Abstract
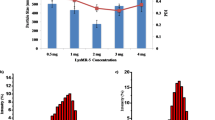
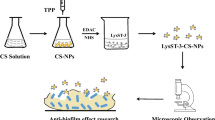
Resistance to antimicrobial agents has created potential problems in finding efficient treatments against bacteria. Thus, using new therapeutics, such as recombinant chimeric endolysin, would be more beneficial for eliminating resistant bacteria. The treatment ability of these therapeutics can be further improved if they are used with biocompatible nanoparticles like chitosan (CS). In this work, covalently conjugated chimeric endolysin to CS nanoparticles (C) and non-covalently entrapped endolysin in CS nanoparticles (NC) were effectively developed and, consequently, qualified and quantified using analytical devices, including FT-IR, dynamic light scattering, and TEM. Eighty to 150 nm and 100 nm to 200 nm in diameter were measured for CS-endolysin (NC) and CS-endolysin (C) using a TEM, respectively. The lytic activity, synergistic interaction, and biofilm reduction potency of nano-complexes were investigated on Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) strains. The outputs revealed a good lytic activity of nano-complexes after 24 h and 48 h of treatment, especially in P. aeruginosa (approximately 40% cell viability after 48 h of treatment with 8 ng/mL), and potential biofilm reduction performance was attained in E. coli strains (about 70% reduction after treatment with 8 ng/mL). The synergistic interaction between nano-complexes and vancomycin was exhibited in E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus strains at 8 ng/mL concentrations, while the synergistic effects of pure endolysin and vancomycin were not remarkable in E. coli strains. These nano-complexes would be more beneficial in suppressing the bacteria with a high level of antibiotic resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Reich, P. J., Boyle, M. G., Hogan, P. G., Johnson, A. J., Wallace, M. A., Elward, A. M., et al. (2016). Emergence of community-associated Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in the neonatal intensive care unit: An infection prevention and patient Safety Challenge. Clinical Microbiology And Infection, 22(645), e1–e8.
Yahav, D., Tau, N., & Shepshelovich, D. (2021). Assessment of data supporting the efficacy of new antibiotics for treating infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 72, 1968–1974.
Pogue, J., Kaye, K., Cohen, D., & Marchaim, D. (2015). Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in the era of multidrug-resistant human pathogens. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 21, 302–312.
Fodor, A., Abate, B. A., Deák, P., Fodor, L., Gyenge, E., Klein, M. G., et al. (2020). Multidrug resistance (MDR) and collateral sensitivity in bacteria, with special attention to genetic and evolutionary aspects and to the perspectives of antimicrobial peptides—A review. Pathogens, 9, 522.
Miller, S. I. (2016). Antibiotic resistance and regulation of the gram-negative bacterial outer membrane barrier by host innate immune molecules. MBio, 7, e01541–e01516.
Rizwan, M., Yahya, R., Hassan, A., Yar, M., Anita Omar, R., Azari, P., Danial Azzahari, A., Selvanathan, V., Rageh Al-Maleki, A., & Venkatraman, G. (2018). Synthesis of a novel organosoluble, biocompatible, and antibacterial chitosan derivative for biomedical applications. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 135(9), 45905.
Naderlou, E., Salouti, M., Amini, B., Amini, A., Narmani, A., Jalilvand, A., Shahbazi, R., et al. (2020). Enhanced sensitivity and efficiency of detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on modified magnetic nanoparticles by photometric systems, Artif Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol, 48, 810–817.
Son, B., Kong, M., & Ryu, S. (2018). The auxiliary role of the amidase domain in cell wall binding and exolytic activity of staphylococcal phage endolysins. Viruses, 10, 284.
Schmelcher, M., Shen, Y., Nelson, D. C., Eugster, M. R., Eichenseher, F., Hanke, D. C., et al. (2015). Evolutionarily distinct bacteriophage endolysins featuring conserved peptidoglycan cleavage sites protect mice from MRSA infection. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 70, 1453–1465.
Oliveira, H., Melo, L. D., Santos, S. B., Nóbrega, F. L., Ferreira, E. C., Cerca, N., et al. (2013). Molecular aspects and comparative genomics of bacteriophage endolysins. Journal of Virology, 87, 3277–3282.
Yang, H., Linden, S. B., Wang, J., Yu, J., Nelson, D. C., & Wei, H. (2015). A chimeolysin with extended-spectrum streptococcal host range found by an induced lysis-based rapid screening method. Scientific Reports, 5, 17257.
Verbree, C. T., Dätwyler, S. M., Meile, S., Eichenseher, F., Donovan, D. M., Loessner, M. J., et al. (2018). Corrected and republished from: Identification of peptidoglycan hydrolase constructs with synergistic staphylolytic activity in cow’s milk. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 84, e002134–e002117.
Kashani, H. H., Schmelcher, M., Sabzalipoor, H., Hosseini, E. S., & Moniri, R. (2018). Recombinant endolysins as potential therapeutics against antibioticresistant Staphylococcus aureus: Current status of research and novel delivery strategies. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 31, e00071–e00017.
Choudhary, R. C., Kumaraswamy, R. V., Kumari, S., Sharma, S. S., Pal, A., Raliya, R., et al. (2019). Zinc encapsulated chitosan nanoparticle to promote maize crop yield. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 127, 126–135.
Yousefi, M., Narmani, A., & Jafari, S. M. (2020). Dendrimers as efficient nanocarriers for the protection and delivery of bioactive phytochemicals. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 278, 102125.
Khaleghi, S., Rahbarizadeh, F., Ahmadvand, D., Malek, M., & Madaah Hosseini, H. R. (2016). The effect of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles surface engineering on relaxivity of magnetoliposome. Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging, 11(5), 340–349.
Kumari, R., Sunil, D., & Ningthoujam, R. S. (2020). Hypoxia-responsive nanoparticle based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: An up-to-date review. Journal of Controlled Release, 319, 135–156.
Khakinahad, Y., Sohrabi, S., Razi, S., Narmani, A., Khaleghi, S., Asadiyun, M., Jafari, H., & Mohammadnejad, J. (2022). Margetuximab conjugated-PEG-PAMAM G4 nano-complex: A smart nano-device for suppression of breast cancer. Biomedical Engineering Letters, 12(3), 317–329.
Chen, Y., Wu, D., Zhong, W., Kuang, S., Luo, Q., Song, L., et al. (2018). Evaluation of the PEG density in the PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles as a drug carrier for curcumin and mitoxantrone. Nanomaterials, 8, 486.
Rezvani, M., Mohammadnejad, J., Narmani, A., & Bidaki, K. (2018). Synthesis and in vitro study of modified chitosan polycaprolactam nano-complex as delivery system. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 113, 1287–1293.
Narmani, A., & Jafari, S. M. (2021). Chitosan-based nanodelivery systems for cancer therapy: Recent advances. Carbohydrate Polymers, 272, 118464.
Golafzani, F. N., Vaziri, A. Z., Javanmardi, M., Seyfan, F., Yazdanifar, M., & Khaleghi, S. (2022). Delivery of miRNA-126 through folic acid-targeted biocompatible polymeric nanoparticles for effective lung cancer therapy. Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers, 37(3), 168–188.
Niu, S., Williams, G. R., Wu, J., Wu, J., Zhang, X., Chen, X., et al. (2019). A chitosan-based cascade-responsive drug delivery system for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 17, 95.
Sathiyaseelan, A., Saravanakumar, K., Mariadoss, A. V. A., & Wang, M.-H. (2020). Biocompatible fungal chitosan encapsulated phytogenic silver nanoparticles enhanced antidiabetic, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 153, 63–71.
Kashani, H. H., Fahimi, H., Goli, Y. D., & Moniri, R. (2017). A novel chimeric endolysin with antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 7, 290.
Azadpour, A., Hajrasouliha, S., & Khaleghi, S. (2022). Green synthesized-silver nanoparticles coated with targeted chitosan nanoparticles for smart drug delivery. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 1(74), 103554.
Chang, Y., Kim, M., & Ryu, S. (2017). Characterization of a novel endolysin LysSA11 and its utility as a potent biocontrol agent against Staphylococcus aureus on food and utensils. Food Microbiology, 68, 112–120.
Bandara, S., Carnegie, C., Johnson, C., Akindoju, F., Williams, E., & Swaby, J. M. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of Zinc/Chitosan-Folic acid complex. Heliyon, 2, e00737.
Kaur, K., Sodhi, R. K., Katyal, A., Aneja, R., Jain, U. K., Katare, O. P., et al. (2015). Wheat germ agglutinin anchored chitosan microspheres of reduced brominated derivative of noscapine ameliorated acute inflammationin experimental colitis. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2, 225–235.
Tan, W., Li, Q., Dong, F., Zhang, J., Luan, F., Wei, L., et al. (2018). Novel cationic chitosan derivative bearing 1,2,3-triazolium and pyridinium: Synthesis, characterization, and antifungal property. Carbohydrate Polymers, 182, 180–187.
Li, Y., Yuan, J., Zhanab, S., Hu, J., Guo, Y., Ding, L., Huang, X., & Xiong, Y. (2021). Dynamic light scattering immunosensor based on metal-organic framework mediated gold growth strategy for the ultra-sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 341, 130030.
Kaur, J., Kour, A., Panda, J. J., Harjai, K., & Chhibber, S. (2020). Exploring endolysin-loaded alginate-chitosan nanoparticles as future remedy for staphylococcal infections. AAPS PharmSciTech, 21, 233.
Karimi Zindashti, G., Khaleghi, S., Nemati Mansur, F., & Rahbarizadeh, F. (2020). The design and preparation of fluorescent labeled chitosan nanoparticles for intestinal delivery. Medical Science Journal of Islamic Azad Univesity-Tehran Medical Branch, 30(4), 352–362.
Khaleghi, S., Rahbarizadeh, F., & Nikkhoi, S. K. (2021). Anti-HER2 VHH targeted fluorescent liposome as bimodal nanoparticle for drug delivery and optical imaging. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery, 16(4), 552–562.
Son, B., Kong, M., Lee, Y., & Ryu, S. (2021). Development of a novel chimeric endolysin, Lys109 with enhanced lytic activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 615887.
Chandrasekaran, M., Kim, K. D., & Chun, S. C. (2020). Antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles: A review. Processes, 8, 1173.
Reddy, D. N. K., Huang, F. Y., Wang, S.-P., & Kumar, R. (2020). Synergistic antioxidant and antibacterial activity of curcumin-C3 encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 26, 5021–5029.
Zhang, H., Feng, M., Chen, S., Shi, W., & Wang, X. (2020). Incorporation of lysozyme into cellulose nanocrystals stabilized β-chitosan nanoparticles with enhanced antibacterial activity. Carbohydrate Polymers, 236, 115974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PA: study concept and design, acquisition of data, drafting of the manuscript. HF: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. SK: statistical analysis, administrative, technical and material support, study supervision, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Ethical code. IR.IAU.PS.REC.1398.347
Consent to Participate
The authors declare that they have consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
The authors declare that they have consent to publish.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, P., Fahimi, H. & Khaleghi, S. Novel Chimeric Endolysin Conjugated Chitosan Nanocomplex as a Potential Inhibitor Against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 478–490 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04484-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04484-z