Abstract
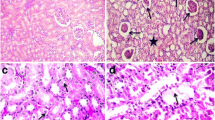
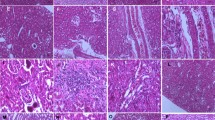
Ultrastructural changes in the kidneys of rats after acute cadmium exposure and the effects of exogenous metallothionein (MT) were studied by transmission electron microscopy. Thirty-six adult Wistar rats were divided into three groups. Cadmium chloride (CdCl2) (3.5 mg/kg/day) was injected subcutaneously in the first group. In the second group, 30 μmol/kg MT was administered in addition to CdCl2. Control rats received 0.5 ml subcutaneous saline solution. Four rats from each group were killed on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 after administration of the compounds. Kidney tissues were taken and fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution for electron microscopic observations. Tissue damage in kidney increased as time passed since the administration of CdCl2 in the first group. Degeneration in the proximal and distal tubules was observed. Increased apoptosis was seen in the proximal tubules epithelium, especially on day 7. Peritubular capillaries became dilated, there was degeneration of the endothelial cells, and the amount of intertubular collagen fibers was increased. On day 1, irregular microvilli in the proximal tubules, deepening of the basal striations, and myelin figures; on day 3, multiple vesicular mitochondria and regions of edema around tubules; on days 5 and 7, increased apoptotic cell in the proximal tubules and widened rough endoplasmic reticulum of the endothelial cells of glomerular capillaries were observed. We observed that the structural alterations that increased depending on the day of Cd administration decreased after exogenous MT administration, the dilation of the peritubular capillaries persisted, and there were degenerated proximal tubules. It was established that cadmium chloride was toxic for kidney cortex and caused structural damage. Exogenous MT partly prevents CdCl2-induced damage.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Liu J, Habeebu SM, Waalkes MP, Klaassen CD (2000) Metallothionein_I/II null mice are sensitive to chronic oral cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 57:167–176
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR, Woods JM (2006) The vascular endothelium as a target of cadmium toxicity. Life Sci 79:1493–1506
Takebayashi S, Jimi S, Segawa M, Takaki A (2003) Mitochondrial DNA deletion of proximal tubules is the result of itai-itai disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 7:18–26
Satarug S, Ujjin P, Vanavanitkun Y, Nishijo M, Baker JR, Moore MR (2004) Effects of cigarette smoking and exposure to cadmium and lead on phenotypic variability of hepatic CYP2A6 and renal function biomarkers in men. Toxicology 204:161–173
Chen L, Jin T, Huang B, Chang X, Lei L, Nordberg GF, Nordberg M (2006) Plasma metallothionein antibody and cadmium-induced renal dysfunction in an occupational population in China. Toxicol Sci 9:104–112
Satarug S, Nishijo M, Lasker JM, Edwards RJ, Moore MR (2006) Kidney dysfunction and hypertension: role for cadmium, p450 and heme oxygenases? Tohoku J Exp Med 208:179–202
Wolff NA, Abouhamed M, Verroust PJ, Thevenod F (2006) Megalin-dependent internalization of cadmium-metallothionein and cytotoxicity in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:782–791
Waalkes MP, Anver MR, Diwan BA (1999) Chronic toxic and carcinogenic effects of oral cadmium in the Noble (NBL7cr) rat: induction of neoplastic and proliferative lesions of the adrenal, kidney, prostate and testes. J Toxicol Environ Health 58:199–214
Brzoska MM, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2005) Bone metabolism of male rats chronically exposed to cadmium. Toxicol Appl Pharm 207:195–211
Barbier O, Dauby A, Jacquillet G, Tauc M, Poujeol P, Cougnon M (2005) Zinc and cadmium interactions in a renal cell line derived from rabbit proximal tubule. Nephron Physiol 99:74–84
Stinson LJ, Darmon AJ, Dagnino L, D’Souza SJA (2003) Delayed apoptosis post-cadmium injury in renal proximal tubule epithelial cells. Am J Nephrol 23:27–37
Aşar M, Kayışlı VA, İzgut-Uysal VN, Akkoyunlu G (2004) Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural changes in the renal cortex of cadmium-treated rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 97:249–263
Brzoska MM, Kaminski M, Dziki M, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2004) Changes in the structure and function of the kidney of rats chronically exposed to cadmium. II. Histoenzymatic studies. Arch Toxicol 78:226–231
Thophon S, Pokethitiyook P, Chalermwat K, Upatham ES, Sahaphong S (2004) Ultrastructural alterations in the liver and kidney of white sea bass, Lates calcarifer, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ Toxicol 19:11–19
Hijova E (2004) Metallothioneins and zinc: their functions and interactions. Bratisl Lek Listy 105:230–234
Theocharis SE, Margeli AP, Klijanienko JT, Kouraklis GP (2004) Metallothionein expression in human neoplasia. Histopathology 45:103–118
Jin T, Nordberg M (1998) Toxicokinetics and biochemistry of cadmium with special emphasis on the role of metallothionein. Neurotoxicology 19:529–535
McAleer MF, Tuan RS (2004) Cytotoxicant-induced trophoblast dysfunction and abnormal pregnancy outcomes: role of zinc and metallothionein. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 72:361–370
Sato M, Kondoh M (2002) Recent studies on metallothionein: protection against toxicity of heavy metals and oxygen free radicals. Tohoku J Exp Med 196:9–22
Somji S, Garrett SH, Sens MA, Gurel V, Sens DA (2004) Expression of metallothionein isoform 3 (MT-3) determines the choice between apoptotic or necrotic cell death in Cd+2 exposed human proximal tubule cells. Toxicol Sci 80:358–366
Shimoda R, Naqamine T, Takaqi H, Mori M, Waalkes MP (2001) Induction of apoptosis in cells by cadmium: quantitative negative correlation between basal or induced metallothionein concentration and apoptotic rate. Toxicol Sci 64:208–215
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Choudhuri JS (1999) Metallothionein: an intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:267–294
Min KS, Morishita F, Tetsuchikawahana N, Onasaka S (2005) Induction of hepatic and renal metallothionein synthesis by ferric nitrilotriacetate in mice: the role of MT as an antioxidant. Toxicol Appl Pharm 204:9–17
Shaikh ZA, Vu TT, Zaman K (1999) Oxidative stress as a mechanism of chronic cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and renal toxicity and protection by antioxidants. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 154:256–263
Kara H, Karataş F, Canatan H, Servi K (2005) Effects of exogenous metallothionein on acute cadmium toxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 104:223–232
Niewenhuis RJ, Dimitriu C, Prozialeck WC (1997) Ultrastructural characterization of the early changes in intercellular junctions in response to cadmium (Cd+2) exposure in LLC-PK1 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm 142:1–12
Fukumoto M, Kujiraoka T, Hara M, Shibasaki T, Hosoya T, Yoshida M (2001) Effect of cadmium on gap junctional intercellular communication in primary cultures of rat renal proximal tubular cells. Life Sci 69:247–254
Jacquillet G, Barbier O, Cougnon M, Tauc M, Namorado MC, Martin D, Reyes JL, Poujeol P (2006) Zinc protects renal function during cadmium intoxication in the rat. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F127–F137
Jimi S, Uchiyama M, Takaki A, Suzumiya J, Hara S (2004) Mechanism of cell death induced by cadmium and arsenic. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1011:325–331
Thevenod F (2003) Nephrotoxicity and the proximal tubule. Insights from cadmium. Nephron Physiol 93:87–93
Choi JH, Rhee SJ (2003) Effects of vitamin E on renal dysfunction in chronic cadmium-poisoned rats. J Med Food 6:209–215
Matsuura K, Takasugi M, Kunifuji Y, Horie A, Kuroiwa A (1991) Morphological effects of cadmium on proximal tubular cells in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 31:171–182
Condron RJ, Schroen CJ, Marshall AT (1994) Morphometric analysis of renal proximal tubules in cadmium-treated rats. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 26:51–58
Chishti MA, Rotkiewicz T (1993) Hepatic and renal ultrastructural changes in cockerels exposed to cadmium chloride and subsequent interaction with organophosphate insecticide. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 12:35–45
Brzoska MM, Kaminski M, Supernak-Bobko D, Zwierz K, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2003) Changes in the structure and function of the kidney of rats chronically exposed to cadmium. I. Biochemical and histopathological studies. Arch Toxicol 77:344–352
Morales AI, Vincente-Sanchez C, Jerkic M, Santiago JM, Sanchez-Gonzales PD, Perez-Barriocanal F, Lopez-Novoa JM (2006) Effect of quercetin on metallothionein, nitric oxide synthases and cyclooxygenase-2 expression on experimental chronic cadmium nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharm 210:128–135
Prozialeck WC, Lamar PC, Lynch SM (2003) Cadmium alters the localization of N-cadherin, E-cadherin and beta-catenin in the proximal tubule epithelium. Toxicol Appl Pharm 189:180–195
DaltonTP, He L, Wang B, Miller ML, Jin L, Stringer KF, Chang X, Baxter CS, Nebert DW (2005) Identification of mouse SLC39A8 as the transporter responsible for cadmium-induced toxicity in the testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3401–3406
Kuester RK, Waalkes MP, Goering PL, Fisher BL, McKuskey RS, Sipes IG (2002) Differential hepatotoxicity induced by cadmium in Fischer 344 and Sprague–Dawley rats. Toxicol Sci 65:151–159
Liu J, Habeebu SS, Liu Y, Klaassen CD (1998) Acute CdMT injection is not a good model to study chronic Cd nephropathy: comparison of chronic CdCl2 and CdMT exposure with acute CdMT injection in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharm 153:48–58
Chaumont SB, Maupoil V, Berthelot A (2006) Metallothionein induction in the liver, kidney, heart and aorta of cadmium and isoproterenol treated rats. J Appl Toxicol 26:47–55
Liu Y, Liu J, Habeebu SS, Klaassen CD (1999) Metallothionein protects against the nephrotoxicity produced by chronic CdMT exposure. Toxicol Sci 50:221–227
Liu F, Jan KY (2000) DNA damage in arsenite- and cadmium-treated bovine aortic endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 28:55–63
Liu J, Zhang Y, Huang D, Song G (2005) Cadmium induced MTs synthesis via oxidative stress in yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biochem 280:139–145
Han XY, Xu ZR, Wang YZ, Huang WC (2006) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res 110:251–263
Jurczuk M, Brzoska MM, Moniuszku-Jakoniuk J, Galazyn-Sidorczuk M, Kulikowska-Karpinska E (2004) Antioxidant enzymes activity and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of rats exposed to cadmium and ethanol. Food Chem Toxicol 42:429–438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukner, A., Colakoglu, N., Kara, H. et al. Ultrastructural Changes in the Kidney of Rats with Acute Exposure to Cadmium and Effects of Exogenous Metallothionein. Biol Trace Elem Res 119, 137–146 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-0049-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-0049-1