Abstract
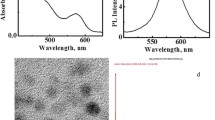
Recently, quantum dots derived from trace elements like cadmium and selenium have attracted widespread interest in biology and medicine. They are rapidly being used as novel tools for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In this report, we evaluated the distribution of silica-coated cadmium selenide (CdSe) quantum dots (QDs) following intravenous injection into male Swiss albino mice as a model system for determining tissue localization using in vivo fluorescence and ex vivo elemental analysis by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Trioctylphosphine oxide-capped CdSe quantum dots were synthesized and rendered water soluble by overcoating with silica, using aminopropyl silane (APS) as silica precursor. ICP-OES was used to measure the cadmium content to indicate the concentration of QDs in blood, organs and excretion samples collected at predetermined time intervals. Meanwhile, the distribution and aggregation state of QDs in tissues were also investigated in cryosections of the organs by fluorescence microscopy. We have demonstrated that the liver and kidney were the main target organs for QDs. Our systematic investigation clearly shows that most of the QDs were metabolized in the liver and excreted via faeces and urine in vivo. A fraction of free QDs, maintaining their original form, could be filtered by glomerular capillaries and excreted via urine as small molecules within 5 days.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICP-OES:
-
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy
- TOPO:
-
Trioctylphosphine oxide
- APS:
-
Aminopropyl silane
- TOP:
-
Trioctylphosphine
- QDs:
-
Quantum dots
- QD 705:
-
Quantum dots 705
References
Alivisatos AP, Gu W, Larabell C (2005) Quantum dots as cellular probes. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:55–76
Azzazy HME, Mansour MMH, Kazmierczak SC (2006) Nanodiagnostics: a new frontier in clinical laboratory medicine. Clin Chem 52:1238–1246
Leary SP, Liu CY, Apuzzo MLJ (2006) Toward the emergence of nanoneurosurgery: part II—nanomedicine: diagnostics and imaging at the nanoscale level. Neurosurgery 58:805–823
Pinaud F, Michalet X, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, Iyer G, Weiss S (2006) Advances in fluorescence imaging with quantum dot bio-probes. Biomaterials 27:1679–1687
Smith AM, Ruan G, Rhyner MN, Nie S (2006) Engineering luminescent quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Ann Biomed Eng 34:3–14
Derfus AM, Chan WCW, Bhatia S (2004) Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor nanocrystals. Nano Lett 4:11–18
Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, Sundaresan G, Wu AM, Gambhir SS, Weiss S (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307:538–544
Ballou B, Lagerholm BC, Ernst LA, Bruchez MP, Waggoner AS (2004) Noninvasive imaging of quantum dots in mice. Bioconjug Chem 15(1):79–86
Ryman-Rasmussen J, Riviere JE, Monteiro-Riviere NA (2007) Variables influencing interactions of untargeted quantum dot nanoparticles with skin cells and identification of biochemical modulators. Nano Lett 7:1344–1348
Peng XA, Peng XG (2001) Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. J Am Chem Soc 123:183–184
Pellegrino T, Kudera S, Liedl T, Javier AM, Manna L, Parak WJ (2005) On the development of colloidal nanoparticles towards multifunctional structures and their possible use for biological applications. Small 1:48–63
Darbandi M, Thomann R, Nann T (2005) Single quantum dots in silica spheres by microemulsion synthesis. Chem Mater 17:5720–5725
Selvan ST, Patra PK, Ang CY, Ying JY (2007) Synthesis of silica-coated semiconductor and magnetic quantum dots and their use in the imaging of live cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:2448–2452
Chen L, Zurita AJ, Ardelt PU, Giordano RJ, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2004) Design and validation of a bifunctional ligand display system for receptor targeting. Chem Biol 11(8):1081–1091
Han R, Yu M, Zheng Q, Wang L, Hong Y, Sha Y (2009) A facile synthesis of small-sized, highly photoluminescent, and monodisperse CdSeS QD/SiO2 for live cell imaging. Langmuir 25:12250–12255
Bakalova R, Zhelev Z, Aoki I, Ohba H, Imai Y, Kanno I (2006) Silica-shelled single quantum dot micelles as imaging probes with dual or multimodality. Anal Chem 78:5925–5932
Akerman ME, Chan WC, Laakkonen P, Bhatia SN, Ruoslahti E (2002) Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(20):12617–12621
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LW, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22(8):969–976
Lim YT, Kim S, Nakayama A, Stott NE, Bawendi MG, Frangioni JV (2003) Selection of quantum dot wavelengths for biomedical assays and imaging. Mol Imaging 2(1):50–64
Yang RSH, Chang LW, Wu JP, Tsai MH, Wang HJ, Kuo YC, Yeh TK, Yang CS, Lin P (2007) Persistent tissue kinetics and redistribution of nanoparticles, quantum dot 705, in mice: ICPMS quantitative assessment. Environ Health Perspect 115:1339–1343
Vinayakan R, Shanmugapriya T, Nair PV, Ramamurthy P, Thomas KG (2007) An approach for optimizing the shell thickness of core–shell quantum dots using photoinduced charge transfer. J Phys Chem C 111:10146–10149
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dickey DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach. McGraw Hill, New York, p 201
Ghazani AA, Lee JA, Klostranec J, Xiang Q, Dacosta RS, Wilson BC, Tsao MS, Chan WC (2006) High throughput quantification of protein expression of cancer antigens in tissue microarray using quantum dot nanocrystals. Nano Lett 6(12):2881–2886
Larson DR, Zipfel WR, Williams RM, Clark SW, Bruchez MP, Wise FW, Webb WW (2003) Water-soluble quantum dots for multiphoton fluorescence imaging in vivo. Science 300(5624):1434–1436
Morgan NY, English S, Chen W, Chernomordik V, Russo A, Smith PD, Gandjbakhche A (2005) Real time in vivo non-invasive optical imaging using near-infrared fluorescent quantum dots. Acad Radiol 12(3):313–323
Hoshino A, Fujioka K, Oku T, Suga M, Sasaki YF, Ohta T, Yasuhara M, Suzuki K, Yamamoto K (2004) Physicochemical properties and cellular toxicity of nanocrystal quantum dots depend on their surface modification. Nano Lett 4:2163–2169
Lovric J, Bazzi HS, Cuie Y, Fortin GRA, Winnik FM, Maysinger D (2005) Unmodified cadmium telluride quantum dots induce reactive oxygen species formation leading to multiple organelle damage and cell death. Chem Biol 12:1227–1234
Riegler J, Nann T (2004) Application of luminescent nanocrystals as labels for biological molecules. Anal Bioanal Chem 379:913–919
Duconge F, Pons T, Pestourie C, Herin L, Theze B, Gombert K, Mahler B, Hinnen F, Kühnast B, Dolle F, Dubertret B, Tavitian B (2008) Fluorine-18-labeled phospholipid quantum dot micelles for in vivo multimodal imaging from whole body to cellular scales. Bioconjug Chem 19:1921–1926
Chen Z, Chen H, Meng H, Xing G, Gao X, Sun B, Shi X, Yuan H, Zhang C, Liu R, Zhao F, Zhao Y, Fang X (2008) Bio-distribution and metabolic paths of silica coated CdSeS quantum dots. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230:364–371
Schipper ML, Iyer G, Koh AL, Cheng Z, Ebenstein Y, Aharoni A, Keren S, Bentolila LA, Li J, Rao J, Chen X, Banin U, Wu AM, Sinclair R, Weiss S, Gambhir SS (2009) Particle size, surface coating, and PEGylation influence the biodistribution of quantum dots in living mice. Small 5:126–134
Soo Choi H, Liu W, Misra P, Tanaka E, Zimmer JP, Itty Ipe B, Bawendi MG, Frangioni JV (2007) Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 25:1165–1170
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, New Delhi, for the financial assistance as research grant (Order No.BT/PR9904/NNT/28/63/2007) given to Dr. Annie Abraham, Principal Investigator, DBT project; Dr. K. George Thomas, Scientist, National Institute of Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (CSIR), Trivandrum, India for supplying nanomaterials; UGC, Govt. of India for the research fellowship to Vinayakan R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vibin, M., Vinayakan, R., John, A. et al. Biokinetics and In Vivo Distribution Behaviours of Silica-Coated Cadmium Selenide Quantum Dots. Biol Trace Elem Res 142, 213–222 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8763-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8763-5