–2):95–101
Cederberg J, Basu S, Eriksson UJ (2001) Increased rate of lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation in experimental diabetic pregnancy. Diabetologia 44:744–766
Naziroglu M, Simsek M, Kutlu M (2004) Moderate exercise with a dietary vitamin C and E combination protects against streptozotocin-induced oxidative damage to the blood and improves fetal outcomes in pregnant rats. Clin Chem Lab Med 42(5):511–517
Siman CM, Eriksson UJ (1997) Vitamin E decreases the occurrence of malformations in the offspring of diabetic rats. Diabetes 46:1054–1061
Kinalski M, Sledzievvski A, Telejko B, Zarzycki W, Kinalska I (1999) Antioxidant therapy and streptozotocin-induced diabetes in pregnant rats. Acta Diabetol 36:113–117
Cemek M, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Hazman O, Konuk M, Bulut S, Birdane YO (2010) The roles of melatonin and vitamin e plus selenium in prevention of oxidative stress induced by naloxone-precipitated withdrawal in heroin-addicted rats. Biol Trace Elem Res (in press)
Cemek M, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Hazman O, Bulut S, Konuk M, Birdane Y (2010) Antioxidant enzyme and element status in heroin addiction or heroin withdrawal in rats: effect of melatonin and vitamin E plus Se. Biol Trace Elem Res 139:41–54
Klein EA (2009) Selenium and vitamin E: interesting biology and dashed hope. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(5):283–285
Montilla P, Vardgas JF, Tunezz IF, Muñoz de Agueda MC, Valdelvira ME, Cabrera ES (1998) Oxidative stress in diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin: monoxide, NO stimulates insulin secretion by inducing calcium release from protective effects of melatonin. J Pineal Res 25:94–100
Tesoriere L, D’arpa D, Conti S, Giaccone V, Pintaudi AM, Livrea MA (1999) Melatonin protects human red blood cells from oxidative hemolysis: new insights into the radical-scavenging activity. J Pineal Res 27:95–105
Okatani Y, Wakatsuki A, Morioka N, Watanabe K (1999) Melatonin inhibits the vasorelaxant action of peroxynitrite in human umbilical artery. J Pineal Res 27:111–115
Armagan A, Uz E, Yilmaz HR, Soyupek S, Oksay T, Ozcelik N (2006) Effects of melatonin on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat testis. Asian J Androl 8(5):595–600
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li YA (1998) simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Durak I, Yurtarslani Z, Canbolat O, Akyol OA (1993) Methodological approach to superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity assay based on inhibition of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction. Clin Chim Acta 214:103–104
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Aebi Y (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Kinalski M, Sledziewski A, Telejko B, Zarzycki W, Kinalska I (2000) Lipid peroxidation and scavenging enzyme activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Acta Diabetol 37(4):179–183
Reece EA, Wu YK (1997) Prevention of diabetic embryopathy in offspring of diabetic rats with use of a cocktail of deficient substrates and antioxidant. Am J Obstet Gynecol 176:790–798
Gultekin F, Delibas N, Yasar S, Kilinc I (2001) In vivo changes in antioxidant systems and protective role of melatonin and a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E on oxidative damage in erythrocytes induced by chlorpyrifos-ethyl in rats. Arch Toxicol 75:88–96
Karaoz E, Gultekin F, Akdogan M, Oncu M, Gokcimen A (2002) Protective role of melatonin and a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E on lung toxicity induced by chlorpyrifos-ethyl in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 54:97–108
Nicholls DG, Budd SL (2000) Mitochondria and neuronal survival. Physiol Rev 80:315–360
Siu AW, Reiter RJ, To CH (1998) The efficacy of vitamin E and melatonin as an oxidant against lipid peroxidation in rat retinal homogenates. J Pineal Res 24:229–244
Siu AW, Reiter RJ, To CH (1999) Pineal indolamines and vitamin E reduce nitric oxide-induced lipid peroxidation in rat retinal homogenates. J Pineal Res 27:122–128
Baydas G, Canatan H, Turkoglu A (2002) Comparative analysis of the protective effects of melatonin and vitamin E on streptozocin-induced diabetes mellitus. J Pineal Res 32:225–228
Batcioglu K, Karagözler AA, Ozturk IC, Genc M, Bay A, Ozturk F et al (2005) Comparison of chemopreventive effects of vitamin E plus selenium versus melatonin in 7, 12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mouse brain damage. Cancer Detect Prev 29(1):54–58
Ozturk F, Ozturk IC, Batcioglu K, Vardi N (2006) The effect of melatonin on 7, 12-dimethyl-benz[a]anthracene injury in comparison with vitamin E+ selenium in mouse kidneys. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 20(4):359–364
Kara H, Cevik A, Konar V, Dayangac A, Servi K (2008) Effects of selenium with vitamin E and melatonin on cadmium-induced oxidative damage in rat liver and kidneys. Biol Trace Elem Res 125(3):236–244
Konar V, Kara H, Yilmaz M, Dayangac A, Karatas F (2007) Effects of selenium and vitamin E, in addition to melatonin, against oxidative stress caused by cadmium in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 118(2):131–137
Kara H, Cevik A, Konar V, Dayangac A, Yilmaz M (2007) Protective effects of antioxidants against cadmium-induced oxidative damage in rat testes. Biol Trace Elem Res 120(1–3):205–211
Oktem F, Ozguner F, Yilmaz HR, Uz E, Dündar B (2006) Melatonin reduces urinary excretion of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, albumin and renal oxidative markers in diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33(1–2):95–101
Naziroglu M, Karaoğlu A, Aksoy AO (2004) Selenium and high dose vitamin E administration protects cisplatin-induced oxidative damage to renal, liver and lens tissues in rats. Toxicology 195(2–3):221–230
Naziroğlu M (2003) Enhanced testicular antioxidant capacity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: protective role of vitamins C and E and selenium. Biol Trace Elem Res 94(1):61–72
Cemek M, Büyükben A, Büyükokuroglu ME, Aymelek F, Tür L (2010) Protective roles of vitamin E (≤alpha≥-tocopherol), Selenium and vitamin E plus Selenium in organophosphate toxicity in vivo: a comparative study. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 96:113–118
Cemek M, Büyükokuroglu ME, Büyükben A, Aymelek F, Özcan L (2010) Effects of vitamin E and selenium on tissue bio-element status in organophosphate toxicity in rats. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 98:9–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guney, M., Erdemoglu, E. & Mungan, T. Selenium–Vitamin E Combination and Melatonin Modulates Diabetes-Induced Blood Oxidative Damage and Fetal Outcomes in Pregnant Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1091–1102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8951-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8951-3