Abstract
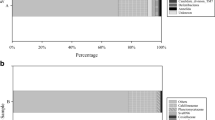
Marine invertebrates, particularly ascidians, constitute an important source of potential active and biofunctional natural products. The microbial diversity associated with ascidians is little recognized, although these microorganisms play a vital role in marine ecosystems. The objective of this study was to investigate bacterial population diversity in four ascidian samples: Phallusia nigra, Phallusia fumigata, Eudistoma viride, and Rhopalaea macrothorax, collected from the North Bay, Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Microbial strains identified up to the species level revealed 236 distinct species/ribotypes out of 298 bacterial strains. Of 298 ascidian-associated bacteria, 72 isolates belong to the class Gammaproteobacteria and the genus Endozoicomonas. The results from this investigation will contribute a broaden knowledge of microbial diversity associated to marine ascidians, and as a promising source for the discovery of new natural products.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarjuelo, I., Posada, D., Crandall, K. A., Pascual, M., & Turon, X. (2001). Cryptic species of Clavelina (Ascidiacea) in two different habitats: Harbours and rocky littoral zones in the northwestern Mediterranean. Marine Biology, 139, 455–462.
Erwin, P. M., Lopez-Legentil, S., & Schuhmann, P. W. (2010). The pharmaceutical value of marine biodiversity for anti-cancer drug discovery. Ecological Economics, 70(2), 445–451.
Kwan, J. C., Donia, M. S., Han, A. W., Hirose, E., Haygood, M. G., & Schmidt, E. W. (2012). Genome streamlining and chemical defense in a coral reef symbiosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of Sciences, 109(50), 20655–20660.
York, A., Gallager, S., Taylor, R., Vine, N., & Lerner, S., 2008. Using a towed optical habitat mapping system to monitor the invasive tunicate species Didemnum sp. along the northeast continental shelf. Oceans 1–9
Blunt, J. W., Copp, B. R., Keyzers, R. A., Munro, M. H., & Prinsep, M. R. (2015). Marine natural products. Natural Product Reports, 32(2), 116–211.
Anderson, S. A., Northcote, P. T., & Page, M. J. (2010). Spatial and temporal variability of the bacterial community in different chemotypes of the New Zealand marine sponge Mycalehentscheli. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 72(3), 328–342.
Yokobori, S., Kurabayashi, A., Neilan, B. A., Maruyama, T., & Hirose, E. (2006). Multiple origins of the ascidian-Prochloron symbiosis: molecular phylogeny of photo symbiotic and non-symbiotic colonial ascidians inferred from18SrDNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 40(1), 8–19.
Martínez-Garcia, M., Koblízek, M., Lopez-Legentil, S., & Anton, J. (2011). Epibiosis of oxygenic phototrophs containing chlorophylls a, b, c and d on the colonial ascidian Cystodytes dellechiajei. Microbial Ecology, 61(1), 13–19.
Kojima, A., & Hirose, E. (2012). Transfer of prokaryotic algal symbionts from a tropical ascidian (Lissoclinum punctatum) colony to its larvae. Zoological Science, 27, 124–127.
Erwin, P. M., Pineda, M. C., Webster, N., Turon, X., & Lopez-Legentil, S. (2014). Down under the tunic: Bacterial biodiversity hot spots and widespread ammonia-oxidizing archaea in coral reef ascidians. The ISME Journal, 8(3), 575–588.
Tianero, M. D. B., Kwan, J. C., Wyche, T. P., Presson, A. P., Koch, M., Barrows, L. R., & Schmidt, E. W. (2015). Species specificity of symbiosis and secondary metabolism in ascidians. The ISME Journal, 9(3), 615–628.
Schmidt, E. W. (2014). The secret to a successful relationship: lasting chemistry between ascidians and their symbiotic bacteria. Invertebrate Biology, 134, 88–102.
Leal, M. C., Sheridan, C., Osinga, R., Dionisio, G., Rocha, R. J. M., Silva, B., Rosa, R., & Calado, R. (2014). Marine microorganism-invertebrate assemblages: Perspectives to solve the “supply problem” in the initial steps of drug discovery. Marine Drugs, 12(7), 3929–3952.
Jensen, P. R., & Fenical, W. (1996). Marine bacterial diversity as a resource for novel microbial products. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 17(5-6), 346–351.
Koike, I., & Suzuki, T. (1996). Nutritional diversity of symbiotic ascidians in a Fijian seagrass meadow. Ecological Research, 11(3), 381–386.
Donia, M. S., Fricke, W. F., Partensky, F., Cox, J., Elshahawi, S. I., White, J. R., Phillippy, A. M., Schatz, M. C., Piel, J., & Haygood, M. G. (2011). Complex microbiome underlying secondary and primary metabolism in the tunicate-prochloron symbiosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(51), E1423–E1432.
Munchhoff, J., Hirose, E., Maruyama, T., Sunairi, M., Burns, B. P., & Neilan, B. A. (2007). Host specificity and phylogeography of the prochlorophyte Prochloron sp., an obligate symbiont in didemnid ascidians. Environmental Microbiology, 9(4), 890–899.
Chen, L., Fu, C., & Wang, G. (2016). Microbial diversity associated with ascidians: A review of research methods and application. Symbiosis, 71, 19–26.
Zhang, Y., Adnani, N., Braun, D. R., Ellis, G. A., Barns, K. J., Parker-Nance, S., Guzei, I. A., & Bugni, T. S. (2016). Micromonohalimanes A and B: Antibacterial halimane-type diterpenoids from a marine micromonospora species. Journal of Natural Products, 79(11), 2968–2972.
Andreo, M. A., Jimenez, P. C., Siebra, J. B., Costa-Lotufo, L. V., Vessecchi, R., Niehues, M., Lopes, J. L., & Lopes, N. P. (2012). Systematic UPLC-ESI-MS/MS study on the occurrence of staurosporine and derivatives in associated marine microorganisms from Eudistoma vannamei. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 23(2), 335–343.
Benson, H. J. (2002). Microbiological applications. A laboratory manual in general microbiology (8th ed.). The McGraw-Hill Company.
Ellaiah, P., Kalyan, D., Rao, V. S., & Rao, B. V. (1996). Isolation and characterization of bioactive actinomycetes from marine sediments. Hindustan Antibiotics Bulletin, 38(1-4), 48–52.
Kuster, E., & Williams, S. (1964). Selection of media for the isolation of Streptomyces. Nature, 202(4935), 928–929.
Williams, S. T., & Cross, T. (1971). Actinomycetes, methods in microbiology (Vol. 4). Academic Press.
Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., Kingston, R. E., Moore, D. D., Scidman, J. G., Smith, J. A., & Struhl, K. (1994). Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley. NewYork., 2.0.1–2.14.8.
Gordon, R. E., & Mihm, J. M. (1957). A comparative study of some strains received as nocardiae. Journal of Bacteriology, 73(1), 15–27.
Leon, J., Liza, L., Soto, I., Cuadra, D., Patino, L., & Zerpa, R. (2007). Bioactives actinomycetes of marine sediment from the central coast of Peru. Revista Peruana de Biología, 14, 259–270.
Kurahashi, M., & Yokota, A. (2007). Endozoicomonas elysicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a γ-proteobacterium isolated from the sea slug Elysia ornata. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 30(3), 202–206.
Yang, C. S., Chen, M. H., Arun, A. B., Chen, C. A., Wang, J. T., & Chen, W. M. (2010). Endozoicomonas montiporae sp. nov., isolated from the encrusting pore coral Montipora aequituberculata. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60(5), 1158–1162.
Muramatsu, Y., Uchino, Y., Kasai, H., Suzuki, K., & Nakagawa, Y. (2007). Ruegeria mobilis sp. nov., a member of the Alphaproteobacteria isolated in Japan and Palau. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57(6), 1304–1309.
Brettar, I., Christen, R., & Hofle, M. G. (2002). Rheinheimera baltica gen. nov., sp. nov., a blue coloured bacterium isolated from the central Baltic Sea. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 52(Pt 5), 1851–1857.
Campbell, B. J., Christian, J., Kostka, J. E., Luther, G. W., & Cary, S. C. (2001). Growth and phylogenetic properties of novel bacteria belonging to the Epsilon sub division of the Proteobacteria enriched from Alvinella pompejana and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(10), 4566–4572.
Maldonado, L. A., Stach, J. E., Pathom-aree, W., Ward, A. C., Bull, A. T., & Goodfellow, M. (2005). Diversity of cultivable actinobacteria in geographically widespread marine sediments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 87, 8–11.
Garnier, M., Labreuche, Y., Garcia, C., Robert, M., & Nicolas, J. L. (2007). Evidence for the involvement of pathogenic bacteria in summer mortalities of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Microbial Ecology, 53(2), 187–196.
Bruck, T. B., Bruck, W. M., Santiago-Vazquez, L. Z., McCarthy, P. J., & Kerr, R. G. (2007). Diversity of the bacterial communities associated with the azooxanthellate deep water octocorals Leptogorgia minimata, Iciligorgia schrammi, and Swiftia exertia. Marine Biotechnology, 9(5), 561–576.
Mohamed, M., Cicirelli, E. M., Kan, J., Chen, F., Fuqua, C., & Hill, R. T. (2008). Diversity and quorum-sensing signal production of Proteobacteria associated with marine sponges Naglaa. Environmental Microbiology, 10(1), 75–86.
Comeau, A. M., Buenaventura, E., & Suttle, C. A. A. (2005). Persistent, productive, and seasonally dynamic vibrio phage population with in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(9), 5324–5331.
Riesenfeld, C. S., Murray, A. E., & Baker, B. J. (2008). Characterization of the microbial community and polyketide biosynthetic potential in the palmerolide producing tunicate Synoicum adareanum. Journal of Natural Products, 71(11), 1812–1818.
Venter, C. J., Remington, K., Heidelberg, J. F., Halpern, A. L., Rusch, D., Eisen, L. A., et al. (2004). Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science, 304(5667), 66–74.
Sfanos, K., Harmody, D., Dang, P., Ledger, A., Pomponi, S., McCarthy, P., & Lopez, J. (2005). A molecular systematic survey of cultured microbial associates of deep-water marine invertebrates. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 28(3), 242–264.
Zhang, H., Lee, Y. K., Zhang, W., & Lee, H. K. (2006). Culturable actinobacteria from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perleve: isolation and phylogenetic diversity by 16 S rRNA gene-RFLP analyses. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 90(2), 159–169.
Hosoya, S., & Yokota, A. (2007). Pseudovibrio japonicas sp. nov., isolated from coastal seawater in Japan. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57(9), 1952–1955.
Sertan-de Guzman, A. A., Predicala, R. Z., Bernardo, E. B., Neilan, B. A., Elardo, S. P., Mangalidan, G. C., et al. (2007). Pseudovibrio denitrificans strain Z143-1, a heptylprodigiosin-producing bacterium isolated from a Philippine tunicate. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 277(2), 188–196.
Gontang, E. A., Fenical, W., & Jensen, P. R. (2007). Phylogenetic diversity of Gram-positive bacteria cultured from marine sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(10), 3272–3282.
Ettoumi, B., Raddadi, N., Borin, S., Daffonchio, D., Boudabous, A., & Cherif, A. (2009). Diversity and phylogeny of culturable spore-forming Bacilli isolated from marine sediments. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 49(S1), S13–S23.
Anand, T. P., Bhat, A. W., Shouche, Y. S., Roy, U., Siddharth, J., & Sarma, S. P. (2006). Antimicrobial activity of marine bacteria associated with sponges from the waters off the coast of South East India. Microbiological Research, 161(3), 252–262.
Shnit-Orland, M., & Kushmaro, A. (2009). Coral mucus associated bacteria: a possible first line of defense. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 67(3), 371–380.
Bredholdt, H., Galatenko, O. A., Engelhardt, K., Fjaervik, E., Terekhova, L. P., & Zotchev, S. B. (2007). Rare actinomycete bacteria from the shallow water sediments of the Trondheim fjord, Norway: isolation, diversity and biological activity. Environmental Microbiology, 9(11), 2756–2764.
Fiedler, H., Bruntner, C., Bull, A. T., Ward, A. C., Goodfellow, M., Potterat, O., et al. (2005). Marine actinomycetes as a source of novel secondary metabolites. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 87(1), 37–42.
Chelossi, E., Mancini, I., Sepcic, K., Turk, T., & Faimali, M. (2006). Comparative antibacterial activity of polymeric 3-alkyl pyridinium salts isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Reniera sarai and their synthetic analogues. Biomolecular Engineering, 23(6), 317–323.
Webster, N. S., & Hill, R. T. (2001). The culturable microbial community of the Great Barrier Reef sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile is dominated by an α-Proteobacterium. Marine Biology, 138(4), 843–851.
Mincer, T. J., Fenical, W., & Jensen, P. R. (2005). Culture-dependent and culture-independent diversity within the obligate marine actinomycete genus Salinispora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(11), 7019–7028.
Surajit, D., Lyla, P. S., & Ajmal Khan, S. (2006). Marine microbial diversity and ecology: importance and future perspectives. Current Science, 90, 1325–1335.
Klaus, J. S., Janse, I., Heikoop, J. M., Sanford, R. A., & Fouke, B. W. (2007). Coral microbial communities, zooxanthellae and mucus along gradients of seawater depth and coastal pollution. Environmental Microbiology, 9(5), 1291–1305.
Fraune, S., & Bosch, T. C. G. (2007). Long-term maintenance of species-specific bacterial microbiota in the basal metazoan Hydra. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(32), 13146–13151.
McFall-Ngai, M., Hadfield, M. G., Bosch, T. C. G., Carey, H. V., Domazet-Loso, T., Douglas, A. E., Dubilier, N., Eberl, G., Fukami, T., Gilbert, S. F., Hentschel, U., King, N., Kjelleberg, S., Knoll, A. H., Kremer, N., Mazmanian, S. K., Metcalf, J. L., Nealson, K., Pierce, N. E., Rawls, J. F., Reid, A., Ruby, E. G., Rumpho, M., Sanders, J. G., Tautz, D., & Wernegreen, J. J. (2013). Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(9), 3229–3236.
Jensen, S., Duperron, S., Birkeland, N. K., & Hovland, M. (2010). Intracellular Oceanospirillales bacteria inhabit gills of Acesta bivalves. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 74(3), 523–533.
Morrow, K. M., Moss, A. G., Chadwick, N. E., & Liles, M. R. (2012). Bacterial associates of two Caribbean coral species reveals species-specific distribution and geographic variability. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(18), 6438–6449.
Forget, N. L., & Juniper, K. S. (2013). Free-living bacterial communities associated with tubeworm (Ridgeia piscesae) aggregations in contrasting diffuse flow hydrothermal vent habitats at the Main Endeavour Field, Juan de Fuca Ridge. Microbiology Open, 2(2), 259–275.
Fiore, C. L., Labrie, M., Jarett, J. K., & Lesser, M. P. (2015). Transcriptional activity of the giant barrel sponge, Xestospongia muta holobiont: molecular evidence for metabolic interchange. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 364.
Katharios, P., Seth-Smith, H. M., Fehr, A., Mateos, J. M., Qi, W., Richter, D., Nufer, L., Ruetten, M., Guevara Soto, M., Ziegler, U., Thomson, N. R., Schlapbach, R., & Vaughan, L. (2015). Environmental marine pathogen isolation using mesocosm culture of sharpsnout seabream: striking genomic and morphological features of novel Endozoicomonas sp. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 17609.
Neave, M. J., Apprill, A., Ferrier-Pages, C., & Voolstra, C. R. (2016). Diversity and function of prevalent symbiotic marine bacteria in the genus Endozoicomonas. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100(19), 8315–8324.
Bourne, D. G., Dennis, P. G., Uthicke, S., Soo, R. M., Tyson, G. W., & Webster, N. (2013). Coral reef invertebrate microbiomes correlate with the presence of photosymbionts. The ISME Journal, 7(7), 1452–1458.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatfully acknowledge the financial support given by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Goverenment of India, New Delhi to conduct the survey and research. The authors are thankful to Dr. M. A. Atmanand, Director, National Institute of Ocean Technology, Chennai for providing necessary facilities to perform this research.
Funding
The authors received financial support from Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, New Delhi, to conduct the survey and research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research concept and the experiments were executed by BM, LA and KN. NVV and GD analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. All of the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Consent for Publication
Not applicable. The manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meena, B., Anburajan, L., Nitharsan, K. et al. Taxonomic Composition and Biological Activity of Bacterial Communities Associated with Marine Ascidians from Andaman Islands, India. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193, 2932–2963 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03577-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03577-x