Abstract
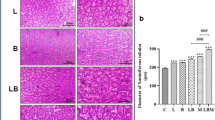
The objectives of this study were to investigate the effects of dietary high molybdenum (Mo) on immune function by determining changes of the subsets of peripheral blood T-cells and serum interleukin (IL)-2 contents. 300 1-day-old avian broilers were divided into four groups and fed on a corn–soybean basal diet as control diet or the same diet amended to contain 500; 1,000; and 1,500 mg/kg of Mo supplied as sodium molybdate dihydrate. In comparison with those of the control group, the percentages of CD3+, CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ were decreased in 1,000 and 1,500 mg/kg of Mo intake groups from 14 days of age to 42 days of age. Also, the serum IL-2 contents were decreased in 1,000 and 1,500 mg/kg of Mo intake groups from 14 days of age to 42 days of age. Histopathologically, hypocellularity appeared in the thymus in 1,000 and 1,500 mg/kg of Mo intake groups. It was concluded that dietary high-Mo (1,000 mg/kg and 1,500 mg/kg) reduced the percentages of peripheral blood T-cell subsets and serum IL-2 contents and caused thymic lesions. The cellular immune function was finally injured in broilers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mendel RR, Bittner F (2006) Cell biology of molybdenum. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1763:621–635
Trumbo P, Yates AA, Schlicker S et al (2001) Dietary reference intakes: vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. J Am Diet Assoc 101:294–301
Novotny JA, Turnlund JR (2006) Molybdenum kinetics in men differ during molybdenum depletion and repletion. J Nutr 136:953–957
Abumrad NN, Schneider AJ, Steel D et al (1981) Amino acid intolerance during prolonged total parenteral nutrition reversed by molybdate therapy. Am J Clin Nutr 34:2551–2559
Bersényi A, Berta E, Kádár I et al (2008) Effects of high dietary molybdenum in rabbits. Acta Vet Hung 56(1):41–55
Haschek WM, Rousseaux CC, Wallig MA (2002) Handbook of toxicologic pathology, 2nd edn. Academic, San Francisco, New York, pp 595–625
Chen T, Cui Y, Bai C et al (2009) Decreased percentages of the peripheral blood T-Cell subsets and the serum IL-2 contents in chickens fed on diets excess in fluorine. Biol Trace Elem Res 132:122–128
Gisela FE, Walter GB, Tina KB (1998) CD4, CD8 and TCR defined T-cell subsets in thymus and spleen of 2- and 7-week old commercial broiler chickens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 62:339–348
Kidd MT, Ferket PR, Qureshi MA (1996) Zinc metabolism with special reference to its role in immunity. World's Poul Sci J 52:309–324
Bonham M, O’Connor JM, Hannigan BM et al (2002) The immune system as a physiological indicator of marginal copper status. Br J Nutr 87:383–403
Vitaly V, Ganusov, Milutinovic Dejan et al (2007) L-2 regulates expansion of CD4-T cell populations by affecting cell death: insights from nodeling CFSE data. J Immunol 179:950–957
Smith KA (1988) Interleukin-2:inception, impact, and implications. Science 240:1169–1176
Acknowledgment
The study was supported by the program for Changjiang scholars and the innovative research team in the University (IRT 0848) and Education Department and Scientific Department of Sichuan Province (09ZZ017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Cui, H., Yang, F. et al. Effect of Dietary High Molybdenum on Peripheral Blood T-Cell Subsets and Serum IL-2 Contents in Broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 142, 517–522 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8768-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8768-0