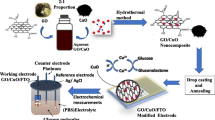
Abstract
Nonenzymatic biosensors do not require enzyme immobilization nor face degradation problem. Hence, nonenzymatic biosensors have recently attracted growing attention due to the stability and reproducibility. Here, a comparative study was conducted to quantitatively evaluate the glucose sensing of pure/oxidized Ni, Co, and their bimetal nanostructures grown on electrospun carbon nanofibers (ECNFs) to provide a low-cost free-standing electrode. The prepared nanostructures exhibited sensitivity (from 66.28 to 610.6 μA mM−1 cm−2), linear range of 2–10 mM, limit of detection in the range of 1 mM, and the response time (< 5 s), besides outstanding selectivity and applicability for glucose detection in the human serum. Moreover, the oxidizable interfering species, such as ascorbic acid (AA), uric acid (UA), and dopamine (DA), did not cause interference. Co–C and Ni-C phase diagrams, solid-state diffusion phenomena, and rearrangement of dissolved C atoms after migration from metal particles were discussed. This study undoubtedly provides new prospects on the nonenzymatic biosensing performance of mono-metal, bimetal, and oxide compounds of Ni and Co elements, which could be quite helpful for the fabrication of biomolecules detecting devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ronkainen, N. J., Halsall, H. B., & Heineman, W. R. (2010). Electrochemical biosensors. Chemical Society Reviews, 39, 1747–1763.
Chen, C., Xie, Q., Yang, D., Xiao, H., Fu, Y., Tan, Y., & Yao, S. (2013). Recent advances in electrochemical glucose biosensors: A review. RSC Advances, 3, 4473–4491.
Wilson, R., & Turner, A. P. F. (1992). Glucose oxidase: An ideal enzyme. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 7, 165–185.
Zhang, Y., Luo, L., Zhang, Z., Ding, Y., Liu, S., Deng, D., Zhao, H., & Chen, Y. (2014). Synthesis of MnCo 2 O 4 nanofibers by electrospinning and calcination: application for a highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Journal of Materials Chemistry B., 2, 529–535.
Hsu, Y.-W., Hsu, T.-K., Sun, C.-L., Nien, Y.-T., Pu, N.-W., & Ger, M.-D. (2012). Synthesis of CuO/graphene nanocomposites for nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor applications. Electrochimica Acta, 82, 152–157.
Zhang, J., Ma, J., Zhang, S., Wang, W., & Chen, Z. (2015). A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on CuO nanoparticles decorated carbon spheres. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical., 211, 385–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.01.100
Lu, N., Shao, C., Li, X., Miao, F., Wang, K., & Liu, Y. (2016). CuO nanoparticles/nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers modified glassy carbon electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose sensors with improved sensitivity. Ceramics International, 42, 11285–11293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.046
Hsin, Y. L., Hwang, K. C., & Yeh, C.-T. (2007). Poly (vinylpyrrolidone)-modified graphite carbon nanofibers as promising supports for PtRu catalysts in direct methanol fuel cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 129, 9999–10010.
Guo, Q., Liu, D., Zhang, X., Li, L., Hou, H., Niwa, O., & You, T. (2014). Pd–Ni alloy nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber composites: Preparation, structure, and superior electrocatalytic properties for sugar analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 86, 5898–5905.
Wang, J.-G., Yang, Y., Huang, Z.-H., & Kang, F. (2011). Coaxial carbon nanofibers/MnO2 nanocomposites as freestanding electrodes for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 56, 9240–9247.
Steigerwalt, E. S., Deluga, G. A., Cliffel, D. E., & Lukehart, C. M. (2001). A Pt- Ru/graphitic carbon nanofiber nanocomposite exhibiting high relative performance as a direct-methanol fuel cell anode catalyst. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 105, 8097–8101.
Huang, J., Wang, D., Hou, H., & You, T. (2008). Electrospun palladium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers and their electrocatalytic activities towards hydrogen peroxide and NADH. Advanced Functional Materials, 18, 441–448.
Cui, K., Song, Y., Guo, Q., Xu, F., Zhang, Y., Shi, Y., Wang, L., Hou, H., & Li, Z. (2011). Architecture of electrospun carbon nanofibers–hydroxyapatite composite and its application act as a platform in biosensing. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical., 160, 435–440.
Nataraj, S. K., Yang, K. S., & Aminabhavi, T. M. (2012). Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers—A state-of-the-art review. Progress in Polymer Science, 37, 487–513.
Park, S.-J., & Im, S.-H. (2008). Electrochemical behaviors of PAN/Ag-based carbon nanofibers by electrospinning. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 29, 777–781.
Hu, G., Zhou, Z., Guo, Y., Hou, H., & Shao, S. (2010). Electrospun rhodium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers for highly selective amperometric sensing of hydrazine. Electrochemistry Communications, 12, 422–426.
Weisweiler, W., Subramanian, N., & Terwiesch, B. (1971). Catalytic influence of metal melts on the graphitization of monolithic glasslike carbon. Carbon. New York, 9, 755–761.
Zhou, H., Yu, Q., Peng, Q., Wang, H., Chen, J., & Kuang, Y. (2008). Catalytic graphitization of carbon fibers with electrodeposited Ni–B alloy coating. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 110, 434–439.
Vashist, S. K., Zheng, D., Al-Rubeaan, K., Luong, J. H. T., & Sheu, F.-S. (2011). Technology behind commercial devices for blood glucose monitoring in diabetes management: A review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 703, 124–136.
Association, A. D., et al. (2014). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care, 37, S81–S90.
Sedighi, A., Montazer, M., & Mazinani, S. (2019). Synthesis of wearable and flexible NiP0. 1-SnOx/PANI/CuO/cotton towards a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 135, 192–199.
Li, Y., Song, Y.-Y., Yang, C., & Xia, X.-H. (2007). Hydrogen bubble dynamic template synthesis of porous gold for nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose. Electrochemistry Communications, 9, 981–988.
Liu, Y., Teng, H., Hou, H., & You, T. (2009). Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on renewable electrospun Ni nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofiber paste electrode. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 24, 3329–3334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.04.032
Luo, L., Li, F., Zhu, L., Ding, Y., Zhang, Z., Deng, D., & Lu, B. (2013). Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel (II) oxide/ordered mesoporous carbon modified glassy carbon electrode. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 102, 307–311.
Ding, Y., Wang, Y., Su, L., Bellagamba, M., Zhang, H., & Lei, Y. (2010). Electrospun Co3O4 nanofibers for sensitive and selective glucose detection. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 26, 542–548.
Liu, L., Wang, Z., Yang, J., Liu, G., Li, J., Guo, L., Chen, S., & Guo, Q. (2018). NiCo2O4 nanoneedle-decorated electrospun carbon nanofiber nanohybrids for sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical., 258, 920–928.
Rajaji, U., Ganesh, P.-S., Chen, S.-M., Govindasamy, M., Kim, S.-Y., Alshgari, R. A., & Shimoga, G. (2021). Deep eutectic solvents synthesis of perovskite type cerium aluminate embedded carbon nitride catalyst: High-sensitive amperometric platform for sensing of glucose in biological fluids. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 102, 312–320.
Mohammadi, M. A., Tabar, F. A., Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A., Bazargan, A. M., Mazinani, S., Keihan, A. H., & Sharif, F. (2021). Preparation and evaluation of electrospun carbon nanofibers infused by metal nanoparticles for supercapacitor electrodes application. Synth. Met., 274, 116706.
Guo, S., Dong, S., & Wang, E. (2010). Three-dimensional Pt-on-Pd bimetallic nanodendrites supported on graphene nanosheet: Facile synthesis and used as an advanced nanoelectrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. ACS Nano, 4, 547–555.
Sakthivel, K., Mani, G., Chen, S.-M., Lin, S.-H., Muthumariappan, A., & Mani, V. (2018). A novel synthesis of non-aggregated spinel nickel ferrite nanosheets for developing non-enzymatic reactive oxygen species sensor in biological samples. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 820, 161–167.
Sharma, R. K., & Ghose, R. (2015). Synthesis of porous nanocrystalline NiO with hexagonal sheet-like morphology by homogeneous precipitation method. Superlattices and Microstructures, 80, 169–180.
Niinisto, L., Utriainen, M., Kroger-Laukkanen, M., & Johansson, L. S. (2000). Studies of metallic thin film growth in an atomic layer epitaxy reactor using M (acac) sub 2(M= Ni, Cu, Pt) precursors. Applied Surface Science, 157, 151–158.
Wu, M., Wang, Q., Li, K., Wu, Y., & Liu, H. (2012). Optimization of stabilization conditions for electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 97, 1511–1519.
Li, L., Zhou, T., Sun, G., Li, Z., Yang, W., Jia, J., & Yang, G. (2015). Ultrasensitive electrospun nickel-doped carbon nanofibers electrode for sensing paracetamol and glucose. Electrochimica Acta, 152, 31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.048
An, C., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, Y., Jiao, L., & Yuan, H. (2014). In situ preparation of 1D Co@ C composite nanorods as negative materials for alkaline secondary batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6, 3863–3869.
Zhang, D.-E., Ni, X.-M., Zhang, X.-J., & Zheng, H.-G. (2006). Synthesis and characterization of Ni–Co needle-like alloys in water-in-oil microemulsion. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 302, 290–293.
Kim, C., Park, S.-H., Cho, J.-I., Lee, D.-Y., Park, T.-J., Lee, W.-J., & Yang, K.-S. (2004). Raman spectroscopic evaluation of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 35, 928–933.
Wang, Y., Serrano, S., & Santiago-Avilés, J. J. (2003). Raman characterization of carbon nanofibers prepared using electrospinning. Synthetic Metals, 138, 423–427.
Van Nguyen, T. D., Sufian, S., Mansor, N., & Yahya, N. (2014). Characterization of carbon nanofibers treated with thermal nitrogen as a catalyst support using point-of-zero charge analysis. Journal of Nanomaterials., 2014, 1–6.
Cançado, L. G., Takai, K., Enoki, T., Endo, M., Kim, Y. A., Mizusaki, H., Jorio, A., Coelho, L. N., Magalhaes-Paniago, R., & Pimenta, M. A. (2006). General equation for the determination of the crystallite size L a of nanographite by Raman spectroscopy. Applied Physics Letters, 88, 163106.
Kim, T., Lee, J., & Lee, K.-H. (2016). Full graphitization of amorphous carbon by microwave heating. RSC Advances, 6, 24667–24674.
Li, D., Li, G., Lv, P., Ullah, N., Wang, C., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., & Wei, Q. (2015). Preparation of a graphene-loaded carbon nanofiber composite with enhanced graphitization and conductivity for biosensing applications. RSC Advances, 5, 30602–30609.
Oya, A., & Otani, S. (1979). Catalytic graphitization of carbons by various metals. Carbon, New York, 17, 131–137.
Oya, A., & Marsh, H. (1982). Phenomena of catalytic graphitization. Journal of Materials Science, 17, 309–322.
Barakat, N. A. M., Kim, B., Park, S. J., Jo, Y., Jung, M.-H., & Kim, H. Y. (2009). Cobalt nanofibers encapsulated in a graphite shell by an electrospinning process. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 19, 7371–7378.
Wang, Y., Serrano, S., & Santiago-Aviles, J. J. (2002). Conductivity measurement of electrospun PAN-based carbon nanofiber. Journal of Material Science Letters, 21, 1055–1057.
Ryu, W.-H., Shin, J., Jung, J.-W., & Kim, I.-D. (2013). Cobalt (II) monoxide nanoparticles embedded in porous carbon nanofibers as a highly reversible conversion reaction anode for Li-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A., 1, 3239–3243.
Li, Y., Xie, M., Zhang, X., Liu, Q., Lin, D., Xu, C., Xie, F., & Sun, X. (2019). Co-MOF nanosheet array: A high-performance electrochemical sensor for non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical., 278, 126–132.
Salimi, A., & Roushani, M. (2005). Non-enzymatic glucose detection free of ascorbic acid interference using nickel powder and nafion sol–gel dispersed renewable carbon ceramic electrode. Electrochemistry Communications, 7, 879–887.
Zhang, L., Yuan, S., & Lu, X. (2014). Amperometric nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite made from nickel (II) hydroxide nanoplates and carbon nanofibers. Microchimica Acta, 181, 365–372.
Tian, H., Jia, M., Zhang, M., & Hu, J. (2013). Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel ion implanted-modified indium tin oxide electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 96, 285–290.
Xu, J., Li, F., Wang, D., Nawaz, M. H., An, Q., Han, D., & Niu, L. (2019). Co3O4 nanostructures on flexible carbon cloth for crystal plane effect of nonenzymatic electrocatalysis for glucose. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 123, 25–29.
Kung, C.-W., Lin, C.-Y., Lai, Y.-H., Vittal, R., & Ho, K.-C. (2011). Cobalt oxide acicular nanorods with high sensitivity for the non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 27, 125–131.
Park, S., Boo, H., & Chung, T. D. (2006). Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Analytica Chimica Acta, 556, 46–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Research Highlights
• Introducing well-stablished method for synthesis nanocomposites of electrospun carbon nanofibers decorated with pure/oxidized metal nanoparticles.
• Designing free-stand nonenzymatic electrodes of electrospun carbon nanofibers with no need to binders and glassy carbon electrode.
• Obtaining biosensors of high sensitivity and wide linear range towards the oxidation of glucose.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A., Mazinani, S., Sharif, F. et al. Improving Nonenzymatic Biosensing Performance of Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers decorated with Ni/Co Particles via Oxidation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 2542–2564 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03833-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03833-8