Abstract
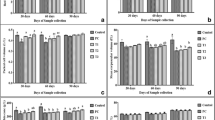
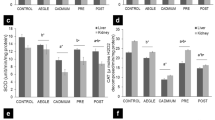
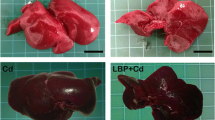
This study assessed the impact of either cadmium chloride (Cd) or sodium selenite (Se) alone or in combination on male Sprague–Dawley rats. For this purpose, body and liver weights, comet and TUNEL assays, histological analysis and levels of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in liver were determined in four groups of male Sprague–Dawley rats. The rats were given subcutaneous doses of 1 mg/kg body weight (BW) of either normal saline (control = Ct) or Cd or Se or Cd plus Se (Cd + Se) on alternate days for 4 weeks. The Cd group showed increased DNA damage, apoptosis and hepatic levels of lipid peroxidation and altered histology. Conversely, the antioxidant levels in this group were decreased as compared with the control group. The Se group also showed DNA damage, apoptosis and altered histology and reduced catalase activity, but it was less severe than the Cd group. In the Cd + Se group, ameliorating effects of Se on Cd-induced changes were observed. While the Se was able to curtail the toxic effect of Cd, the Cd or Se alone were genotoxic and cytotoxic for rats receiving a high pharmacological but non-fatal dose of 1 mg/kg BW.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 February 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04125-4
References
Gałaz yn-Sidorczuk M, Brzóska MM, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2008) Estimation of Polish cigarettes contamination with cadmium and lead, and exposure to these metals via smoking. Environ Monit Assess 137:481–493
Vromman V, Saegerman C, Pussemier L et al (2008) Cadmium in the food chain near non-ferrous metal production sites. Food Addit Contam 25:293–301
Palus J, Rydzynski K, Dziubaltowska E et al (2003) Genotoxic effects of occupational exposure to lead and cadmium. Mutat Res 540:19–28
Waalkes MP (2003) Cadmium carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 533:107–120
Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B et al (2003) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicol 192:95–117
Gennari A, Cortese E, Boveri M (2003) Sensitive endpoints for evaluating cadmium-induced acute toxicity in LLC-PK1 cells. Toxicol 183:211–220
López E, Figueroa S, Oset-Gasquem MJ, González MP (2003) Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced by cadmium in cortical neurons in culture. Br J Pharmacol 138:901–911
Wätjen W, Beyersmann D (2004) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in C6 glioma cells: influence of oxidative stress. Biometals 17:65–78
Shih CM, Ko WC, Yang L et al (2005) Detection of apoptosis and necrosis in normal human lung cells using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Ann NY Acad Sci 1042:488–496
Potten C, Wilson J (2004) How to die. In: Apoptosis. The life and death of cells. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 15–60
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, Bagchi M (2001) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 20:77–88
Yiin SJ, Chern CL, Sheu JY et al (2000) Cadmium induced liver, heart, and spleen lipid peroxidation in rats and protection by selenium. Biol Trace Elem Res 78:219–230
Letavayová L, Vlasakova D, Spallholz JE et al (2008) Toxicity and mutagenicity of selenium compounds in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat Res 638:1–10
Wu Q, Huang K (2004) Effect of long-term Se deficiency on the antioxidant capacities of rat vascular tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 98:73–84
Agay D, Sandre C, Ducros V et al (2005) Optimization of selenium status by a single intraperitoneal injection of Se in Se deficient rat: possible application to burned patient treatment. Free Radic Biol Med 39:762–768
Biswas S, Talukder G, Sharma A (2000) Chromosome damage induced by selenium salt in human peripheral lymphocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 14:405–408
Machado Mda S, Villela IV, Moura DJ et al (2009) 3′3-ditriXuoromethyldiphenyl diselenide: a new organoselenium compound with interesting antigenotoxic and antimutagenic activities. Mutat Res 673:133–140
Wycherly BJ, Moak MA, Christensen MJ (2004) High dietary intake of sodium selenite induces oxidative DNA damage in rat liver. Nutr Cancer 48:78–83
Colado-Megía MI, Sánchez-Sánchez V, Camarero-Jiménez J, O’Shea-Gaya E (2004) Effect of dietary selenium on MDMA (“ecstasy”)-induced neurotoxicity in brain mouse (in Spanish). Mapfre Med 15:53–62
Hasgekar N, Beck JP, Dunkelberg H et al (2006) Influence of antimonite, selenite, and mercury on the toxicity of arsenic in primary rat hepatocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 111:167–183
Zwolak I, Zaporowska H (2009) Preliminary studies on the effect of zinc and selenium on vanadium-induced cytotoxicity in vitro. Acta Biol Hung 60:55–56
Alaejos MS, Diaz Romero FJ, Diaz Romero C (2000) Selenium and cancer: some nutritional aspects. Nutrition 16:376–383
Ognjanović B, Žikić RV, Štajn A et al (1995) The effects of selenium on the antioxidant defense system in the liver of rats exposed to cadmium. Physiol Res 44:293–300
Žikić RV, Štajn AŠ, Ognjanović BI et al (1998) The effect of cadmium and selenium on the antioxidant enzyme activities in rat heart. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 17:259–264
Xiao P, Jia XD, Zhong WJ et al (2002) Restorative effects of zinc and selenium on cadmium induced kidney oxidative damage in rats. Biomed Environ Sci 15:67–74
Combs G, Gray WP (1998) Chemopreventive agents: selenium. Pharmacol Ther 79:179–192
Koyu A, Gokcimen A, Ozguner F, Bayram DS, Kocak A (2006) Evaluation of the effects of cadmium on rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 284(1–2):81–85
Mitsumori K, Shibutani M, Sato S et al (1998) Relationship between the development of hepato-renal toxicity and cadmium accumulation in rats given minimum to large amounts of cadmium chloride in the long term: preliminary study. Arch Toxicol 72(9):545–552
Beer MH, Porter RS, Jones TV (2006) The Merck manual of diagnosis and therapy, 18th edn. Wiley, UK
Nuttall KL (2006) Review: evaluating selenium poisoning. Ann Clin Lab Sci 36:409–420
Singh NP, Mc Coy MT, Tice RR et al (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175(1):184–191
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Jiang ZY, Hunt JV, Wolff SD (1992) Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of xylenol orange for detection of lipid hydroperoxides in low density lipoprotein. Anal Biochem 202:384–391
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total protein bound and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with ellmans reagent. Anal Biochem 25:293–298
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic, New York, pp 673–685
Olive PL, Banath JP (2006) The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat Protoc 1(1):23–29
Kumaravel TS, Jha AN (2006) Reliable comet assay measurements for detecting DNA damage induced by ionising radiation and chemicals. Mutat Res 605(1–2):7–16
Yu RA, He LF, Chen XM (2007) Effects of cadmium on hepatocellular DNA damage, proto-oncogene expression and apoptosis in rats. Biomed Environ Sci 20(2):146–153
Yu RA, Yang CF, Chen XM (2006) DNA damage, apoptosis and C-myc, C-fos, and C-jun over expression induced by selenium in rat hepatocytes. Biomed Environ Sci 19(3):197–204
Cemeli E, Carder J, Anderson D et al (2003) Antigenotoxic properties of selenium compounds on potassium dichromate and hydrogen peroxide. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen 23:53–67
Yu RA, Chen XM (2004) Effects of selenium on rat hepatocellular DNA damage, apoptosis and changes of cell cycle induced by cadmium in vivo. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 38(3):155–158
Cemeli E, Marcos R, Anderson D (2006) Genotoxic and antigenotoxic properties of selenium compounds in the in vitro micronucleus assay with human whole blood lymphocytes and TK6 lymphoblastoid cells. Sci World J 6:1202–1210
Xiang N, Zhao R, Zhong W (2009) Sodium selenite induces apoptosis by generation of superoxide via the mitochondrial-dependent pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63:351–362
Philchenkov A, Zavelevich M, Khranovskaya N, Surai P (2007) Comparative analysis of apoptosis inductions by selenium compounds in human lymphoblastic leukaemia MT-4 cells. Exp Oncol 29:257–261
Zou Y, Yang J, Liu X, Yuan J (2007) Relationship between reactive oxygen species and apoptosis in HepG2 cells induced by sodium selenite. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 36:272–274
Goel A, Fuerst F, Hotchkiss E, Boland CR (2006) Selenomethionine induces p53 mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 5:529–535
Last K, Maharaj L, Perry J (2006) The activity of methylated and non-methylated selenium species in lymphoma cell lines and primary tumours. Ann Oncol 7:773–779
Wang XH, Wei YM, Bai H et al (2004) Apoptosis and regulation of expressions of apoptosis-related gene Bcl-2 and p53 induced by selenium dioxide in three leukaemia cell lines. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 24(10):1160–1163
Rooprai HK, Kyriazis I, Nuttall RK et al (2007) Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptosis by selenium in human malignant brain tumour cells in vitro. Int J Oncol 30:1263–1271
Al-Hashem F, Dallak M, Bashir N et al (2009) Camel’s milk protects against cadmium chloride induced toxicity in white albino rats. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 4(3):107–117
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Mason RP, Walter MF, Mason PE (1997) Effect of oxidative stress on membrane structure: small angle X-ray diffraction analysis. Free Radic Biol Med 23:419–425
Koyuturk M, Yanardag R, Bulkent S, Tunali S (2006) Influence of combined antioxidants against cadmium induced testicular damage. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 21:235–240
Mohanpuria P, Rana NK, Yadav SK (2007) Cadmium induced oxidative stress influence on glutathione metabolic genes of Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze. Environ Toxicol 22(4):368–374
Lazarus M, Orct T, Blanusa M (2006) Effect of selenium pre-treatment on cadmium content and enzymatic antioxidants in tissues of suckling rat. Toxicol Lett 164S1: S191
Saito Y, Takahashi K (2002) Characterization of selenoprotein P as a selenium supply protein. Eur J Biochem 269:5746–5751
Gan L, Liu Q, Xu HB et al (2002) Effects of selenium overexposure on glutathione peroxidase and Thioredoxin reductase gene expressions and activities. Biol Trace Elem Res 89:165–175
Tandon SK, Singh S, Prasad S et al (2003) Reversal of cadmium induced oxidative stress by chelating agent, antioxidant, or their combination in rat. Toxicol Lett 45:211–217
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the Islamic Development Bank Jeddah, Saudi Arabia for funding this post-doctoral research at Newcastle University and Professor Dr. Samina Jalali, Dr. Sarwat Jahan, Dr. Robina Shaheen, Riffat Gillani, Noshaba Memon and Aysha Ambreen for their help and support during the rat trials at Quaid-i-Azam University Islamabad, Pakistan.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04125-4
About this article
Cite this article
Jabeen, F., Chaudhry, A.S. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Effects of Cadmium Chloride and Sodium Selenite Alone or in Combination on the Liver of Male Sprague–Dawley Rats Assessed by Different Assays. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1077–1090 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8946-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8946-0